Abstract
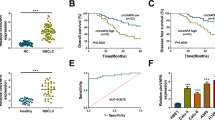
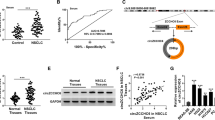
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a well-known tumor suppressor in various cancer types, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Circular RNA (circRNA) has recently been proven to be strongly linked with cancer progression. Here, we aimed to investigate the biological relevance and clinical significance of circRNA derived from PTEN in NSCLC. We found that circ-PTEN (hsa_circ_0094342) was significantly decreased in NSCLC tissues and serum, which was attributed to the upregulation of RNA-binding protein DHX9. Low circ-PTEN was linked with malignant clinical features and poor outcome. Exogenous expression of circ-PTEN markedly inhibited NSCLC cell proliferation in vitro as well as retarded tumor growth in vivo. Circ-PTEN increased the expression of its host gene PTEN via acting as a sponge for miR-155 and miR-330-3p, leading to the inactivation of the carcinogenic PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. The xenograft tumor model also indicated the existence of circ-PTEN/miR-155/miR-330-3p/PTEN regulatory axis in vivo. Our data for the first time demonstrate that circ-PTEN functions as a tumor-inhibiting circRNA in NSCLC through post-transcriptionally regulating PTEN, hinting a promising diagnostic/prognostic biomarker as well as therapeutic target for NSCLC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Walder D, O’Brien M. Looking back and to the future: are we improving “cure” in non-small cell lung cancer? Eur J Cancer. 2017;75:192–4.
Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19:141–57.
Chen I, Chen CY, Chuang TJ. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2015;6:563–79.
Suzuki H, Zuo Y, Wang J, Zhang MQ, Malhotra A, Mayeda A. Characterization of RNase R-digested cellular RNA source that consists of lariat and circular RNAs from pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:e63.
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. Plos Genet. 2013;9:e1003777.
Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N, Brown PO. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30733.
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Veno MT, Kjems J. Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene. 2018;37:555–65.
Zhao ZJ, Shen J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017;14:514–21.
Yang C, Wu D, Gao L, et al. Competing endogenous RNA networks in human cancer: hypothesis, validation, and perspectives. Oncotarget. 2016;7:13479–90.
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:79.
Zeng K, Chen X, Xu M, et al. CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:417.
Mao X, Guo S, Gao L, Li G. Circ-XPR1 promotes osteosarcoma proliferation through regulating the miR-214-5p/DDX5 axis. Hum Cell. 2021;34:122–31.
Papa A, Pandolfi PP. The PTEN(-)PI3K axis in cancer. Biomolecules. 2019;9(4):153.
Gkountakos A, Sartori G, Falcone I, et al. PTEN in lung cancer: dealing with the problem, building on new knowledge and turning the game around. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(8):1141.
Garcia-Cao I, Song MS, Hobbs RM, et al. Systemic elevation of PTEN induces a tumor-suppressive metabolic state. Cell. 2012;149:49–62.
Lee YR, Chen M, Pandolfi PP. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: new modes and prospects. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19:547–62.
Aktas T, Avsar II, Maticzka D, et al. DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome. Nature. 2017;544:115–9.
Worby CA, Dixon JE. PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014;83:641–69.
Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:453–61.
Mao S, Zhang S, Zhou S, et al. A Schwann cell-enriched circular RNA circ-Ankib1 regulates Schwann cell proliferation following peripheral nerve injury. Faseb J. 2019;33:12409–24.
Yan D, Dong W, He Q, et al. Circular RNA circPICALM sponges miR-1265 to inhibit bladder cancer metastasis and influence FAK phosphorylation. EBioMedicine. 2019;48:316–31.
Yu J, Xu QG, Wang ZG, et al. Circular RNA cSMARCA5 inhibits growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;68:1214–27.
Arnaiz E, Sole C, Manterola L, Iparraguirre L, Otaegui D, Lawrie CH. CircRNAs and cancer: Biomarkers and master regulators. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;58:90–9.
Wu N, Yuan Z, Du KY, et al. Translation of yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation machinery. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26:2758–73.
Hu Y, Zhao Y, Shi C, et al. A circular RNA from APC inhibits the proliferation of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by inactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling via interacting with TET1 and miR-888. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11:8068–84.
Funding
This work was supported by Education Scientific Research Fund “Young Seedlings” Project of Liaoning Provincial Department (QN2019015) and 345 Talent Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(I) Conception and design: HYZ; (II) administrative support: HYZ; (III) provision of study materials or patients: YW; (IV) collection and assembly of data: ZBW and JBL; (V) data analysis and interpretation: YW; (VI) manuscript writing: HYZ; (VII) final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (No. 2018PS249K), and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All animals were handled in strict accordance with the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” and the “Principles for the Utilization and Care of Vertebrate Animals”, and all animal work was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Wang, Z., Lu, J. et al. Circular RNA circ-PTEN elevates PTEN inhibiting the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Human Cell 34, 1174–1184 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00526-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-021-00526-y