Abstract
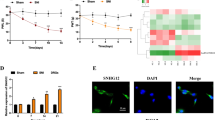
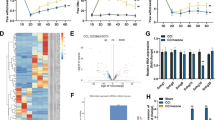
This study aims to explore the functions and mechanisms of long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 5 (SNHG5) in chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain (NP). An NP rat model was established using the CCI method and the NP severity was evaluated by paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) and paw withdrawal latency (PWL). The expression of SNHG5, CDK9, and SCN9A was quantified in rat dorsal root ganglion, in addition to the detections of apoptosis, pathological changes, neuron number, and the co-localization of Nav1.7 and cleaved caspase-3 with NeuN. In ND7/23 cells, the apoptosis and lactate dehydrogenase concentration were assessed, as well as the relationship between SNHG5, CDK9, and SCN9A. In the dorsal root ganglion of CCI-treated rats, SNHG5 and SCN9A were upregulated and downregulation of SNHG5 suppressed SCN9A expression, increased the PWT and PWL, blocked neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis, and alleviated NP. Mechanistically, SNHG5 recruited CDK9 to enhance SCN9A-encoded Nav1.7 expression and promoted peripheral neuronal apoptosis and injury. In addition, SCN9A overexpression nullified the alleviative effects of SNHG5 deficiency on NP and neuron loss in CCI rats. In conclusion, SNHG5 promotes SCN9A-encoded Nav1.7 expression by recruiting CDK9, thereby facilitating neuron loss and NP after spinal nerve injury, which may offer a promising target for the management of NP.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Zhang Q, Zhu D, Li Q. LncRNA CRNDE exacerbates neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury-induced(CCI) rats through regulating miR-146a-5p/WNT5A pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12:7348–59.
Attal N. Pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: the latest recommendations. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175:46–50.
Pedowitz EJ, Abrams RMC, Simpson DM. Management of neuropathic pain in the geriatric population. Clin Geriatr Med. 2021;37:361–76.
Liu P, Cheng J, Ma S, Zhou J. Paeoniflorin attenuates chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain by suppressing spinal NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28:1495–508.
Zhang L, Chen X, Wu L, Li Y, Wang L, Zhao X, Zhao T, Zhang L, Yan Z, Wei G. Ameliorative effects of escin on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;267: 113503.
Chu LW, Cheng KI, Chen JY, Cheng YC, Chang YC, Yeh JL, Hsu JH, Dai ZK, Wu BN. Loganin prevents chronic constriction injury-provoked neuropathic pain by reducing TNF-alpha/IL-1beta-mediated NF-kappaB activation and Schwann cell demyelination. Phytomedicine. 2020;67: 153166.
Liu ZY, Song ZW, Guo SW, He JS, Wang SY, Zhu JG, Yang HL, Liu JB. CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling contributes to neuropathic pain via central sensitization mechanisms in a rat spinal nerve ligation model. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25:922–36.
Li Y, North RY, Rhines LD, Tatsui CE, Rao G, Edwards DD, Cassidy RM, Harrison DS, Johansson CA, Zhang H, Dougherty PM. DRG voltage-gated sodium channel 1.7 Is upregulated in paclitaxel-induced neuropathy in rats and in humans with neuropathic pain. J Neurosci. 2018;38:1124–36.
Moutal A, Cai S, Yu J, Stratton HJ, Chefdeville A, Gomez K, Ran D, Madura CL, Boinon L, Soto M, Zhou Y, Shan Z, Chew LA, Rodgers KE, Khanna R. Studies on CRMP2 SUMOylation-deficient transgenic mice identify sex-specific Nav1.7 regulation in the pathogenesis of chronic neuropathic pain. Pain. 2020;161:2629–51.
Niu HL, Liu YN, Xue DQ, Dong LY, Liu HJ, Wang J, Zheng YL, Zou AR, Shao LM, Wang K. Inhibition of Nav1.7 channel by a novel blocker QLS-81 for alleviation of neuropathic pain. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42:1235–47.
Wu S, Bono J, Tao YX. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA): a target in neuropathic pain. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23:15–20.
Jin S., Tian S., Ding H., Yu Z., Li M. SNHG5 knockdown alleviates neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury via sponging miR‑142‑5p and regulating the expression of CAMK2A. Mol Med Rep. 2022;26.
Chen M, Yang Y, Zhang W, Li X, Wu J, Zou X, Zeng X. Long noncoding RNA SNHG5 knockdown alleviates neuropathic pain by targeting the miR-154-5p/CXCL13 axis. Neurochem Res. 2020;45:1566–75.
Sun W, Ma M, Yu H, Yu H. Inhibition of lncRNA X inactivate-specific transcript ameliorates inflammatory pain by suppressing satellite glial cell activation and inflammation by acting as a sponge of miR-146a to inhibit Na(v) 1.7. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:9888–98.
