Abstract
Background
It has amply been documented that mammary tumor cells may exhibit an increased lipogenesis. Biliary acids are currently recognized as signaling molecules in the intestine, in addition to their classical roles in the digestion and absorption of lipids. The aim of our study was to evaluate the impact of lithocholic acid (LCA) on the lipogenesis of breast cancer cells. The putative cytotoxic effects of LCA on these cells were also examined.
Methods
The effects of LCA on breast cancer-derived MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were studied using MTT viability assays, Annexin-FITC and Akt phosphorylation assays to evaluate anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic properties, qRT-PCR and Western blotting assays to assess the expression of the bile acid receptor TGR5 and the estrogen receptor ERα, and genes and proteins involved in apoptosis (Bax, Bcl-2, p53) and lipogenesis (SREBP-1c, FASN, ACACA). Intracellular lipid droplets were visualized using Oil Red O staining.
Results
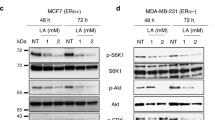
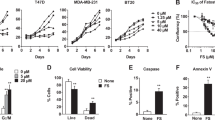
We found that LCA induces TGR5 expression and exhibits anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Also, an increase in pro-apoptotic p53 protein expression and a decrease in anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein expression were observed after LCA treatment of MCF-7 cells. In addition, we found that LCA reduced Akt phosphorylation in MCF-7 cells, but not in MDA-MB-231 cells. We also noted that LCA reduced the expression of SREBP-1c, FASN and ACACA in both breast cancer-derived cell lines and that cells treated with LCA contained low numbers of lipid droplets compared to untreated control cells. Finally, a decrease in ERα expression was observed in MCF-7 cells treated with LCA.
Conclusions
Our data suggest a potential therapeutic role of lithocholic acid in breast cancer cells through a reversion of lipid metabolism deregulation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Robles-Escajeda, U. Das, N.M. Ortega, K. Parra, G. Francia, J.R. Dimmock, A. Varela-Ramirez, R.J. Aguilera, A novel curcumin-like dienone induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 39, 265–277 (2016)
R. Sharma, R. Sharma, T.P. Khaket, C. Dutta, B. Chakraborty, T.K. Mukherjee, Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell. Oncol. 40, 199–208 (2017)
S. Beloribi-Djefaflia, S. Vasseur, F. Guillaumond, Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Oncogenesis 5, 1–10 (2016)
J.A. Menendez, R. Lupu, Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 763–777 (2007)
J.A. Menendez, R. Lupu, Fatty acid synthase regulates estrogen receptor-α signaling in breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 6, 1–11 (2017)
J.M. Harvey, G.M. Clark, C.K. Osborne, D.C. Allred, Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 17, 1474–1481 (1999)
P. Lefebvre, B. Cariou, F. Lien, F. Kuipers, B. Staels, Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiol. Rev. 89, 147–191 (2009)
P.B. Hylemon, H. Zhou, W.M. Pandak, S. Ren, G. Gil, P. Dent, Bile acids as regulatory molecules. J. Lipid. Res. 50, 1509–1520 (2009)
B.W. Katona, S. Anant, D.F. Covey, W.F. Stenson, Characterization of enantiomeric bile acid-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 3354–3564 (2009)
A.A. Goldberg, A. Beach, G.F. Davies, T.A. Harkness, A. Leblanc, V.I. Titorenko, Lithocholic bile acid selectively kills neuroblastoma cells, while sparing normal neuronal cells. Oncotarget 2, 761–782 (2011)
A.A. Goldberg, V.I. Titorenko, A. Beach, J.T. Sanderson, Bile acids induce apoptosis selectively in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer cells. Peer J. 1, e122 (2013)
A.A. Goldberg, V.R. Richard, P. Kyryakov, S.D. Bourque, A. Beach, M.T. Burstein, A. Glebov, O. Koupaki, T. Boukh-Viner, C. Gregg, M. Juneau, A.M. English, D.Y. Thomas, V.I. Titorenko, Chemical genetic screen identifies lithocholic acid as an anti-aging compound that extends yeast chronological life span in a TOR-independent manner, by modulating housekeeping longevity assurance processes. Aging 2, 393–414 (2010)
