Abstract
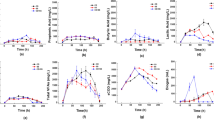
Deficiency of trace metals exacerbates instability in the methanogenic phase of two-phase thermophilic AD. The addition of a micronutrient supplement containing calcium, magnesium, cobalt and nickel was found to help process recovery, increasing methane production by up to 40%. In this study, next gen sequencing was used to identify the changes brought by addition of the micronutrients in the bacterial community of the methanogenic phase of food waste processing. The diversity of the community before supplementation was considerably low and a single species of Phylum Thermotogae was the sole dominant bacterial group. The addition of a micronutrient supplement comprising of Ca, Mg, Co and Ni caused a potent increase in the diversity of the community and species belonging to Arcobacter, Clostridium, Pseudomonas, Bacteroides and Coprothermobacter were particularly enriched. This suggested that the action of the micronutrients resulted in an increase in the functional diversity and redundancy of the bacterial community and limiting hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis in favour of acetotrophic methanogenesis. These factors would contribute to the observed increased stability and higher productivity in the micronutrient supplemented thermophilic AD process.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajoo KS, Karam DS, Ismail A, Arifin A (2020) Evaluating the leachate contamination impact of landfills and open dumpsites from developing countries using the proposed Leachate Pollution Index for Developing Countries (LPIDC). Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 14:100372
Vasco-Correa J, Khanal S, Manandhar A, Shah A (2018) Anaerobic digestion for bioenergy production: global status, environmental and techno-economic implications, and government policies. Bioresource Technol 247:1015–1026
Menon A, Lyng (2020) Circular bioeconomy solutions: driving anaerobic digestion of waste streams towards production of high value medium chain fatty acids. Rev Environ Sci Bio in press
Fuess LT, Kiyuna LSM, Júnior ADNF, Persinoti GF, Squina FM, Garcia ML, Zaiat M (2017) Thermophilic two-phase anaerobic digestion using an innovative fixed-bed reactor for enhanced organic matter removal and bioenergy recovery from sugarcane vinasse. Appl Energ 189:480–491
Alavi-Borazjani SA, Capela I, Tarelho LA (2020) Over-acidification control strategies for enhanced biogas production from anaerobic digestion: a review. Biomass Bioenerg 143:105833
Kleyböcker A, Liebrich M, Verstraete W, Kraume M, Würdemann H (2012) Early warning indicators for process failure due to organic overloading by rapeseed oil in one-stage continuously stirred tank reactor, sewage sludge and waste digesters. Bioresource Technol 123:534–541
David A, Govil T, Tripathi AK, McGeary J, Farrar K, Sani RK (2018) Thermophilic anaerobic digestion: enhanced and sustainable methane production from co-digestion of food and lignocellulosic wastes. Energies 11:2058
Menon A, Wang JY, Giannis A (2017) Optimization of micronutrient supplement for enhancing biogas production from food waste in two-phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manage 59:465–475
Yılmaz S, Sahan T (2020) Utilization of pumice for improving biogas production from poultry manure by anaerobic digestion: a modeling and process optimization study using response surface methodology. Biomass Bioenerg 138:1056601
Li W, Guo J, Cheng H, Wang W, Dong R (2017) Two-phase anaerobic digestion of municipal solid wastes enhanced by hydrothermal pretreatment: viability, performance and microbial community evaluation. Appl Energ 189:613–622
Abdelsalam E, Samer M, Attia Y, Abdel-Hadi M, Hassan H, Badr Y (2016) Comparison of nanoparticles effects on biogas and methane production from anaerobic digestion of cattle dung slurry. Renew Energ 87:592–598
Raskin L, Poulsen LK, Noguera DR, Rittmann BE, Stahl DA (1994) Quantification of methanogenic groups in anaerobic biological reactors by oligonucleotide probe hybridization. Appl Environ Microb 60:1241–1248
Yu D, Kurola J, Lähde K, Kymäläinen M, Sinkkonen A, Romantschuk M (2014) Biogas production and methanogenic archaeal community in mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion processes. J Environ Manage 143:54–60
Kim E, Lee J, Han G, Hwang S (2018) Comprehensive analysis of microbial communities in full-scale mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digesters treating food waste-recycling wastewater. Bioresource Technol 259:442–450
Wintsche B, Glaser K, Sträuber H, Centler F, Liebetrau J, Harms H, Kleinsteuber S (2016) Trace elements induce predominance among methanogenic activity in anaerobic digestion. Front Microbiol 7:2034
Satpathy P, Steinigeweg S, Cypionka H, Engelen B (2016) Different substrates and starter inocula govern microbial community structures in biogas reactors. Environ Technol 37:1441–1450
