Abstract
Objective
Thiamethoxam (TMX) is a systemic insecticide used to combat plant pests that might significantly affect food security. Therefore, the current study aimed to evaluate its mammalian toxicity against male albino rats following short-term administration of sublethal doses.
Methods
Two groups, control and treatment rats (eight males each), were orally administered distilled water and 1/20 LD50 (78.0 mg/kg B.W.) doses of TMX daily for 14 days. The biochemical, hematological, genotoxic, and histopathological responses were subsequently described.
Results
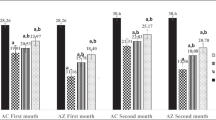
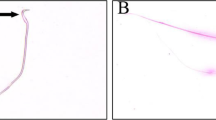
The results revealed significant decreases in the specific activities of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE), and Mg+-ATPase in the TMX-treated rats compared to those in the control group. Additionally, alterations in blood parameters were reported for treated individuals. Significant increases in the number of tailings (14%), tail length (3.43 µm), tail DNA (3.62%), and tail moment (12.56%) as well as the frequency of micronucleated erythrocytes (MNs) were found in the TMX-treated animals. Moreover, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of blood samples revealed swollen mitochondria with light-dense cristae, vacuoles (V), nuclei (N) (contained migrated chromatin), and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) in comparison to the firm structure of the negative control.
Conclusion
TMX exposure, especially at low doses, is an alarming sign of possible health hazards.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available within the article or its supplementary materials. The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and/or] its supplementary materials.
References
Matsuda K, Ihara M, Sattelle DB (2020) Neonicotinoid insecticides: molecular targets, resistance, and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 60:241–255. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010818-02174
Abouelghar GE, Yassien RI, El-Bermawy ZA-E, Ammar HA, Shalaby YA-E (2020) Sublethal toxicity of thiamethoxam insecticide in albino mice: biochemical, oxidative damage and histopathological evaluations. Adv. J. Toxicol. Curr. Res. 4:017–028. https://doi.org/10.37871/ajtcr.id33
Bagri P, Kumar V, Sikka AK (2015) An in vivo assay of the mutagenic potential of imidacloprid using sperm head abnormality test and dominant lethal test. Drug Chem Toxicol 38:342–348. https://doi.org/10.3109/01480545.2014.966832
Goulson D (2013) Review: an overview of the environmental risks posed by neonicotinoid insecticides. J Appl Ecol 50:977–987. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12111
Sparks TC, Nauen R (2015) IRAC: Mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pest Biochem Physiol 121:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.11.014
Jeschke P, Nauen R, Schindler M, Elbert A (2011) Overview of the status and global strategy for neonicotinoids. J Agric Food Chem 59:2897–2908. https://doi.org/10.1021/JF101303G/ASSET/IMAGES/MEDIUM/JF-2010-01303G_0011.GIF
Elhamalawy OH, Al-Anany FS, El Makawy AI (2022) Thiamethoxam-induced hematological, biochemical, and genetic alterations and the ameliorated effect of Moringa oleifera in male mice. Toxicol Rep 9:94–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOXREP.2021.12.012
Rodrigues KJA, Santana MB, Do Nascimento JLM, Picanço-Diniz DLW, Maués LAL, Santos SN, Ferreira VMM, Alfonso M, Durán R, Faro LRF (2010) Behavioral and biochemical effects of neonicotinoid thiamethoxam on the cholinergic system in rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2009.04.021
Lu C, Chang C-H, Palmer C, Zhao M, Zhang Q (2018) Neonicotinoid residues in fruits and vegetables: an integrated dietary exposure assessment approach. Environ Sci Technol 52:3175–3184. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05596
Tomlin CDS (2006) The pesticide manual. A world compendium, 14th edn. British Crop Protection Council, Surry
Arfat Y, Mahmood N, Tahir MU, Rashid M, Anjum S, Zhao F, Li D-J, Sun Y-L, Hu L, Zhihao C, Yin C, Shang P, Qian A-R (2014) Effect of imidacloprid on hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in male albino mice. Toxicol Rep 1:554–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.08.004
Gul ST, Ahamd I, Saleemi MK, Ahmad M, Ahmad L, Khan A (2020) Toxico-pathological effects of thiamethoxam on hemato-biochemical and productive performance of commercial laying hens. Pak Vet J 40:449–454. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2020.052
Gul ST, Khan A, Ahmad M, Anwar MF, Khatoon A, Saleemi MK, Akram MN (2018) Effect of sublethal doses of thiamethoxam (a neonicotinoid) on hemato-biochemical parameters in broiler chicks. Toxin Rev 37:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2017.1336731
Gul ST, Khan RL, Saleemi MK, Ahmad M, Hussain R, Khan A (2022) Amelioration of toxicopathological effects of thiamethoxam in broiler birds with vitamin E and selenium. Toxin Rev 41:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2020.1864647
