Abstract
Purpose
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most malignant subtype of astrocytic tumors with the worst prognosis in all its progressive forms. Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 (BRMS1) is a metastasis suppressor gene that controls malignancy in multiple tumors. As yet, however, its clinical and functional significance in mutant P53 GBM remains inconclusive. Here, we attempted to study the importance of BRMS1 in mutant P53 GBM.
Methods
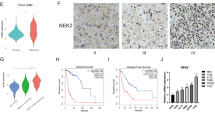
BRMS1 expression was evaluated in 74 human astrocytoma tissues by qRT-PCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry. BRMS1 expression in the astrocytoma tissues was correlated with clinicopathological parameters, the P53 mutation status and BRMS1 downstream targets, and compared with TCGA and NCI-60 datasets. siRNA-mediated knockdown of BRMS1 was performed in selected GBM cell lines to evaluate the functional role of BRMS1.
Results
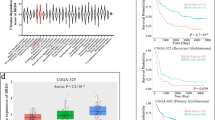
Our study revealed an enhanced expression of BRMS1 in GBM which was associated with a poor patient survival, and this observation was corroborated by the TCGA dataset. We also found a positive correlation between BRMS1 expression and a mutant P53 status in GBM which was associated with a poor prognosis. In vitro BRMS1 silencing reduced the growth of mutant P53 GBM cells and repressed their colonization and migration/invasion by modulating EGFR-AKT/NF-κB signaling. Transcriptional profiling revealed a positive and negative correlation of uPA and ING4 expression with BRMS1 expression, respectively.
Conclusion
Our data indicate upregulation of BRMS1 in high grade astrocytomas which correlates positively with mutant P53 and a poor patient survival. Silencing of BRMS1 in mutant P53 GBM cell lines resulted in a reduced cellular growth and migration/invasion by suppressing the EGFR-AKT/NF-kB signaling pathway. BRMS1 may serve as a predictive biomarker and therapeutic target in mutant P53 GBM.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the manuscript or its supplementary files, and if more is needed, it shall be made available by the authors upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- BRMS1 :
-
Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1
- wt/mut P53:
-
wild/mutant P53
- MSG:
-
Metastasis suppressor gene
- UPA :
-
Urokinase plasminogen activator
- ING4 :
-
Inhibitor of growth family-4
- EGFR :
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- NT-siRNA:
-
Non-targeting-small interfering RNA
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- TCGA:
-
The Cancer Genome Atlas
- CPTAC:
-
Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium
References
Q.T. Ostrom, H. Gittleman, J. Xu, C. Kromer, Y. Wolinsky, C. Kruchko, J.S. Barnholtz-Sloan, CBTRUS Statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro-Oncol 18(suppl_5), v1-v75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/now207
D.N. Louis, H. Ohgaki, O.D. Wiestler, W.K. Cavenee, P.C. Burger, A. Jouvet, B.W. Scheithauer, P. Kleihues, The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 114(2), 97–109 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0243-4
P.Y. Wen, S. Kesari, Malignant gliomas in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 359(5), 492–507 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra0708126
F.B. Furnari, T. Fenton, R.M. Bachoo, A. Mukasa, J.M. Stommel, A. Stegh, W.C. Hahn, K.L. Ligon, D.N. Louis, C. Brennan, L. Chin, R.A. DePinho, W.K. Cavenee, Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to treatment. Genes Dev. 21(21), 2683–2710 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1596707
D.N. Louis, A. Perry, G. Reifenberger, A. von Deimling, D. Figarella-Branger, W.K. Cavenee, H. Ohgaki, O.D. Wiestler, P. Kleihues, D.W. Ellison, The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 131(6), 803–820 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1
G. Alzial, O. Renoult, F. Paris, C. Gratas, A. Clavreul, C. Pecqueur, Wild-type isocitrate dehydrogenase under the spotlight in glioblastoma. Oncogene 41(5), 613–621 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-02056-1
A.M. Molinaro, J.W. Taylor, J.K. Wiencke, M.R. Wrensch, Genetic and molecular epidemiology of adult diffuse glioma. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 15(7), 405–417 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-019-0220-2
D.R. Welch, P.S. Steeg, C.W. Rinker-Schaeffer, Molecular biology of breast cancer metastasis. Genetic regulation of human breast carcinoma metastasis. Breast Cancer Res.: BCR 2(6), 408–416 (2000)
R.S. Samant, M.J. Seraj, M.M. Saunders, T.S. Sakamaki, L.A. Shevde, J.F. Harms, T.O. Leonard, S.F. Goldberg, L. Budgeon, W.J. Meehan, C.R. Winter, N.D. Christensen, M.F. Verderame, H.J. Donahue, D.R. Welch, Analysis of mechanisms underlying BRMS1 suppression of metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 18(8), 683–693 (2000)
