Abstract
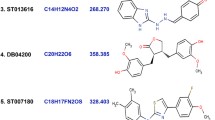
Inhibition of BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase plays a crucial role in the management of chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). The suppression of CML is getting harder because of a distinct pattern of resistance. Developing new types of ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors along with ABL2, CSF1R, KIT, LCK, PDGFRA, and PDGFRB inhibitors is the main objective of this study that may overcome the drug resistance issue. The current study has been conducted using a kinase database containing 177,000 bioactive molecules, the top 135 molecules were selected with the best docking score and subjected to comprehensive ADMET profiling, multi-target analysis. Based on consensus molecular docking score (AutoDock, Chimera, Achilles, and Mcule), 22 molecules have been screened out which later undertaken for ADME/T profiling. After profiling of ADME/T data, selected molecules subjected to docking with multiple targets. Finally, molecular dynamics simulations had performed to screen the binding accuracy of the four lead molecules with ABL1. MD simulations of the desired complex (ABL1, ABL2, CSF1R, KIT, LCK, PDGFRA, and PDGFRB, among them ABL1 was the prime target) performed and found that PCID 10181160 and PCID 72724706 are the most promising inhibitors comparing to imatinib. These lead molecules are the potential CML inhibitors that could resolve the resistance pattern. Further chemical synthesis, wet lab analysis, and experimental validation deserve the utmost attention.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The experimental data used to support the findings of this study are included in the article.
References
Dickson CJ, Madej BD, Skjevik ÅA, Betz RM, Teigen K, Gould IR, Walker RC (2014) Lipid14: the amber lipid force field. J Chem Theory Comput 10(2):865–879
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, Resta DJ, Reese SF, Ford JM, Talpaz M (2001) The activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med 344(14):1038–1042
Dundas J, Ouyang Z, Tseng J, Binkowski A, Turpaz Y, Liang J (2006) CASTp: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins with structural and topographical mapping of functionally annotated residues. Nucleic Acids Res 34(2):116–118
Eadie LN, Dang P, Goyne JM, Hughes TP, White DL (2018) ABCC6 plays a significant role in the transport of nilotinib and dasatinib, and contributes to TKI resistance in vitro, in both cell lines and primary patient mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0192180
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O’Brien S, Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM (1999) The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 341(3):164–172
Goldman JM, Melo JV (2003) Chronic myeloid leukemia—advances in biology and new approaches to treatment. N Engl J Med 349(15):1451–1464
Hassan NM, Alhossary AA, Mu Y, Kwoh CK (2017) Protein–ligand blind docking using QuickVina-W with inter-process spatio-temporal integration. Sci Rep 7(1):15451
Huang B (2009) MetaPocket: a meta approach to improve protein–ligand binding site prediction. OMICS 13(4):325–330
Isa MA, Majumdhar RS, Haider S (2018) In silico docking and molecular dynamics simulation of 3-dehydroquinate synthase (DHQS) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Model 24(6):132
Jabbour E, Kantarjian H (2014) Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2014 update on diagnosis, monitoring, and management. Am J Hematol 89(5):547–556
Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI (2002) Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem 23(16):1623–1641
Kang ZJ, Liu YF, Xu LZ, Long ZJ, Huang D, Yang Y, Liu Q (2016) The Philadelphia chromosome in leukemogenesis. Chin J Cancer 35(1):48
Krieger E, Vriend G (2014) YASARA View—molecular graphics for all devices—from smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 30(20):2981–2982
Krieger E, Vriend G (2015) New ways to boost molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 36(13):996–1007
Krieger E, Koraimann G, Vriend G (2002) Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—a self-parameterizing force field. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 47(3):393–402
Krieger E, Nielsen JE, Spronk CA, Vriend G (2006) Fast empirical pKa prediction by Ewald summation. J Mol Graph Model 25(4):481–486
