Abstract
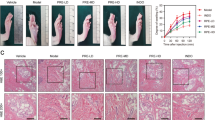
The present study was conducted to evaluate the effect of methanol extract of Corydalis Tuber (CTE) on the levels of inflammatory mediators in Raw264.7 cells activated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and on paw edema in rats. CTE dose-dependently decreased release of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), which elevated by LPS. The inhibitions of NO and PGE2 by CTE were due to the suppression of iNOS expression and of COX-2 activity, respectively. CTE also inhibited the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and the phosphorylation of inhibitory kappa B (IκB), determined by western blot analysis. In addition, CTE inhibited the production of TNF-α, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Furthermore, administration of CTE significantly inhibited the formation of paw edema by carrageenan in rats. Histopathologically, CTE effectively inhibited increases of hind paw skin thickness and inflammatory cell infiltrations. These findings demonstrate that CTE has inhibitory effect on inflammatory markers in LPS-activated Raw264.7 cells and on paw edema in carrageenan-stimulated rats, showing the possibility of anti-inflammatory use of Corydalis Tuber.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beloeil H, Ababneh Z, Chung R, Zurakowski D, Mulkern RV, Berde CB (2006) Effects of bupivacaine and tetrodotoxin on Carrageenan-induced hind paw inflammation in rats (part 1): hyperalgesia, edema, and systemic cytokines. Anesthesiology 105:128–138
Bogdan C (2001) Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nat Immunol 2:907–916
Caivano M, Cohen P (2000) Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in mediating lipopolysaccharide-stimulated induction of cyclooxygenase-2 and IL-1 beta in Raw264 macrophages. J Immunol 164:3018–3025
Cassim B, Mody G, Bhoola K (2002) Kallikrein cascade and cytokines in inflamed joints. Pharmacol Ther 94:1–34
Chang CK, Lin MT (2001) DL-Tetrahydropalmatine may act through inhibition of amygdaloid release of dopamine to inhibit an epileptic attack in rats. Neurosci Lett 307:163–166
Chen F, Castranova V, Shi X (2001) New insight into the role of nuclear factor-κB in cell growth regulation. Am J Pathol 159:387–397
Chu WM (2013) Tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Lett 328:222–225
Delgado AV, McManus AT, Chambers JP (2003) Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 1-beta, interleukin 2, and interleukin 6 by rat leukocyte subpopulations after exposure to substance P. Neuropeptides 37:355–361
Goetz FW, Planas JV, MacKenzie S (2004) Tumor necrosis factors. Dev Comp Immunol 28:487–497
Hinson RM, Williams JA, Shacter E (1996) Elevated interleukin 6 is induced by prostaglandin E2 in a murine model of inflammation: possible role of cyclooxygenase-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:4885–4890
Hsu A, Bray TM, Helferich WG, Doerge DR, Ho E (2010) Differential effects of whole soy extract and soy isoflavones on apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Exp Biol Med 235:90–97
Hu W, Heo S-I, Wang M-H (2009) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of Kalopanax pictus leaf. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 52:360–366
Hung TM, Ngoc TM, Youn UJ, Min BS, Na M, Thuong PT, Bae K (2008) Anti-amnestic activity of pseudocoptisine from corydalis tuber. Biol Pharm Bull 31:159–162
Karin M (1999) How NF-kappaB is activated: the role of the IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex. Oncogene 18:6867–6874
Kim S, Hwang S, Jang Y, Park M, Markelonis G, Oh T, Kim YC (1999) Protopine from corydalis ternata has anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities. Planta Med 65:218–221
Kobayashi Y (2010) The regulatory role of nitric oxide in proinflammatory cytokine expression during the induction and resolution of inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 88:1157–1162
Kubo M, Matsuda H, Tokuoka K, Kobayashi Y, Ma S, Tanaka T (1994) Studies of anti-cataract drugs from natural sources. I. Effects of a methanolic extract and the alkaloidal components from corydalis tuber on in vitro aldose reductase activity. Biol Pharm Bull 17:458–459
Lee TH, Son M, Kim SY (2010) Effects of corydaline from corydalis Tuber on gastric motor function in an animal model. Biol Pharm Bull 33:958–962
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-κB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Luqman S, Pezzuto JM (2010) NF-kappaB: a promising target for natural products in cancer chemoprevention. Phytother Res 24:949–963
Magnani M, Crinelli R, Bianchi M, Antonelli A (2000) The ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic system and other potential targets for the modulation of nuclear factor-kB (NF-kB). Curr Drug Targets 1:387–399
Matsuda H, Shiomoto H, Naruto S, Namba K, Kubo M (1988) Anti-thrombic action of methanol extract and alkaloidal components from corydalis tuber. Planta Med 54:27–33
Morris CJ (2003) Carrageenan-induced paw edema in the rat and mouse. Methods Mol Biol 225:115–121
Murakami A, Ohigashi H (2007) Targeting NOX, INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. Int J Cancer 121:2357–2363
Omote K, Hazama K, Kawamata T, Kawamata M, Nakayaka Y, Toriyabe M, Namiki A (2001) Peripheral nitric oxide in carrageenan-induced inflammation. Brain Res 912:171–175
Palmer RM, Ashton DS, Moncada S (1988) Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature 333:664–666
Pekthong D, Martin H, Abadie C, Bonet A, Heyd B, Mantion G, Richert L (2008) Differential inhibition of rat and human hepatic cytochrome P450 by andrographis paniculata extract and andrographolide. J Ethnopharmacol 115:432–440
Rafi MM, Yadav PN, Reyes M (2007) Lycopene inhibits LPS-induced proinflammatory mediator inducible nitric oxide synthase in mouse macrophage cells. J Food Sci 72:S069–94
Sakata D, Yao C, Narumiya S (2010) Prostaglandin E2, an immunoactivator. J Pharmacol Sci 112:1–5
Salvemini D, Wang ZQ, Wyatt PS, Bourdon DM, Marino MH, Manning PT, Currie MG (1996) Nitric oxide: a key mediator in the early and late phase of carrageenan-induced rat paw inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 118:829–838
Vergnolle N (2003) The enteric nervous system in inflammation and pain: the role of proteinase-activated receptors. Can J Gastroenterol 17:589–92
Vergnolle N, Ferazzini M, D’Andrea MR, Buddenkotte J, Steinhoff M (2003) Proteinase-activated receptors: novel signals for peripheral nerves. Trends Neurosci 26:496–500
Yim JH, Lee OH, Choi UK, Kim YC (2009) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of ethanolic extracts of Glycine max (L.) Merr and Rhynchosia nulubilis seeds. Int J Mol Sci 10:4742–4753
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2011–0,030,124).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W. Y. Choi and S. J. Park contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, W.Y., Park, S.J., Lee, J.R. et al. Modulation of inflammatory mediators by corydalis tuber in LPS-stimulated Raw264.7 cells and its inhibitory effects on carrageenan-stimulated paw edema in rats. Orient Pharm Exp Med 14, 319–328 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0153-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0153-7