Abstract
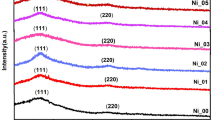
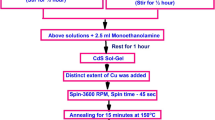
In the current study, pristine and Co@CdS nanocrystalline thin films were fabricated on glass substrates by sol–gel spin coating technique. The structural and optical properties of fabricated films were systematically evaluated. The fabricated films are polycrystalline in nature and have a cubic structure. An investigation of the structure reveals that Co ions have been fully integrated into the CdS lattice. Crystallite size, microstrain, and lattice parameters were calculated using the Debye–Scherrer formula. The crystallite size of the pristine CdS thin films was observed to be 12.05 nm and decreased to 9.73 nm with Co-doping. Also, the microstrain and dislocation density of the films increased with an increase in Co-doping concentration. The 1-LO and 2-LO Raman peaks were found to be shifted toward the lower frequency side. Transmittance, refractive index, and extinction coefficient were examined to identify the changes in optical characteristics caused by Co-doping. The doping process improves the energy bandgap of the CdS nanocrystalline thin film which was in the range of 2.46 to 2.56 eV. The doping also alters the photoluminescence characteristics of CdS, leading to a change in peak toward shorter wavelengths for Co@CdS. The RMS roughness and average grain size of the films decreased with doping. These findings suggest that synthesized films could be a potential material used for optoelectronic applications.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Schuler, M. Python, M. Valle Del Olmo, E. De Chambrier, Sol. Energy 81, 1159–1165 (2007)
S.C. Tjong, H. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 45(2), 1–88 (2004)
K.C. Preetha, K.V. Murali, A.J. Ragina, K. Deepa, T.L. Remadevi, Curr. Appl. Phys. 12(1), 53–59 (2012)
D. Barreca, A. Gasparotto, C. Maragno, E. Tondello, J. Electrochem. Soc. 151(6), 428–35 (2004)
T. Gao, T.H. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. B 108(52), 20045–20049 (2004)
W. Lee, N.P. Dasgupta, H.J. Jung, J.R. Lee, R. Sinclair, F.B. Prinz, Nanotechnology 21, 485402 (2010)
S. Pence, E. Varner, C.W. Bastes Jr, Mater. Lett. 23, 13–16x (2010)
I. Plaza, G. González-Díaz, F. Sánchez-Quesada, M. Rodríguez-Vidal, Thin Solid Films 120, 31–36 (2010)
S. Petillona, A. Dinger, M. Grün, M. Hetterich, V. Kazukauskas, C. Klingshirn, J. Cryst. Growth 201–202, 453–456 (1999)
M.S. Munirah, K.A. Aziz, S.A. Rahman, Z.R. Khan, Mat. Sci. Semicon. Proc. 16, 1894–1898 (2013)
I. Rathinamala, J. Pandiarajan, N. Jeyakumaran, N. Prithivikumaran, Int. J. Thin. Film Sci. Tec. 3, 113–120 (2014)
T. Chtouki, Y. El Kouari, B. Kulyk, A. Louardi, A. Rmili, H. Erguig, B. Elidrissi, Soumahoro, B. Sahraoui, J. Alloys. Compd. 696,1292–1297 (2017)
R. Kumar, R. Das, M. Gupta, V. Ganesan, Superlattice. Microst. 59, 29–37 (2013)
M. Qorbani, N. Naseri, O. Moradlou, R. Azimirad, A.Z. Moshfegh, Appl. Catal. 162, 210–216 (2015)
R. Das, R. Kumar, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 239–246 (2012)
R. Das, R. Kumar, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 697–703 (2013)
P.K. Sahu, R. Das, R. Lalwani, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 18296–18306 (2017)
A. Oudhia, N. Shukla, P. Bose, R. Lalwani, A. Choudhary, Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects. 7, 69–74 (2016)
P. Velusamy, R. Xing, R.R. Babu, E. Elangovan, J. Viegas, S. Liu, M. Sridharan, Sens. Actuators. B. Chem. 297, 126718 (2019)
J. Trajić, M. Gilić, N. Romčević, M. Romčević, G. Stanišić, B. Hadžić, M. Petrović, Y.S. Yahia, Sci. Sinter. 47, 145–152 (2015)
F. Foucher, G. Lopez-Reyes, N. Bost, F. Rull-Perez, P. Rüßmann, F. Westall, J. Raman. Spectrosc. 44(6), 916–925 (2013)
Y. Peng, X. Hu, X. Xu, X. Chen, J. Peng, J. Han, S. Dimitrijev, Opt. Mater. Express. 6, 2725–2733 (2016)
R.R. Prabhu, M. Abdul Khadar, Bull. Mater. Sci. 31(3), 511–515 (2008)
R. Das, R. Kumar, J Mater. Sci. 43, 5972–5976 (2008)
K.R. Gbashi, M.A. Muhi, A.A. Jabbar, N.B. Mahmood, R.F. Hasan, App. Phy. A. 126, 628 (2020)
P.K. Sahu, R. Das, R. Lalwani, App. Phy. A 124, 665 (2018)
N.M. Ravindra, S. Auluck, V.K. Srivastava, Phys. State Solid B 93, k155–k160 (1979)
P.J.L. Herve, L.K.J. Vandamme, J. Appl. Phys. 77, 5476–5477 (1995)
D.R. Penn, Phys. Rev. 128, 2093–2097 (1962)
J.A. Van Vechten, I. Phys, Rev. 182, 891–905 (1969)
D.K. Ghosh, L.K. Samanta, G.C. Bhar, Infrared Phys. 24, 34–47 (1984)
G.A. Samara, Phys. Rev. B 27, 3494–3505 (1983)
K.R. Gbashi, App. Phy. A 26, 275 (2020)
Acknowledgements
The Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg administration, is to be thanked for providing the authors with funding and lab space. Additionally, the authors would like to express their gratitude to the UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research, Indore, India, for facilitating XRD and AFM facilities at their center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B., Lalwani, R. & Das, R. Spectroscopic Studies of CdS Nanocrystalline Thin Films Synthesized by Sol–Gel Spin Coating Technique for Optoelectronic Application: Influence of Co-Doping. Braz J Phys 53, 42 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-023-01257-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13538-023-01257-1