Hussain AGR, Noreen S, Abbas G, Chodhary IR, Khan A, Ahmed Z, Khan MK, Akram K, Ulhaq M, Ahmad N, Ali F, Niaz M (2020) Dose and time-related pathological and genotoxic studies on thiamethoxam in fresh water fish (Labeo rohita) in Pakistan. Pak Vet J 40:151–156. https://doi.org/10.29261/pakvetj/2020.002
Chaudhry A, Kaur S, Bhinder P, Barna B (2012) Imidacloprid and thiamethoxam induced mutations in internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) of Anopheles stephensi. Toxicol Int 19:201. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-6580.97223
El Okle OS, El Euony OI, Khafaga AF, Lebda MA (2018) Thiamethoxam induced hepatotoxicity and pro-carcinogenicity in rabbits via motivation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and anti-apoptotic pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:4678–4689. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-017-0850-0
Habotta OA, Ateya A, Saleh RM, El-Ashry ES (2021) Thiamethoxam-induced oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation, and disturbance of steroidogenic genes in male rats: palliative role of Saussurea lappa and Silybum marianum. Environ Toxicol 36:2051–2061. https://doi.org/10.1002/TOX.23322
Khaldoun-Oularbi H, Bouzid N, Boukreta S, Makhlouf C, Derriche F, Djennas N (2017) Thiamethoxam Actara® induced alterations in kidney liver cerebellum and hippocampus of male rats. J Xenobiot. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2017.7149
Wang X, Anadón A, Wu Q, Qiao F, Ares I, Martínez-Larrañaga MR, Yuan Z, Martínez MA (2018) Mechanism of neonicotinoid toxicity: impact on oxidative stress and metabolism. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1146/ANNUREV-PHARMTOX-010617-052429
Şenyildiz M, Kilinc A, Ozden S (2018) Investigation of the genotoxic and cytotoxic effects of widely used neonicotinoid insecticides in HepG2 and SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicol Ind Health 34:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233718762609
Al-Sarar AS, Abobakr Y, Bayoumi AE, Hussein HI (2015) Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of abamectin, chlorfenapyr, and imidacloprid on CHOK1 cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:17041–17052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4927-3
Şekeroğlu V, Şekeroğlu ZA, Kefelioğlu H (2013) Cytogenetic effects of commercial formulations of deltamethrin and/or thiacloprid on wistar rat bone marrow cells. Environ Toxicol 28:524–531. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20746
Sorensen KC, Stucki JW, Warner RE, Wagner ED, Plewa MJ (2005) Modulation of the genotoxicity of pesticides reacted with redox-modified smectite clay. Environ Mol Mutagen 46:174–181. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.20144
Feki A, Ben Saad H, Bkhairia I, Ktari N, Naifar M, Boudawara O, Droguet M, Magné C, Nasri M, Ben Amara I (2019) Cardiotoxicity and myocardial infarction-associated DNA damage induced by thiamethoxam in vitro and in vivo: protective role of Trigonella foenum-graecum seed-derived polysaccharide. Environ Toxicol 34:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/TOX.22682
Yan SH, Wang JH, Zhu LS, Chen AM, Wang J (2016) Thiamethoxam induces oxidative stress and antioxidant response in zebrafish (Danio rerio) livers. Environ Toxicol 31:2006–2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/TOX.22201
Maienfisch P, Gsell L, Rindlisbacher A (1999) Synthesis and insecticidal activity of CGA 293 343: a novel broad-spectrum insecticide. Pest Sci 55:351–435
NRCNA (2011) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National research council of the national academies. The National Academics Press, Washington
Nassar AMKK, Salim YM, Malhat FM (2016) Assessment of pesticide residues in human blood and effects of occupational exposure on hematological and hormonal qualities. Pakistan J Biol Sci 19:95–105. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2016.95.105
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Taussky HH, Shorr E, Kurzmann G (1953) A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosohorus. J Biol Chem 202:675–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)66180-0
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(19)52451-6
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4827(88)90265-0
Schmid W (1976) The micronucleus test for cytogenetic analysis. In: Hollaender A (ed) Chemical mutagens. Springer, Boston, pp 31–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4684-0892-8_2
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212. https://doi.org/10.1083/JCB.17.1.208
SAS (2016) Statistical analysis system. Version 9.3
Shahjahan M, Islam MJ, Hossain MT, Mishu MA, Hasan J, Brown C (2022) Blood biomarkers asdiagnostic tools: An overview of climate-driven stress responses in fish. Sci Total Environ 843:156910
Benjamin MM (1978) Outline of veterinary clinical pathology. Iowa State University Press