V. Sepe, B. Renga, C. Festa, C. Finamore, D. Masullo, A. Carino, S. Cipriani, E. Distrutti, S. Fiorucci, A. Zampella, Investigation on bile acid receptor regulators. Discovery of cholanoic acid derivatives with dual G-protein coupled bile acid receptor 1 (GPBAR1) antagonistic and farnesoid X receptor (FXR) modulatory activity. Steroids 105, 59–67 (2015)
A. Kawaguchi, H. Tomoda, S. Nozoe, S. Omura, S. Okuda, Mechanism of action of cerulenin on fatty acid synthetase. Effect of cerulenin on iodoacetamide-induced malonyl-CoA decarboxylase activity. J. Biochem. 92, 7–12 (1982)
H. Duboc, Y. Taché, A.F. Hofmann, The bile acid TGR5 membrane receptor: From basic research to clinical application. Dig. Liver Dis. 46, 302–312 (2014)
H. Sato, A. Macchiarulo, C. Thomas, A. Gioiello, M. Une, A.F. Hofmann, R. Saladin, K. Schoonjans, R. Pellicciari, J. Auwerx, Novel potent and selective bile acid derivatives as TGR5 agonists: Biological screening, structure−activity relationships, and molecular modeling studies. J. Med. Chem. 51, 1831–1841 (2008)
Y. Kawamata, R. Fujii, M. Hosoya, M. Harada, H. Yoshida, M. Miwa, S. Fukusumi, Y. Habata, T. Itoh, Y. Shintani, S. Hinuma, Y. Fujisawa, M. Fujino, A G protein-coupled receptor responsive to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 9435–9440 (2003)
T.W. Pols, L.G. Noriega, M. Nomura, J. Auwerx, K. Schoonjans, The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5 as an emerging target in metabolism and inflammation. J Hepatol. 54, 1263–1272 (2011)
J.S. Fridman, S.W. Lowe, Control of apoptosis by p53. Oncogene 22, 9030–9040 (2003)
C.C. Harris, Structure and function of the p53 tumor suppressor gene: Clues for rational cancer therapeutic strategies. J Natl. Cancer Inst. 88, 1442–1455 (1996)
H.A. Giebler, I. Lemasson, J.K. Nyborg, p53 recruitment of CREB binding protein mediated through phosphorylated CREB: a novel pathway of tumor suppressor regulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 4849–4858 (2000)
T. Arnould, S. Vankoningsloo, P. Renard, A. Houbion, N. Ninane, C. Demazy, J. Remacle, M. Raes, CREB activation induced by mitochondrial dysfunction is a new signaling pathway that impairs cell proliferation. EMBO J. 21, 53–63 (2002)
S. Cory, D.C.S. Huang, J.M. Adams, The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22, 8590–8607 (2003)
Rahimi A, Lee YY, Abdella H, Doerflinger M, Gangoda L, Srivastava R, Xiao K, Ekert PG, Puthalakath H. Role of p53 in cAMP/PKA pathway mediated apoptosis. Apoptosis 18, 1492–1499 (2013)
S.M. Vogel, M.R. Bauer, A.C. Joerger, R. Wilcken, T. Brandt, D.B. Veprintsev, T.J. Rutherford, A.R. Fersht, F.M. Boeckler, Lithocholic acid is an endogenous inhibitor of MDM4 and MDM2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 16906–16910 (2012)
M. Yoeli-Lerner, A. Toker, Akt/PKB signaling in cancer: A function in cell motility and invasion. Cell Cycle 5, 603–605 (2006)
B.S. Tan, K.H. Tiong, H.L. Choo, F.F. Chung, L.W. Hii, S.H. Tan, I.K. Yap, S. Pani, N.T. Khor, S.F. Wong, R. Rosli, S.K. Cheong, C.O. Leong, Mutant p53-R273H mediates cancer cell survival and anoikis resistance through AKT-dependent suppression of BCL2-modifying factor (BMF). Cell Death Dis. 6, e1826 (2015)
C.R. Loehberg, P.L. Strissel, R. Dittrich, R. Strick, J. Dittmer, A. Dittmer, B. Fabry, W.A. Kalender, T. Koch, D.L. Wachter, N. Groh, A. Polier, I. Brandt, L. Lotz, I. Hoffmann, F. Koppitz, S. Oeser, A. Mueller, P.A. Fasching, M.P. Lux, M.W. Beckmann, M.G. Schrauder, Akt and p53 are potential mediators of reduced mammary tumor growth by cloroquine and the mTOR inhibitor RAD001. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83, 480–488 (2012)
A. Astanehe, D. Arenillas, W.W. Wasserman, P.C. Leung, S.E. Dunn, B.R. Davies, G.B. Mills, N. Auersperg, Mechanisms underlying p53 regulation of PIK3CA transcription in ovarian surface epithelium and in ovarian cancer. J. Cell Sci. 121, 664–674 (2008)