Singh R, Bhardwaj V, Das P, Purohit R. Natural analogues inhibiting selective cyclin-dependent kinase protein isoforms: a computational perspective. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2020;38:5126–35.
Hsieh MC, Peng HY, Ho YC, Lai CY, Cheng JK, Chen GD, Lin TB. Transcription repressor Hes1 contributes to neuropathic pain development by modifying CDK9/RNAPII-dependent spinal mGluR5 transcription. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:4177.
Dong J, Xia R, Zhang Z, Xu C. lncRNA MEG3 aggravated neuropathic pain and astrocyte overaction through mediating miR-130a-5p/CXCL12/CXCR4 axis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13:23004–19.
Zhao L, Song C, Huang Y, Lei W, Sun J. MMP-9 regulates CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in the early phase of neuropathic pain in chronic sciatic nerve constriction injury (CCI) rats. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9:2020–7.
Zhang Q, Liu W, Zhang HM, Xie GY, Miao YR, Xia M, Guo AY. hTFtarget: a comprehensive database for regulations of human transcription factors and their targets. Genom Proteom Bioinform. 2020;18:120–8.
Xue Y, Chidiac C, Herault Y, Gaveriaux-Ruff C. Pain behavior in SCN9A (Nav1.7) and SCN10A (Nav1.8) mutant rodent models. Neurosci Lett. 2021;753:135844.
Hu JZ, Rong ZJ, Li M, Li P, Jiang LY, Luo ZX, Duan CY, Cao Y, Lu HB. Silencing of lncRNA PKIA-AS1 attenuates spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain through epigenetic downregulation of CDK6 expression. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:50.
Wang W, Min L, Qiu X, Wu X, Liu C, Ma J, Zhang D, Zhu L. Biological function of long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) Xist. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 645647.
Shen Q, Zheng J, Wang X, Hu W, Jiang Y, Jiang Y. LncRNA SNHG5 regulates cell apoptosis and inflammation by miR-132/PTEN axis in COPD. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;126: 110016.
Wang M, Xie Y, Shao Y, Chen Y. LncRNA snhg5 attenuates status epilepticus induced inflammation through regulating NF-kappaBeta signaling pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 2022;45:86–93.
Zhou Z, Cao J, Liu X, Li M. Evidence for the butyrate metabolism as key pathway improving ulcerative colitis in both pediatric and adult patients. Bioengineered. 2021;12:8309–24.
Jiang ZS, Zhang JR. LncRNA SNHG5 enhances astrocytes and microglia viability via upregulating KLF4 in spinal cord injury. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120:66–72.
Han Y, Huang Y, Yang Q, Jia L, Zheng Y, Li W. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 mediates periodontal inflammation through the NF-kappaB signalling pathway. J Clin Periodontol. 2022;49:1038–51.
Sundar V, Vimal S, Sai Mithlesh MS, Dutta A, Tamizhselvi R, Manickam V. Transcriptional cyclin-dependent kinases as the mediators of inflammation-a review. Gene. 2021;769: 145200.
Ni W, Zhang F, Zheng L, Wang L, Liang Y, Ding Y, Yik JHN, Haudenschild DR, Fan S, Hu Z. Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 (CDK9) inhibitor atuveciclib suppresses intervertebral disk degeneration via the inhibition of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8: 579658.
Yang X, Luo W, Li L, Hu X, Xu M, Wang Y, Feng J, Qian J, Guan X, Zhao Y, Liang G. CDK9 inhibition improves diabetic nephropathy by reducing inflammation in the kidneys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021;416: 115465.
Wu J, Renn CL, Faden AI, Dorsey SG. TrkB.T1 contributes to neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury through regulation of cell cycle pathways. J Neurosci. 2013;33:12447–63.
Gomez K, Vallecillo TGM, Moutal A, Perez-Miller S, Delgado-Lezama R, Felix R, Khanna R. The role of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in neuropathic pain. Pain. 2020;161:2674–89.
Su CJ, Zhang JT, Zhao FL, Xu DL, Pan J, Liu T. Resolvin D1/N-formyl peptide receptor 2 ameliorates paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain through the activation of IL-10/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1091753.
Funding
Thanks for the grant from the Fujian Provincial Health Technology Project (Project number: 2022CXA023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WCS and CRS conceived the ideas. WCS, CRS and ZXT designed the experiments. WCS, CRS, ZXT, ZXB and LNC performed the experiments. WCS, CRS, ZXT and LNC analyzed the data. WCS, CRS and ZXT provided critical materials. WCS, CRS, LNC and ZXB wrote the manuscript. WCS and CRS supervised the study. All the authors have read and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were conducted per the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University (No. IACUC FJMU 2023–0038).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Chen, R., Zhu, X. et al. Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 5 facilitates neuropathic pain in spinal nerve injury by promoting SCN9A expression via CDK9. Human Cell 37, 451–464 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-01019-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-01019-w