Abstract
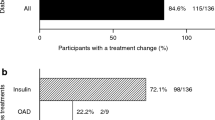
Ramadan fasting is usually a challenge for both Muslim patients with diabetes and their health care providers. The challenge is even greater in patients with type 1 diabetes. Existing clinical guidelines categorize patients with type 1 diabetes as very-high-risk patients, and therefore, they are advised not to fast. However, many patients with type 1 diabetes choose to fast despite medical advice. In this study, we examine the feasibility of Ramadan fasting in adult patients with type 1 diabetes and define the frequency of acute complications in these patients during Ramadan. In this retrospective study, patients aged 18 years or older with type 1 diabetes who choose to fast during the month of Ramadan in the year 2015 were interviewed during their first visit after Ramadan, and their records were reviewed to determine the number of days in which patients broke the fast, frequency of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis, and frequency of hospitalization during Ramadan. The 73 patients included in the study were able to fast an average of 26.8 days which corresponds to 92% of total fasting days. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia caused the patients to break the fast in 2.36 and 2.78% of the total fasting days, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hui E, Bravis V, Hassanein M, Hanif W, Malik R, Chowdhury TA, et al. Management of people with diabetes wanting to fast during Ramadan. BMJ. 2010;340:c3053.
Al-Arouj M, Bouguerra R, Buse J, Hafez S, Hassanein M, Ibrahim MA, et al. Recommendations for management of diabetes during Ramadan. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2305–11.
Al-Arouj M, Assaad-Khalil S, Buse J, Fahdil I, Fahmy M, Hafez S, et al. Recommendations for management of diabetes during Ramadan: update 2010. Diabetes Care. 2010;33:1895–902.
Ibrahim M, Abu Al Magd M, Annabi FA, Assaad-Khalil S, Ba-Essa EM, Fahdil I, et al. Recommendations for management of diabetes during Ramadan: update 2015. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2015;3:e000108.
Salti I, Bénard E, Detournay B, Bianchi-Biscay M, Le Brigand C, Voinet C, et al. A population-based study of diabetes and its characteristics during the fasting month of Ramadan in 13 countries: results of the epidemiology of diabetes and Ramadan 1422/2001 (EPIDIAR) study. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(10):2306–11.
Elmehdawi RR, Mukhtad NA, Allaghi NI, Elmajberi SJ. Fasting of Ramadan in peoples with diabetes in Benghazi, Libya: an exploratory study. Libyan J Med. 2010;5:5036. doi: 10.3402/ljm.v5i0.5036.
Musleh A, Beshyah S, Abu Awad S, Kahwatih M, Al Jubeh J. Experience with diabetic adolescents observing Ramadan fasting. Ibnosina J Med BS. 2015;7(6):223–7.
Azar ST, Khairallah WG, Merheb MT, Zantout MS, Fliti F. Insulin therapy during Ramadan fast for patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Med Liban. 2008;56(1):46.
Elmehdawi R, Ehmida M, Elmagrehi H. Incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis during Ramadan fasting in Benghazi-Libya. Oman Med J. 2009;24(2):99–102.
Reiter J, Wexler ID, Shehadeh N, Tzur A, Zangen D. Type 1 diabetes and prolonged fasting. Diabet Med. 2007;24(4):436–9.
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required; thus, verbal consent was obtained from all the subjects during the interview. The study did not include any active involvement of human subjects, and since there was no dedicated ethical review committee in the institution at the time of our study, we obtained ethical and administrative clearance from department of medicine at the institution which oversees the study clinics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbarsha, A., Elmehdawi, R., Eljazwi, I. et al. Feasibility of Ramadan fasting in adults with type 1 diabetes: an observational study. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 38, 191–194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-017-0575-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-017-0575-0