M. Agostini, L.Y. Almeida, D.C. Bastos, R.M. Ortega, F.S. Moreira, F. Seguin, K.G. Zecchin, H.F. Raposo, H.C. Oliveira, N.D. Amoêdo, T. Salo, R.D. Coletta, E. Graner, The fatty acid synthase inhibitor orlistat reduces the growth and metastasis of orthotopic tongue oral squamous cell carcinomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 13, 585–595 (2014)
B. Corominas-Faja, E. Cuyàs, J. Gumuzio, J. Bosch-Barrera, O. Leis, Á.G. Martin, J.A. Menendez, Chemical inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses self-renewal growth of cancer stem cells. Oncotarget 5, 8306–8316 (2014)
R. Singh, V. Yadav, S. Kumar, N. Saini, MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis in breast cancer cells by targeting FASN, HMGCR, ACACA and CYP27B1. Sci. Rep. 5, 1–15 (2015)
M. Lu, J.Y. Shyy, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 is negatively modulated by PKA phosphorylation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 290, C1477–C1486 (2006)
T. Yamamoto, H. Shimano, N. Inoue, Y. Nakagawa, T. Matsuzaka, A. Takahashi, N. Yahagi, H. Sone, H. Suzuki, H. Toyoshima, N. Yamada, Protein kinase A suppresses sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1C expression via phosphorylation of liver X receptor in the liver. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 11687–11695 (2007)
M.A. Welte, Expanding roles for lipid droplets. Curr. Biol. 25, R470–R481 (2015)
P.T. Bozza, J.P. Viola, Lipid droplets in inflammation and cancer. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 82, 243–250 (2010)
L. Tirinato, C. Liberale, S. Di Franco, P. Candeloro, A. Benfante, R. La Rocca, L. Potze, R. Marotta, R. Ruffilli, V.P. Rajamanickam, M. Malerba, F. De Angelis, A. Falqui, E. Carbone, M. Todaro, J.P. Medema, G. Stassi, E. Di Fabrizio, Lipid droplets: a new player in colorectal cancer stem cells unveiled by spectroscopic imaging. Stem Cells 33, 35–44 (2015)
H. Abramczyk, J. Surmacki, M. Kopec, A.K. Olejnik, K. Lubecka-Pietruszewska, K. Fabianowska-Majewska, The role of lipid droplets and adipocytes in cancer. Raman imaging of cell cultures: MCF10A, MCF7, and MDA-MB-231 compared to adipocytes in cancerous human breast tissue. Analyst 140, 2224–2235 (2015)
G. Pérez-Tenorio, O. Stal, Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Brit. J. Cancer 86, 540–545 (2002)
O. Stal, G. Pérez-Tenorio, L. Akerberg, B. Olsson, B. Nordenskjöld, L. Skoog, L.E. Rutqvist, Akt kinases in breast cancer and the results of adjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer Res 5, R37–R44 (2003)
J. Bostner, E. Karlsson, M.J. Pandiyan, H. Westman, L. Skoog, T. Fornander, B. Nordenskjöld, O. Stal, Activation of Akt, mTOR, and the estrogen receptor as a signature to predict tamoxifen treatment benefit. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 137, 397–406 (2013)
R.A. Campbell, P. Bhat-Nakshatri, N.M. Patel, D. Constantinidou, S. Ali, H. Nakshatri, Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor α: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 9817–9824 (2001)
A. Belkaid, S.R. Duguay, R.J. Ouellette, M.E. Surette, 17β-estradiol induces stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 expression in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 15, 1–14 (2015)
M.J. Duffy, Estrogen receptors: Role in breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 43, 325–347 (2006)
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a grant from La Ligue Contre le Cancer de la Charente et de Loire Atlantique. Trang H. Luu was also funded by a research fellowship from the Vietnam Ministry of Education and Training and the Phu Tho Pharmacy College.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luu, T.H., Bard, JM., Carbonnelle, D. et al. Lithocholic bile acid inhibits lipogenesis and induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cell Oncol. 41, 13–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0353-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-017-0353-5