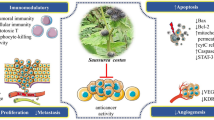
Abstract
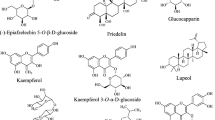
The key ingredients in a wide range of Ayurvedic, Siddha, and homeopathic medications are medicinal plants which have an impact on the treatment wide range of ailments and disorders while also contributing to humanity’s overall health. To obtain commercial value and worldwide acceptance, herbal medications must contain standardized extracts. Documenting the physico-chemical, chemical, and biological features of legitimate medicinal plants/extracts are one of the existing standardization procedures. Acacia, a large genus housing about 160 species, belongs to the Fabaceae family. Acacia ferruginea, a potential herb with medicinal utilization is endemic to the tropical region. Plants have been exploited as a viable medicine formulation source due to advances in phytochemistry over the last few decades. The present documentation intends to recapitulate detailed information on the plant comprising morphological features, physico-chemical characteristics, phytochemical composition and pharmaceutical properties reported through scientific validation and along with its cultivation and conservation challenges. The goal of this study is to detail the medical benefits and phytochemical potential of Acacia ferruginea, and conscientious efforts are needed to explore its benefits and validation of its traditional uses through clinical applications. The current documentation robustly covers the literature on A. ferruginea from 1965 to Dec 2021 and also includes findings of our recent studies on this plant. Providing up-to-date information on its botanical aspects for easy recognition of the plant, as well as its historical background/origin along with our original findings and the assessment comprises investigations that have been on the plant’s numerous qualities and activities. The presence of flavonoids, alkaloids, phenolics, tannins, and saponins is revealed by qualitative/quantitative studies. The bark of the plant has been extensively studied and the plant possesses antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-haemorrhoidal, and larvicidal properties. This precise record of details pertaining to standardization of extracts of A. ferruginea will assist producers of natural formulations as a ready reckoner.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Dr. N Sasidharan (Dr. B P Pal Fellow), Kerala Forest Research Institute, Peechi
G. Renu, Sanjana JuliasThilakar, D. Narasimhan, Centre for Floristic Research, Department of Botany, Madras Christian College, Tambaram
Acacia ferruginea DC., Prodr. 2: 458. 1825; Hook. f., Fl. Brit. India 2: 295. 1878
Mimosa ferruginea (DC.) Roxb., Fl. Ind. 2: 561. 1832, non Rottl., 1803.
https://indiabiodiversity.org/document/show/1718. Accessed 23 Nov. 2021.
Senegalia ferruginea - Useful Tropical Plants (theferns.info).
References
Deb J, Kumar DG (2014) Pharmacognostical studies on stem bark of Acacia ferruginea DC Der. Pharmacia Lettre 6(3):61–66
Deb J, Singh A, Rathore DS, Dash GK, Deb NK (2015) Studies on antidiabetic activity of Acacia ferruginea DC. stem bark. Indian J Pharm Biol Res 3(4):9267
Deshmukh SP, Bhajipale NS (2018) A review on Acacia species of therapeutics importance. Int J Pharm Biol Sci Arch 6(4):24–34
Devi SR, Prasad MNV (1991) Tannins and related polyphenols from ten common Acacia species of India. Biores Technol 36(2):189–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(91)90179-N
Faujdar S, Sharma S, Sati B, Pathak AK, Paliwal SK (2016) Comparative analysis of analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of bark and leaves of Acacia ferruginea DC. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 5(1):70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2016.02.002
Faujdar S, Sati B, Sharma S, Pathak AK, Paliwal SK (2019) Phytochemical evaluation and anti-hemorrhoidal activity of bark of Acacia ferruginea DC. J Tradit Complement Med 9(2):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcme.2018.02.003
Flora of Kolhapur District, Yadav SR, Sardesai MM (2002) Flora of Maharastra State Dicotyledones, vol I, Lakshminarasimhan P. & Prasanna P. V, 2000
Gamble, Fl. Pres. Madras 428(303). 1919
Govaerts R, et al (2020) Senegalia ferruginea in Kew Science Plants of the World online. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the internet. Accessed: 2020 Aug 20. Reference page.
International Plant Names Index (2019) Senegalia ferruginea. accessed 20 Aug 2019
Jeevitha M, Ravi PV, Subramaniyam V et al (2021) Exploring the phyto- and physicochemical evaluation, fluorescence characteristics, and antioxidant activities of Acacia ferruginea DC: an endangered medicinal plant. Futur J Pharm Sci 7:228. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00375-4
Kavitha A, Deepthi N, Ganesan R, Gladwin Joseph SC (2014) Common dryland trees of Karnataka: bilingual field guide. Ashoka Trust for Research in Ecology and the Environment, Bangalore
Kota CS, Hemanth Kumar V, Sunitha Reddy M (2017a) Evaluation of antioxidant activity in Polyherbal extract. World J Pharm Res 6(12):1422–1427
Kota CS, HemanthKumar V, SunithaReddy M (2017b) Activity of polyherbal extract against bacteria causing skin infections in diabetic patients. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 10(5):147–149
Loganayaki N, Siddhuraju P, Manian S (2011) Estudiocomparativo de la actividadantioxidante in vitro de las legumbres Acacia auriculiformis y Acacia ferruginea con la legumbreconvencional Cajanus cajan. CYTA 9(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/19476330903484216
Malathi H (2021) Evaluation of the cytotoxic effects of thorn extracts from medicinal plants on the sf21 cell line. Asian J Pharm 15:1
Matthew KM (1983) The flora of Tamil Nadu Carnatic. Diocesan Press, Madras
Modi RK, Mathad S, Mathad YN (2016) In vitro antimicrobial screening of a few ethno-medicinal plants of Mimosoideae of Gulbarga-Karnataka, India. Int J Pharm Life Sci 7(1):4860–4863
Mutha RE, Tatiya AU, Surana SJ (2021) Flavonoids as natural phenolic compounds and their role in therapeutics: an overview. Future J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-020-00161-8
Orwa C, Mutua A, Kindt R, Jamnadass R, Anthony S (2009) Agro forestreeDatabase:a tree reference and selection guide version 4.0 (http://www.worldagroforestry.org/sites/treedbs/treedatabases.asp)
Pullaiah et al (2001) Flora of Eastern Ghats Vol. 2.