Le Coutre P, Ottmann OG, Giles F, Kim DW, Cortes J, Gattermann N, Kuliczkowski K (2008) Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR–ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is active in patients with imatinib-resistant or-intolerant accelerated-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 111(4):1834–1839
Maier JA, Martinez C, Kasavajhala K, Wickstrom L, Hauser KE, Simmerling C (2015) ff14SB: improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J Chem Theory Comput 11(8):3696–3713
Mandlik V, Singh S (2016) Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation study of inositol phosphorylceramide synthase–inhibitor complex in leishmaniasis: insight into the structure based drug design. F1000Research. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.9151.2
Mauro MJ (2006) Defining and managing imatinib resistance. ASH Educ Program B 1:219–225
Meng XY, Zhang HX, Mezei M, Cui M (2011) Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 7(2):146–157
Mitra S, Dash R (2018) Structural dynamics and quantum mechanical aspects of shikonin derivatives as CREBBP bromodomain inhibitors. J Mol Graph Model 83:42–52
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Huey R, Olson AJ (1996) Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins: parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10(4):293–304
Nagasundaram N, Zhu H, Liu J, Karthick V, Chakraborty C, Chen L (2015) Analysing the effect of the mutation on protein function and discovering potential inhibitors of CDK4: molecular modeling and dynamics studies. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0133969
Pascoini AL, Federico LB, Arêas ALF, Verde BA, Freitas PG, Camps I (2018) In silico development of new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 1:15
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Quintás-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, Cortes J (2007) Flying under the radar: the new wave of BCR–ABL inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(10):834
Rask-Andersen M, Zhang J, Fabbro D, Schiöth HB (2014) Advances in kinase targeting: current clinical use and clinical trials. Trends Pharmacol Sci 35(11):604–620
Sánchez-Linares I, Pérez-Sánchez H, Cecilia JM, García JM (2012) High-throughput parallel blind virtual screening using BINDSURF. BMC Bioinform 13(14):S13
Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J, Sawyers CL (2002) Multiple BCR–ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2(2):117–125
Shah RR, Morganroth J, Shah DR (2013) Hepatotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors: clinical and regulatory perspectives. Drug Saf 36(7):491–503
Skelton AA, Fenter P, Kubicki JD, Wesolowski DJ, Cummings PT (2011) Simulations of the quartz (1011)/water interface: a comparison of classical force fields, ab initio molecular dynamics, and X-ray reflectivity experiments. J Phys Chem C 115(5):2076–2088
Steinberg M (2007) Dasatinib: a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Ther 29(11):2289–2308
Stewart JJ (1990) MOPAC: a semiempirical molecular orbital program. J Comput Aided Mol Des 4(1):1–103
Szklarczyk D, Santos A, von Mering C, Jensen LJ, Bork P, Kuhn M (2015) STITCH 5: augmenting protein–chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D380–D384
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25(9):1157–1174
Zoete V, Daina A, Bovigny C, Michielin O (2016) SwissSimilarity: a web tool for low to ultra-high throughput ligand-based virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model 56(8):1399–1404
Acknowledgements
Support to CBRL from Achilles blind docking server, OpenEye Scientific Software Inc. (Santa Fe, NM, USA) gratefully acknowledged. The research work had planned and conducted by AR, NHN & SCR. NQ and RM approved the research workflow, and proofread the article.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
Arifur Rahman has no conflict of interest. Nazmul Hasan Naheed has no conflict of interest. Sabreena Chowdhury Raka has no conflict of interest. Nazmul Qais has no conflict of interest. A. Z. M. Ruhul Momen has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, A., Naheed, N.H., Raka, S.C. et al. Ligand-based virtual screening, consensus molecular docking, multi-target analysis and comprehensive ADMET profiling and MD stimulation to find out noteworthy tyrosine kinase inhibitor with better efficacy and accuracy. ADV TRADIT MED (ADTM) 20, 645–661 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00406-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00406-9