Abstract
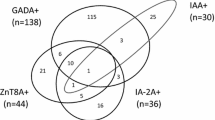
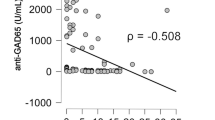
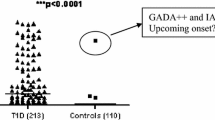
The purpose of this study is to screen for diabetes-related antibodies in newly diagnosed type I diabetes Saudi children, and their non-diabetic siblings. We studied 69 newly diagnosed type 1 diabetic Saudis (35 girls, 34 boys), 60 non-diabetic siblings (1 to 17 years), and 42 age- and sex-matched controls not having type 1 diabetes. Their sera were tested for insulin autoantibodies (IAA), antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65A) and protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 antibodies (IA-2) using 125I radioimmunoassays. Fifty-two percent of patients were significantly positive for IAA compared to controls (4.9 %). A total of 50.7 % of patients were also significantly positive for IA-2 compared to controls (4.8 %) (p < 0.0001). GAD65 antibody was detected in 81.2 % of the patients and in none of the controls (p < 0.0001). Both IAA and IA-2 are significantly higher among younger age group, unlike GAD65A, which is significantly higher among older age groups. In non-diabetic siblings, the frequencies of IAA, IA-2, and GAD65A were 6.8, 5.2, and 10.2 % (0.039), respectively, which were higher than in controls. IAA and IA-2 titers were significantly high among younger age group (<0.027), and GAD65A is significantly higher among older age group. A total of 21.6 % of diabetics were positive for all the three antibodies and 3.4 % in siblings. A total of 35.3 % were positive for two antibodies and none in siblings, while 39.2 % were positive for one antibody and 11.9 % in siblings. The combined GAD65 and IA-2 was positive in 81.3 % of young age, 80 % of middle, and in 100 % of the old age group. The screening of type 1 diabetes among Saudis showed the presence of diabetes-related antibodies in 96.1 % of all newly diagnosed patients, compared to 11.9 % of controls (non-diabetic siblings). IAA and IA-2 were significantly higher among younger age groups; GAD65A was significantly higher among older age. The combined GAD65 and IA-2 tests can be considered as a sensitive marker for predicting the occurrence of the disease in individuals at risk of type 1 diabetes in Saudis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Imagawa A, Hanafusa T, Miyagawa J, Matsuzawa Y. A proposal of three distinct subtypes of type 1 diabetes mellitus based on clinical and pathological evidence. Ann Med. 2000;32(8):539–43.
Hitman GA. The immunogenetics of insulin-dependent diabetes. Eye (Lond). 1993;7(Pt 2):209–13.
Libman IM, Barinas-Mitchell E, Marcovina S, Bacha F, Hannon T, Tfayli H, et al. Beta-cell autoimmunity in overweight non-diabetic youth: any implications? Pediatric diabetes. 2011;12(3 Pt 2):207–11.
Colman PG, McNair PD, Gellert S, Kewming K, Schmidli RS, Steele CE, et al. Development of autoantibodies to islet antigens during childhood: implications for preclinical type 1 diabetes screening. Pediatric diabetes. 2002;3(3):144–8.
Poussier P, Schiffrin A, Ciampi A, Tam E, Colle E, Lalla D, et al. The risk of developing disease for siblings of patients with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Clin Invest Med. 1991;14(1):1–8.
Tuomi T, Bjorses P, Falorni A, Partanen J, Perheentupa J, Lernmark A, et al. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase and insulin-dependent diabetes in patients with autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81(4):1488–94.
Tarn AC, Thomas JM, Dean BM, Ingram D, Schwarz G, Bottazzo GF, et al. Predicting insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet. 1988;1(8590):845–50.
Gorsuch AN, Spencer KM, Lister J, McNally JM, Dean BM, Bottazzo GF, et al. Evidence for a long prediabetic period in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1981;2(8260–61):1363–5.
Bingley PJ. Interactions of age, islet cell antibodies, insulin autoantibodies, and first-phase insulin response in predicting risk of progression to IDDM in ICA+ relatives: the ICARUS data set. Islet Cell Antibody Register Users Study. Diabetes. 1996;45(12):1720–8.
Palmer JP, Asplin CM, Clemons P, Lyen K, Tatpati O, Raghu PK, et al. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983;222(4630):1337–9.
Vardi P, Ziegler AG, Mathews JH, Dib S, Keller RJ, Ricker AT, et al. Concentration of insulin autoantibodies at onset of type I diabetes. Inverse log-linear correlation with age. Diabetes Care. 1988;11(9):736–9.
Ziegler AG, Ziegler R, Vardi P, Jackson RA, Soeldner JS, Eisenbarth GS. Life-table analysis of progression to diabetes of anti-insulin autoantibody-positive relatives of individuals with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1989;38(10):1320–5.
Ongagna JC, Levy-Marchal C. Anti-37 kDa antibodies are associated with the development of IDDM in individuals with islet cell antibodies. Diabetologia. 1995;38(3):370–5.
Verge CF, Gianani R, Kawasaki E, Yu L, Pietropaolo M, Jackson RA, et al. Prediction of type I diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes. 1996;45(7):926–33.
Baekkeskov S, Nielsen JH, Marner B, Bilde T, Ludvigsson J, Lernmark A. Autoantibodies in newly diagnosed diabetic children immunoprecipitate human pancreatic islet cell proteins. Nature. 1982;298(5870):167–9.
Gorus FK, Goubert P, Semakula C, Vandewalle CL, De Schepper J, Scheen A, et al. IA-2-autoantibodies complement GAD65-autoantibodies in new-onset IDDM patients and help predict impending diabetes in their siblings. The Belgian Diabetes Registry Diabetologia. 1997;40(1):95–9.