RexImmanuel R, Ganapathy M (2020) Ameliorative effect of multipurpose tree species (MPT’S) on coastal degraded soils. Plant Arch 20(1):801–807
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2013) Acacia ferruginea inhibits tumor progression by regulating inflammatory mediators-(TNF-a, iNOS, COX-2, IL-1ß, IL-6, IFN-γ, IL-2, GM-CSF) and pro-angiogenic growth factor- VEGF. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(6):3909–3919. https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.6.3909
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2014) Protective effect of Acacia ferruginea against ulcerative colitis via modulating inflammatory mediators, cytokine profile and NF-κB signal transduction pathways. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 33(2):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2014008425
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2015) Acacia ferruginea inhibits cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and urotoxicity by modulating cytokines in mice. J Immunotoxicol 12(2):154–163. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2014.914988
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2016) Acacia ferruginea inhibits inflammation by regulating inflammatory iNOS and COX-2. J Immunotoxicol 13(1):127–135. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2015.1017625
Sakthivel KM, Guruvayoorappan C (2018) Targeted inhibition of tumor survival, metastasis and angiogenesis by Acacia ferruginea mediated regulation of VEGF, inflammatory mediators, cytokine profile and inhibition of transcription factor activation. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 95(May):400–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.04.012
Sankara Rao K, Arun Singh R, Deepak Kumar, Swamy RK, Page N (2016) Digital Flora of Eastern Ghats. http://easternghats.ces.iisc.ernet.in/plants.php?name=Acaciaferruginea. accessed 8 Nov 2021
Sowndhararajan K, Kang SC (2013) Protective effect of ethyl acetate fraction of Acacia ferruginea DC. against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 148(1):175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.007
Sowndhararajan K, Joseph JM, Manian S (2013) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of Indian acacias: Acacia leucophloea (Roxb) willd, Acacia ferruginea dc, Acacia dealbata link and Acacia pennata (l) willd. Int J Food Prop 16(8):1717–1729. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2011.604895
Sowndhararajan K, Hong S, Jhoo JW, Kim S, Chin NL (2015) Effect of acetone extract from the stem bark of Acacia species (A. dealbata, A ferruginea and A. leucophloea) on antioxidant enzymes status in hydrogen peroxide-induced HepG2 cells. Saudi J Biol Sci 22(6):685–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.03.010
Sowndhararajan K, Santhanam R, Hong S, Jhoo JW, Kim S (2016) Suppressive effects of acetone extract from the stem bark of three Acacia species on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 6(8):658–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2016.06.005
Suresh G, Rao JV (1998) Intercropping sorghum with nitrogen fixing trees in semiarid India. Agrofor Syst 42(2):181–194. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006154725098
Suresh G, Rao JV (2000) The influence of Nitrogen-fixing trees and fertilizer nitrogen levels on the growth, yield and Nitrogen uptake of Cowpea on a rainfed Alfiso. Expl Agric 36:41–50
Thippeswamy S, Mohana DC, Abhishek RU, Manjunath K (2013) Effect of plant extracts on inhibition of Fusarium verticillioides growth and its toxin fumonisin B 1 production. J Agric Technol 9(4):889–900
Thippeswamy S, Abhishek R, Manjunath K, Mohana D (2015) Evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant properties of some traditional medicinal plants from India. Int J Green Pharm 9(1):50. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-8258.150925
Tomou E-M, Lytra K, Chrysargyris A, Tzortzakis N, Skaltsa H (2021) NMR fingerprint comparison of cultivated Sideritis spp. from cyprus. Agronomy 11:1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11081503
Tropicos.org (2019) Senegalia ferruginea. Missouri Botanical Garden. Published on the internet. accessed 2019 Aug 20.
Vahitha R, Venkatachalam MR, Murugan K, Jebanesan A (2002) Larvicidal efficacy of Pavoniazeylanica L. and Acacia ferruginea DC against Culex quinquefasciatus Say. Bioresource Technol 82(2):203–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00175-4
Ved DK, Sureshchandra ST, Barve V, Srinivas V, Sangeetha S, Ravikumar K, Kartikeyan R, Kulkarni V, Kumar AS, Venugopal SN, Somashekhar BS, Sumanth MV, Begum N, Rani S, Surekha KV, Desale N (2016) (envis.frlht.org/frlhtenvis.nic.in). FRLHT's ENVIS Centre on Medicinal Plants, Bengaluru. http://envis.frlht.org/plant_details.php?disp_id=26
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science and Higher Education for Women for support and facilities. M Jeevitha acknowledges funding received from the Department of Science and Technology, under the WOS-A scheme for the study (SR/WOS-A/CS-25/2018).
Funding
One of the authors Mrs. M. Jeevitha acknowledges funding received from Department of Science and Technology, under WOS-A scheme for the study (SR/WOS-A/CS-25/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors. This article does not contain any studies involving human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
M. Jeevitha has no conflict of interest. Shubashini K. Sripathi has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeevitha, M., Sripathi, S.K. A systematic documentation on a rare medicinal plant Acacia ferruginea: a ready reckoner. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 23, 1065–1089 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-022-00647-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-022-00647-1