Hataba AA, Keshta AT, Mead H, El-Shafey N (2014) Hematological, Biochemical and Histologicalalterations induced by oral administration of Thiamethoxam and Acetamiprid in male rats. Biochem Lett 10(1):113–125
Nassar AMK (2016) Acetylcholinesterase: a universal toxicity biomarker. J Agric Env Sci 15:28
Abu TM (2005) Adverse impact of insecticides on the health of Palestinian farm workers in the Gaza strip: a hematologic biomarker study. Int J Occup Environ Health 11:144–149. https://doi.org/10.1179/oeh.2005.11.2.144
Smina AH, Samira B, Mohamed D, Houria B (2016) Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase, glutathione S-transferase and catalase activities in the land snail Helix aspersa exposed to thiamethoxam. J Ent Zool 4:369–374
Umar AM, Aisami A (2020) Acetylcholinesterase enzyme (AChE) as a biosensor and biomarker for pesticides: a mini review. Bull Environ Sci Sustain Manag 4:7–12
Dhananjayan V, Ravichandran B, Anitha N, Rajmohan H (2012) Assessment of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities in blood plasma of agriculture workers. Indian J Occup Environ Med 16:127. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5278.111755
Demirci Ö, Güven K, Asma D, Öğüt S, Uğurlu P (2018) Effects of endosulfan, thiamethoxam, and indoxacarb in combination with atrazine on multi-biomarkers in Gammarus kischineffensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:749–758
Serafini S, de Freitas Souza C, Baldissera MD, Baldisserotto B, Segat JC, Baretta D, Zanella R, da Silva AS (2019) Fish exposed to water contaminated with eprinomectin show inhibition of the activities of AChE and Na+/K+-ATPase in the brain, and changes in natural behavior. Chemosphere 223:124–130
Temiz Ö, Kargın D (2024) Physiological responses of oxidative damage, genotoxicity and hematological parameters of the toxic effect of neonicotinoid-thiamethoxam in Oreochromis niloticus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 104377
Thaker J (1996) Effects of chromium(VI) on some ion-dependent ATPases in gills, kidney and intestine of a coastal teleost Periophthalmus dipes. Toxicology 112:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483X(96)86481-X
Vasić V, Momić T, Petković M, Krstić D (2008) Na+, K+-ATPase as the target enzyme for organic and inorganic compounds. Sensors 8:8321–8360. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8128321
Čolović MB, Vasić VM, Avramović NS, Gajić MM, Djurić DM, Krstić DZ (2015) In vitro evaluation of neurotoxicity potential and oxidative stress responses of diazinon and its degradation products in rat brain synaptosomes. Toxicol Lett 233:29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.01.003
Comoglio L, Amin O, Roque A, Betancourt-Lozano M, Anguas D, Haro BM (2005) Evaluation of sublethal biomarkers in Litopenaeus vannamei on foodborne exposure to methyl parathion. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2004.10.006
Ma J, Zhu J, Wang W, Ruan P, Rajeshkumar S, Li X (2019) Biochemical and molecular impacts of glyphosate-based herbicide on the gills of common carp. Environ Pollut 252:1288–1300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.040
Reddy AN, Venugopal NBRK, Reddy SLN (1992) Effect of endosulfan 35 EC on ATPases in the tissues of a freshwater field crab Barytelphusa guerini. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 48:216–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00194374/METRICS
Parvez S, Sayeed I, Raisuddin S (2006) Decreased gill ATPase activities in the freshwater fish Channa punctata (Bloch) exposed to a diluted paper mill effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:62–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.07.010
Uçkun M, Özmen M (2021) Evaluating multiple biochemical markers in Xenopus laevis tadpoles exposed to the pesticides thiacloprid and trifloxystrobin in single and mixed forms. Environ Toxicol Chem 40:2846–2860. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5158
Wang YYL, Cai Y-E, Kazmi SSUH, Yang J, Wang Y, Li P, Liu W, Wang Z (2023) Temperature-dependent effects of neonicotinoids on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front Mar Sci 9:1101737
Yang D, Zhang X, Yue L, Hu H, Wei X, Guo Q, Zhang B, Fan X, Xin Y, Oh Y, Gu N (2021) Thiamethoxam induces nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice via methionine metabolism disturb via nicotinamide N-methyltransferase overexpression. Chemosphere 273:129727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129727
Jacobsen-Pereira CH, dos Santos CR, Troina Maraslis F, Pimentel L, Feijó AJL, Iomara Silva C, de Medeiros GS, Costa Zeferino R, Curi Pedrosa R, Weidner Maluf S (2018) Markers of genotoxicity and oxidative stress in farmers exposed to pesticides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.10.004
Kocaman AY, Topaktaş M (2007) In vitro evaluation of the genotoxicity of acetamiprid in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 48:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1002/EM.20309