P.R. Bucciarelli, K.S. Tan, N.P. Chudgar, W. Brandt, J. Montecalvo, T. Eguchi, Y. Liu, R. Aly, W.D. Travis, P.S. Adusumilli, D.R. Jones, BRMS1 expression in surgically resected lung adenocarcinoma predicts future metastases and is associated with a poor prognosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 13(1), 73–84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.10.006
M.A. Kodura, S. Souchelnytskyi, Breast carcinoma metastasis suppressor gene 1 (BRMS1): update on its role as the suppressor of cancer metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 34(4), 611–618 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-015-9583-z
Z. Yang, F. Liu, Z.L. Yang, BRMS1 and HPA as progression, clinical biological behaviors, and poor prognosis-related biomarkers for gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol.: AIMM 24(4), 275–282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1097/PAI.0000000000000183
S. Zhang, Q.D. Lin, W. Di, Suppression of human ovarian carcinoma metastasis by the metastasis-suppressor gene, BRMS1. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer: Off. J. Int. Gynecol. Cancer Soc. 16(2), 522–531 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1438.2006.00547.x
Y. Zhang, J. Guan, Y. Sun, J. Chai, T. Zou, W. Gong, Z. Zhu, X. Liu, Q. Hou, X. Song, Effect of BRMS1 on tumorigenicity and metastasis of human rectal cancer. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 70(1), 505–509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-9948-x
D.R. Welch, C.A. Manton, D.R. Hurst, Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor 1 (BRMS1): robust biological and pathological data, but still enigmatic mechanism of action. Adv. Cancer Res. 132, 111–137 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acr.2016.05.003
P. Mei, J. Bai, M. Shi, Q. Liu, Z. Li, Y. Fan, J. Zheng, BRMS1 suppresses glioma progression by regulating invasion, migration and adhesion of glioma cells. PLoS ONE 9(5), e98544 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098544
A.J. Levine, J. Momand, C.A. Finlay, The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature 351(6326), 453–456 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/351453a0
K. Watanabe, K. Sato, W. Biernat, O. Tachibana, K. von Ammon, N. Ogata, Y. Yonekawa, P. Kleihues, H. Ohgaki, Incidence and timing of p53 mutations during astrocytoma progression in patients with multiple biopsies. Clin. Cancer Res. 3(4), 523–530 (1997)
C. Sarkar, A.M. Ralte, M.C. Sharma, V.S. Mehta, Recurrent astrocytic tumours–a study of p53 immunoreactivity and malignant progression. Br. J. Neurosurg. 16(4), 335–342 (2002)
P.A. Muller, K.H. Vousden, p53 mutations in cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 15(1), 2–8 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2641
M. Cicek, R. Fukuyama, D.R. Welch, N. Sizemore, G. Casey, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 inhibits gene expression by targeting nuclear factor-kappaB activity. Cancer Res. 65(9), 3586–3595 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3139
Y. Wu, W. Jiang, Y. Wang, J. Wu, H. Saiyin, X. Qiao, X. Mei, B. Guo, X. Fang, L. Zhang, H. Lou, C. Wu, S. Qiao, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis via suppressing osteopontin expression. PLoS ONE 7(8), e42976 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042976
J. Yang, B. Zhang, Y. Lin, Y. Yang, X. Liu, F. Lu, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 inhibits SDF-1alpha-induced migration of non-small cell lung cancer by decreasing CXCR4 expression. Cancer Lett. 269(1), 46–56 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.04.016
I. Morimoto, Y. Sasaki, S. Ishida, K. Imai, T. Tokino, Identification of the osteopontin gene as a direct target of TP53. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 33(3), 270–278 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.10020
M. Eren, A.E. Boe, E.A. Klyachko, D.E. Vaughan, Role of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in senescence and aging. Semin Thromb. Hemost. 40(6), 645–651 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1387883
S.A. Mehta, K.W. Christopherson, P. Bhat-Nakshatri, R.J. Goulet Jr., H.E. Broxmeyer, L. Kopelovich, H. Nakshatri, Negative regulation of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by tumor suppressor p53 in breast cancer cells: implications of p53 mutation or isoform expression on breast cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 26(23), 3329–3337 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210120
E.H. Hall, Y. Liu, A. Xiao, L. Shock, D.L. Brautigan, M.W. Mayo, P.S. Adusumilli, D.R. Jones, Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 promotes a mesenchymal phenotype in lung epithelial cells that express oncogenic K-RasV12 and loss of p53. PLoS ONE 9(4), e95869 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095869