Bingley PJ, Christie MR, Bonifacio E, Bonfanti R, Shattock M, Fonte MT, et al. Combined analysis of autoantibodies improves prediction of IDDM in islet cell antibody-positive relatives. Diabetes. 1994;43(11):1304–10.
Colman PG, McNair P, Margetts H, Schmidli RS, Werther GA, Alford FP, et al. The Melbourne Pre-Diabetes Study: prediction of type 1 diabetes mellitus using antibody and metabolic testing. Med J Aust. 1998;169(2):81–4.
Castano L, Ziegler AG, Ziegler R, Shoelson S, Eisenbarth GS. Characterization of insulin autoantibodies in relatives of patients with type I diabetes. Diabetes. 1993;42(8):1202–9.
Atkinson MA, Maclaren NK, Riley WJ, Winter WE, Fisk DD, Spillar RP. Are insulin autoantibodies markers for insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus? Diabetes. 1986;35(8):894–8.
McEvoy RC, Witt ME, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Rubinstein P. Anti-insulin antibodies in children with type I diabetes mellitus. Genetic regulation of production and presence at diagnosis before insulin replacement. Diabetes. 1986;35(6):634–41.
Srikanta S, Ricker AT, McCulloch DK, Soeldner JS, Eisenbarth GS, Palmer JP. Autoimmunity to insulin, beta cell dysfunction, and development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1986;35(2):139–42.
Kulmala P, Savola K, Petersen JS, Vahasalo P, Karjalainen J, Lopponen T, et al. Prediction of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in siblings of children with diabetes. A population-based study. The Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. J Clin Invest. 1998;101(2):327–36.
Roll U, Ziegler AG. Combined antibody screening for improved prediction of IDDM–modern strategies. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 1997;105(1):1–14.
Greenbaum CJ, Sears KL, Kahn SE, Palmer JP. Relationship of beta-cell function and autoantibodies to progression and nonprogression of subclinical type 1 diabetes: follow-up of the Seattle Family Study. Diabetes. 1999;48(1):170–5.
Vardi P, Dib SA, Tuttleman M, Connelly JE, Grinbergs M, Radizabeh A, et al. Competitive insulin autoantibody assay. Prospective evaluation of subjects at high risk for development of type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1987;36(11):1286–91.
Bingley PJ, Williams AJ, Gale EA. Optimized autoantibody-based risk assessment in family members. Implications for future intervention trials. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(11):1796–801.
Strebelow M, Schlosser M, Ziegler B, Rjasanowski I, Ziegler M. Karlsburg Type I diabetes risk study of a general population: frequencies and interactions of the four major type I diabetes-associated autoantibodies studied in 9419 schoolchildren. Diabetologia. 1999;42(6):661–70.
Kelly MA, Alvi NS, Croft NJ, Mijovic CH, Bottazzo GF, Barnett AH. Genetic and immunological characteristics of type I diabetes mellitus in an Indo-Aryan population. Diabetologia. 2000;43(4):450–6.
Hawa MI, Fava D, Medici F, Deng YJ, Notkins AL, De Mattia G, et al. Antibodies to IA-2 and GAD65 in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: isotype restriction and polyclonality. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(2):228–33.
Bonifacio E, Genovese S, Braghi S, Bazzigaluppi E, Lampasona V, Bingley PJ, et al. Islet autoantibody markers in IDDM: risk assessment strategies yielding high sensitivity. Diabetologia. 1995;38(7):816–22.
Amrouche C, Jamoussi Kamoun H, Trabelsi N, Blouza CS. Latent autoimmune diabetes in Tunisian adults (LADA): identification of autoimmune markers. Tunis Med. 2008;86(4):316–8.
Aguilera E, Casamitjana R, Ercilla G, Oriola J, Gomis R, Conget I. Adult-onset atypical (type 1) diabetes: additional insights and differences with type 1A diabetes in a European Mediterranean population. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1108–14.
Tuomi T, Zimmet P, Rowley MJ, Min HK, Vichayanrat A, Lee HK, et al. Differing frequency of autoantibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase among Koreans, Thais, and Australians with diabetes mellitus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1995;74(2):202–6.
Knip M, Korhonen S, Kulmala P, Veijola R, Reunanen A, Raitakari OT, et al. Prediction of type 1 diabetes in the general population. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1206–12.
Hummel S, Ziegler AG. Early determinants of type 1 diabetes: experience from the BABYDIAB and BABYDIET studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;94(6 Suppl):1821S–3S.
Vahasalo P, Knip M, Karjalainen J, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Lounamaa R, Akerblom HK. Islet cell-specific autoantibodies in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and their siblings at clinical manifestation of the disease. Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. Eur J Endocrinol. 1996;135(6):689–95.
Cinek O, Kolouskova S, Pechova M, Sumnik Z, Sedlakova P, Bendukidze N, et al. Prediction of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in children of first-degree relatives of diabetic patients. Cas Lek Cesk. 2001;140(16):492–6.
Sabbah E, Savola K, Ebeling T, Kulmala P, Vahasalo P, Ilonen J, et al. Genetic, autoimmune, and clinical characteristics of childhood- and adult-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2000;23(9):1326–32.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (grant reference number MS-4-46). We thank Dr. S. Abdelrahman at the Sulimania Pediatric Hospital for referring patients to the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. We further confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all of us. We confirm that we have given due consideration to the protection of intellectual property associated with this work and that there are no impediments to publication, including the timing of publication, with respect to intellectual property.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awadalla, S.A., AL-Hakbani, M. The predictive value of diabetes-related antibodies in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and their siblings. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 37, 248–253 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-016-0480-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-016-0480-y