Abstract
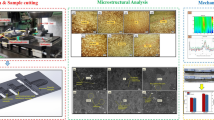
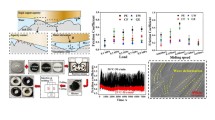
This research presents a comprehensive investigation into the mechanical, tribological, fatigue, and micro-structural properties of 3D printed Nylon 6–6 composites reinforced with biosilica derived from proso millet husk. The biosilica nanoparticles were prepared from proso millet husks via thermo-chemical process and reinforce into the nylon polymer via single screw extruder. The composites, designated from A to E, were printed with varying concentrations of biosilica, ranging from 0 to 4 wt.% reinforced nylon filaments with 50% infill ratio. The printed composites are further subjected to testing in accordance to ASTM standards and the results are evaluated further. According to the results, the tensile and yield strength of composite reveals a progressive improvement in mechanical properties with increasing biosilica content, attributed to efficient load transfer and enhanced rigidity imparted by biosilica particles. Similarly, izod impact toughness and hardness demonstrate similar trends, indicates increased toughness and surface durability with higher biosilica content. The fatigue life cycle assessment of composites is significant. The addition of biosilica improved the strength of nylon composite even it printed by 50 infill ratio. Moreover, the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis reveals distinct microstructural features, including biosilica agglomerations, unfilled voids, and uniform biosilica dispersion, offering insights into the material's internal morphology and reinforcing mechanisms. Additionally, the controlled water absorption and improved wear resistance observed in biosilica-reinforced composites highlight their potential for applications requiring moisture resistance and reduced friction. Overall, the synergistic combination of nylon 6–6 and biosilica presents promising opportunities for the development of high-performance composite materials with enhanced mechanical properties and durability, suitable for diverse engineering applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data within the manuscript are available. No more additional data is available.
References
Alshammari BA, Alsuhybani MS, Almushaikeh AM, Alotaibi BM, Alenad AM, Alqahtani NB, Alharbi AG (2021) Polymers 13(15):2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13152474
Nuriel H, Kozlovich N, Feldman Y, Marom G (2000) Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 31(1):69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-835X(99)00050-0
Pai CC, Jeng RJ, Grossman SJ, Huang JC (1989) Adv Polym Technol 9(2):157–163. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.1989.060090206
Kabir SF, Mathur K, Seyam AFM (2020) Compos Struct 232:111476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111476
Zhang, Z., Gkartzou, E., Jestin, S., Semitekolos, D., Pappas, P. N., Li, X., ... & Dong, H. (2022). Polymers, 14(3), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030470
Kumar R, Singh R, Singh M, Kumar P (2022) J Thermoplast Compos Mater 35(6):799–825. https://doi.org/10.1177/0892705720925119
Kumar R, Singh R, Ahuja IPS, Fortunato A (2020) Compos Struct 253:112772. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112772
Kumar R, Singh R, Ahuja IPS (2021) Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C: J Mech Eng Sci 235(10):1878–1890. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406219848465
Salamati M, Soltanpour M, Fazli A (2020) Int J Adv Manuf Technol 106:4023–4081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04845-1
Alshahrani, H., Vincent Rethnam, A.P. Fibers Polym (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-024-00475-x
Khan, M.K.A., Alshahrani, H. & Arun Prakash, V. Biomass Conv Bioref (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-05196-4
Alshahrani, H., VR, A.P. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1988 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-11418-2
Prakash VRA, MostefaBourchak, Alshahrani H, Juhany KA. Int J Biol Macromol 253 (2023):127068
Krishnamoorthy N, Nagabhooshanam N, Rao PKV, Verma R, Kumar DS, Sankar GA, ... Mohanavel V (2023) Biomass Conv Bioref 1–8
Vijayaraj S, Vijayarajan K (2023) Biomass Conv Bioref 1–11
Terzioğlu P, Yücel S, Kuş Ç (2019) Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 14(1):e2262. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.2262
Özarslan AC, Elalmis YB, Yücel S (2021) J Non-Cryst Solids 561:120755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.120755
Devisetti R, Yadahally SN, Bhattacharya S (2014) LWT-Food Sci Technol 59(2):889–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.07.003
Battegazzore D, Bocchini S, Alongi J, Frache A (2014) RSC Adv 4(97):54703–54712. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA05991C
Yohannan A, Vincent S, Divakaran N, PottikadavathVenugopal AK, Patra S, Ashish K, Mohanty S Polym Compos
Singh, S., Prakash, C., & Gupta, M. K. (2019). In Materials forming, machining and post processing (pp. 75–91). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-18854-2_3
Bagheri A, Parast MSA, Kami A, Azadi M, Asghari V (2022) Eur J Mech A-Solid 96:104713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euromechsol.2022.104713
Embirsh HSA, Stajčić I, Gržetić J, Mladenović IO, Anđelković B, Marinković A, Vuksanović MM (2023) Polymers 15(18):3756
Prakash VRA, Xavier JF, Ramesh G, Maridurai T, Kumar KS, Raj RBS (2022) Biomass Conv Bioref 12(12):5451–5461
Khan MK, Faisal M, Prakash VR (2024) Polym Bull 1–19
Alshahrani H, Arun Prakash VR Fibers Polym (2024):1–11
Ramu S, Senthilkumar N, Deepanraj B (2024) Biomass Conv Bioref 1–10
Venkatesh B, Gandhimathi G, Nagabhooshanam N, Raghu Babu G, SD DB, Kishore KL, Vijay KM, Soudagar MEM (2024) Biomass Conv Bioref 1–10
Alshahrani H, Prakash VA (2022) J Clean Prod 374:133931
Colom X, Carrasco F, Pagès P, Cañavate J (2003) Compos Sci Technol 63(2):161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0266-3538(02)00248-8
Sudhir Kumar Saw, Chandan (2009) Data, thermomechanical properties of jute/bagasse hybrid fibre reinforced epoxy thermoset composites. Bio Res
Low IM, Somers J, Kho HS, Davies IJ, Latella BA (2009) Compos Interfaces 16(7–9):659–669. https://doi.org/10.1163/092764409x12477417562210
Alhuthali AM, Low I-M (2015) Polym Eng Sci 55(12):2685–2697. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.23617
ArunPrakash VR, Jayaseelan V, Mothilal T et al (2020) SILICON 12:2533–2544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-00347-7
Bharath Kumar T, Haseebuddin MR, Raghavendra N, Vishnu Mahesh KR (2018) Mater Today: Proc 5(10):22675–22686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.644
Arun Prakash VR, Xavier JF, Ramesh G et al (2022) Biomass Conv Bioref 12:5451–5461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00938-0
Rajadurai A (2016) Thermo-mechanical characterization of siliconized E-glass fiber/hematite particles reinforced epoxy resin hybrid composite. Appl Surf Sci 384:99–106
Prakash VRA, Bourchak M, Alshahrani H et al (2023). Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04736-2
Thiyagu, T.T., J.V, S.P.K., P, G. et al. Biomass Conv Bioref. 13, 11841–11851 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01941-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rajkumar P and Natarajan U: full research; Kumaravadivel A: testing support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajkumar, P., Natarajan, U. & Kumaravadivel, A. Mechanical, wear, fatigue, and water absorption behavior of proso millet husk derived biosilica reinforced nylon 6–6 composite thick plates for friction stir welding process. Biomass Conv. Bioref. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-05691-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-05691-2