Muranli FDG, Rasgele PG, Kekecoglu M, Kanev M, Ozdemir K (2015) Potential genotoxicity of acetamiprid and propineb singly or in combination in cultured human peripheral blood lymphocytes by using MN assay. Fresen Environ Bull 24:3947–3955
Zhu L, Li W, Zha J, Li N, Wang Z (2019) Chronic thiamethoxam exposure impairs the HPG and HPT axes in adult Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus): docking study, hormone levels, histology, and transcriptional responses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 185:109683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109683
Pan Y, Chang J, Wan B, Liu Z, Yang L, Xie Y, Hao W, Li J, Xu P (2022) Integrative analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals the hepatotoxic mechanism of thiamethoxam on male Coturnix japonica. Environ Pollut 293:118460. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVPOL.2021.118460
Burgos-Aceves MA, Cohen A, Smith Y, Faggio C (2018) MicroRNAs and their role on fish oxidative stress during xenobiotic environmental exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:995–1000
Jaballi I, Ben Saad H, Bkhairia I, Kammoun I, Droguet M, Magné C, Boudawara T, Kallel C, Nasri M, Hakim A, Ben Amara I (2017) Increasing maneb doses induces reactive oxygen species overproduction and nephrotoxicity in adult mice. Toxicol Mech Methods 27:382–393. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2017.1300617
Demsia G, Vlastos D, Goumenou M, Matthopoulos DP (2007) Assessment of the genotoxicity of imidacloprid and metalaxyl in cultured human lymphocytes and rat bone-marrow. Mutat Res/Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 634:32–39
Günal AÇ, Erkmen B, Paçal E, Arslan P, Yildirim Z, Erkoç F (2019) Sub-lethal effects of imidacloprid on Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Water Air Soil Pollut 231:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4366-8
Kataria SK, Chhillar AK, Kumar A, Tomar M, Malik V (2016) Cytogenetic and hematological alterations induced by acute oral exposure of imidacloprid in female mice. Drug Chem Toxicol 39:59–65
Jia G, Wang P, Qiu J, Sun Y, Xiao Y, Zhou Z (2004) Determination of DNA with imidacloprid by a resonance light scattering technique at nanogram levels and its application. Anal Lett 37:1339–1354
Katić A, Kašuba V, Kopjar N, Lovaković BT, Čermak AMM, Mendaš G, Micek V, Milić M, Pavičić I, Pizent A (2021) Effects of low-level imidacloprid oral exposure on cholinesterase activity, oxidative stress responses, and primary DNA damage in the blood and brain of male Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact 338:109287
Li S, Cao Y, Pan Q, Xiao Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Li X, Li Q, Tang X, Ran B (2021) Neonicotinoid insecticides triggers mitochondrial bioenergetic dysfunction by manipulating ROS-calcium influx pathway in the liver. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 224:112690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112690
Sesso A, Belizário JE, Marques MM, Higuchi ML, Schumacher RI, Colquhoun A, Ito E, Kawakami J (2012) Mitochondrial swelling and incipient outer membrane rupture in preapoptotic and apoptotic cells. Anat Rec 295:1647–1659. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.22553
Abdelmeguid N, Ramadan AA, El-Khatib AM (1990) Effects of split fast neutron doses on the liver cells of albino Swiss mice. Folia Morphol (Praha) 38
Montisano DF, Cascarano J, Pickett CB, James TW (1982) Association between mitochondria and rough endoplasmic reticulum in rat liver. Anat Rec 203:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/ar.1092030403
Saleh AA (1993) Histopathological effect of three synthetic pyrethroids on lung and kidney of rat. J Agric Sci Mansoura Univ Egypt 18:288–295
El-Hawashy N, Khedr F (2001) Histopathological effects of calciferol on albino rat, Rattus norvegicus. J Agric Sci Mansoura Univer, Egypt 26:8029–8046
Directives (2010) Directive 2010/63/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off J Eur Union 276(33):75–82
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Atef M. K. Nassar, Hossam El Din H. Abdelhafez, Yehia M. Salim, Khaled Y. Abdel‑Halim declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval studies in animals
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Faculty of Agriculture, Damanhur University, approved the animal care ethics (No DUFA-2022-4), and the standard international guidelines for animal care were followed according to the National Institutes of Health Guide and the EU Directive 2010/63/EU for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals [28, 76].
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nassar, A.M.K., Abdelhafez, H.E.D.H., Salim, Y.M. et al. Cytotoxicity of short-term exposure to sublethal dose of the insecticide thiamethoxam to male albino rats. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-024-00210-2
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-024-00210-2