M. Cicek, R. Fukuyama, M.S. Cicek, S. Sizemore, D.R. Welch, N. Sizemore, G. Casey, BRMS1 contributes to the negative regulation of uPA gene expression through recruitment of HDAC1 to the NF-kappaB binding site of the uPA promoter. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 26(3), 229–237 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-009-9235-1
J. Li, G. Li, Cell cycle regulator ING4 is a suppressor of melanoma angiogenesis that is regulated by the metastasis suppressor BRMS1. Cancer Res. 70(24), 10445–10453 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3040
O.I. Kit, E.M. Frantsiyants, L.S. Kozlova, E.E. Rostorguev, I.V. Balyazin-Parfenov, Y.A. Pogorelova, [A plasminogen regulation system in brain tumors]. Zhurnal voprosy neirokhirurgii imeni. N N Burdenko 81(2), 22–27 (2017). https://doi.org/10.17116/neiro201781222-27
G. Klironomos, V. Bravou, D.J. Papachristou, G. Gatzounis, J. Varakis, E. Parassi, M. Repanti, H. Papadaki, Loss of inhibitor of growth (ING-4) is implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of human astrocytomas. Brain Pathol. 20(2), 490–497 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00325.x
E.G. Van Meir, T. Kikuchi, M. Tada, H. Li, A.C. Diserens, B.E. Wojcik, H.J. Huang, T. Friedmann, N. de Tribolet, W.K. Cavenee, Analysis of the p53 gene and its expression in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 54(3), 649–652 (1994)
G.R. Sareddy, K. Geeviman, C. Ramulu, P.P. Babu, The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib suppresses the growth and induces apoptosis of human glioblastoma cells via the NF-kappaB pathway. J. Neurooncol. 106(1), 99–109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0662-x
G.R. Sareddy, M. Panigrahi, S. Challa, A. Mahadevan, P.P. Babu, Activation of Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway in human astrocytomas. Neurochem. Int. 55(5), 307–317 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2009.03.016
D. Babu, A. Mudiraj, N. Yadav, B.V.K.C. Y, M. Panigrahi, P. Prakash Babu, Rabeprazole has efficacy per se and reduces resistance to temozolomide in glioma via EMT inhibition. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr) (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00609-w
F. Varghese, A.B. Bukhari, R. Malhotra, A. De, IHC Profiler: an open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS ONE 9(5), e96801 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096801
L. Du, C.S. Lyle, T.B. Obey, W.A. Gaarde, J.A. Muir, B.L. Bennett, T.C. Chambers, Inhibition of cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by specific inhibition of basal JNK activity: evidence that mitotic Bcl-2 phosphorylation is JNK-independent. J. Biol. Chem. 279(12), 11957–11966 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304935200
D.S. Chandrashekar, B. Bashel, S.A.H. Balasubramanya, C.J. Creighton, I. Ponce-Rodriguez, B. Chakravarthi, S. Varambally, UALCAN: A Portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8), 649–658 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
X. Liu, E. Ehmed, B. Li, J. Dou, X. Qiao, W. Jiang, X. Yang, S. Qiao, Y. Wu, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 modulates SIRT1-dependent p53 deacetylation through interacting with DBC1. Am. J. Cancer Res. 6(6), 1441–1449 (2016)
R. Koyama, M. Tamura, T. Nakagaki, T. Ohashi, M. Idogawa, H. Suzuki, T. Tokino, Y. Sasaki, Identification and characterization of a metastatic suppressor BRMS1L as a target gene of p53. Cancer Sci. 108(12), 2413–2421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13420
J.N. Weinstein, Spotlight on molecular profiling: “Integromic” analysis of the NCI-60 cancer cell lines. Mol. Cancer Ther. 5(11), 2601–2605 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-06-0640
F. Azuaje, K. Tiemann, S.P. Niclou, Therapeutic control and resistance of the EGFR-driven signaling network in glioblastoma. Cell. Commun. Signal.: CCS 13, 23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-015-0098-6
K.E. Cahill, R.A. Morshed, B. Yamini, Nuclear factor-kappaB in glioblastoma: insights into regulators and targeted therapy. Neuro Oncol. 18(3), 329–339 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov265
L.M. Kelly, Y. Buggy, A. Hill, N. O’Donovan, C. Duggan, E.W. McDermott, N.J. O’Higgins, L. Young, M.J. Duffy, Expression of the breast cancer metastasis suppressor gene, BRMS1, in human breast carcinoma: lack of correlation with metastasis to axillary lymph nodes. Tumour Biol. 26(4), 213–216 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1159/000086955
K.S. Vaidya, S. Harihar, P.A. Phadke, L.J. Stafford, D.R. Hurst, D.G. Hicks, G. Casey, D.B. DeWald, D.R. Welch, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor-1 differentially modulates growth factor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 283(42), 28354–28360 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M710068200
D.G. Hicks, B.J. Yoder, S. Short, S. Tarr, N. Prescott, J.P. Crowe, A.E. Dawson, G.T. Budd, S. Sizemore, M. Cicek, T.K. Choueiri, R.R. Tubbs, D. Gaile, N. Nowak, M.A. Accavitti-Loper, A.R. Frost, D.R. Welch, G. Casey, Loss of breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 protein expression predicts reduced disease-free survival in subsets of breast cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 12(22), 6702–6708 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0635
B.V. Ventura, C. Quezada, S.C. Maloney, B.F. Fernandes, E. Antecka, C. Martins, S. Bakalian, S. di Cesare, M.N. Burnier Jr., Expression of the metastasis suppressor BRMS1 in uveal melanoma. Ecancermedicalscience 8, 410 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3332/ecancer.2014.410
R.C. Zimmermann, D.R. Welch, BRMS1: a multifunctional signaling molecule in metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 39(3), 755–768 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09871-0
B.J. Metge, A.R. Frost, J.A. King, D.L. Dyess, D.R. Welch, R.S. Samant, L.A. Shevde, Epigenetic silencing contributes to the loss of BRMS1 expression in breast cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 25(7), 753–763 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-008-9187-x
A.S. Nagji, Y. Liu, E.B. Stelow, G.J. Stukenborg, D.R. Jones, BRMS1 transcriptional repression correlates with CpG island methylation and advanced pathological stage in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Pathol. 221(2), 229–237 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2707
P.A. Phadke, K.S. Vaidya, K.T. Nash, D.R. Hurst, D.R. Welch, BRMS1 suppresses breast cancer experimental metastasis to multiple organs by inhibiting several steps of the metastatic process. Am. J. Pathol. 172(3), 809–817 (2008). https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2008.070772
M.D. Edmonds, D.R. Hurst, K.S. Vaidya, L.J. Stafford, D. Chen, D.R. Welch, Breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 coordinately regulates metastasis-associated microRNA expression. Int. J. Cancer 125(8), 1778–1785 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.24616
G. Fulci, N. Ishii, E.G. Van Meir, p53 and brain tumors: from gene mutations to gene therapy. Brain Pathol. 8(4), 599–613 (1998)
L.M. Cook, X. Cao, A.E. Dowell, M.T. Debies, M.D. Edmonds, B.H. Beck, R.A. Kesterson, R.A. Desmond, A.R. Frost, D.R. Hurst, D.R. Welch, Ubiquitous Brms1 expression is critical for mammary carcinoma metastasis suppression via promotion of apoptosis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 29(4), 315–325 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-012-9452-x
C.M. Lopes-Ramos, J.N. Paulson, C.Y. Chen, M.L. Kuijjer, M. Fagny, J. Platig, A.R. Sonawane, D.L. DeMeo, J. Quackenbush, K. Glass, Regulatory network changes between cell lines and their tissues of origin. BMC Genom. 18(1), 723 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4111-x
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Chandra Sekhar from the Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences, India, for helping in the clinicopathological assessments. We also acknowledge all members of the PPB laboratory, especially Dr. Anwita Mudiraj and Dr. Ravindra Pramod Deshpande for their valuable contributions to the manuscript.
Funding
We acknowledge the financial assistance to the Lab from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, DST- SERB Core grant, file No. SR/CSRI/196/2016, and CRG/2020/005021, Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India, BT/PR18168/MED/29/1064/2016, BT/PR17686/MED/30/1664/2016, and financial support to the University of Hyderabad-IoE by the Ministry of Education, Govt. of India F11/9/2019-U3 (A), and DST-FIST, and UGC-SAP for the department. D.B. acknowledges the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) India for the student fellowship (Award no: DBT/2013/UOH/79).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DB and PPB designed the study. DB and CR performed the experiments. DB and MP collected the tumor samples and the related clinical information. DB, CR, MP and PPB analyzed the data. DB drafted the manuscript. DB and PPB finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (IEC), University of Hyderabad, Hyderabad (TS), India, with IEC reference number UH/IEC/2016/180. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest/Competing interests
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 290 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, D., Chintal, R., Panigrahi, M. et al. Distinct expression and function of breast cancer metastasis suppressor 1 in mutant P53 glioblastoma. Cell Oncol. 45, 1451–1465 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00729-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-022-00729-x