Vanwonterghem I, Jensen PD, Ho DP, Batstone DJ, Tyson GW (2014) Linking microbial community structure, interactions and function in anaerobic digesters using new molecular techniques. Curr Opin Biotech 27:55–64
De la Rubia M, Romero L, Sales D, Perez M (2005) Temperature conversion (mesophilic to thermophilic) of municipal sludge digestion. AIChE J 51:2581–2586
Menon A, Ren F, Wang JY, Giannis A (2016) Effect of pretreatment techniques on food waste solubilization and biogas production during thermophilic batch anaerobic digestion. J Mater Cycles Waste 18:222–230
Bouskova A, Dohanyos M, Schmidt JE, Angelidaki I (2005) Strategies for changing temperature from mesophilic to thermophilic conditions in anaerobic CSTR reactors treating sewage sludge. Water Res 39:1481–1488
Youcai Z, Tao Z (2021) Simultaneous anaerobic fermentation biohydrogen and biomethane production from food waste. In: Youcai Z, Tao Z (ed), Biohydrogen production and hybrid process development. Elsevier, pp 239–310
Ondov BD, Bergman NH, Phillippy AM (2011) Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinformatics 12:385
Zannoni D, De Philippis R (2014) Microbial bioenergy: hydrogen production. Springer
Verhaart MR, Bielen AA, Oost JVD, Stams AJ, Kengen SW (2010) Hydrogen production by hyperthermophilic and extremely thermophilic bacteria and archaea: mechanisms for reductant disposal. Environ Technol 31:993–1003
Bonch‐Osmolovskaya E (2008) Thermotogales, eLS
Omar B, El-Gammal M, Abou-Shanab R, Fotidis IA, Angelidaki I, Zhang Y (2019) Biogas upgrading and biochemical production from gas fermentation: impact of microbial community and gas composition. Bioresource Technol 286:121413
Cerrillo M, Viñas M, Bonmatí A (2016) Overcoming organic and nitrogen overload in thermophilic anaerobic digestion of pig slurry by coupling a microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresource Technol 216:362–372
Labatut RA, Angenent LT, Scott NR (2014) Conventional mesophilic vs. thermophilic anaerobic digestion: a trade-off between performance and stability? Water Res 53:249–258
Kim M, Ahn YH, Speece R (2002) Comparative process stability and efficiency of anaerobic digestion; mesophilic vs. thermophilic. Water Res 36:4369–4385
Moset V, Poulsen M, Wahid R, Højberg O, Møller HB (2015) Mesophilic versus thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: methane productivity and microbial ecology. Microb Biotechnol 8:787–800
Sierocinski P, Bayer F, Yvon-Durocher G, Burdon M, Großkopf T, Alston M, Swarbreck D, Hobbs PJ, Soyer OS, Buckling A (2018) Biodiversity-function relationships in methanogenic communities. Mol Ecol 27:4641–4651
Ferry JG (2012) Methanogenesis: ecology, physiology, biochemistry & genetics. Springer Science & Business Media
Großkopf T, Soyer OS (2016) Microbial diversity arising from thermodynamic constraints. ISME J 10:2725–2733
Gomez P, Paterson S, De Meester L, Liu X, Lenzi L, Sharma M, McElroy K, Buckling A (2016) Local adaptation of a bacterium is as important as its presence in structuring a natural microbial community. Nat Commun 7:1–8
Li X, Wu S, Shen Y, Ning Y, Zhang X, Sun X, Zhang B, Chen J (2015) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by four novel isolated bacteria. Pol J Environ Stud 24:1677–1682
Kunath BJ, Delogu F, Naas AE, Arntzen MØ, Eijsink VG, Henrissat B, Hvidsten TR, Pope PB (2019) From proteins to polysaccharides: lifestyle and genetic evolution of Coprothermobacter proteolyticus. ISME J 13:603–617
Sasaki K, Morita M, Sasaki D, Nagaoka J, Matsumoto N, Ohmura N, Shinozaki H (2011) Syntrophic degradation of proteinaceous materials by the thermophilic strains Coprothermobacter proteolyticus and Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus. J Biosci Bioeng 112:469–472
Palatsi J, Viñas M, Guivernau M, Fernandez B, Flotats X (2011) Anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste: main process limitations and microbial community interactions. Bioresource Technol 102:2219–2227
Tandishabo K, Nakamura K, Umetsu K, Takamizawa K (2012) Distribution and role of Coprothermobacter spp. in anaerobic digesters. J Biosci Bioeng 114:518–520
Meslé M, Dromart G, Haeseler F, Oger PM (2015) Classes of organic molecules targeted by a methanogenic microbial consortium grown on sedimentary rocks of various maturities. Front Microbiol 6:589
De Vrieze J, Hennebel T, Boon N, Verstraete W (2012) Methanosarcina: the rediscovered methanogen for heavy duty biomethanation. Bioresource Technol 112:1–9
Pobeheim H, Munk B, Lindorfer H, Guebitz GM (2011) Impact of nickel and cobalt on biogas production and process stability during semi-continuous anaerobic fermentation of a model substrate for maize silage. Water Res 45:781–787
Kim J, Shin SG, Han G, O’Flaherty V, Lee C, Hwang S (2011) Common key acidogen populations in anaerobic reactors treating different wastewaters: molecular identification and quantitative monitoring. Water Res 45:2539–2549
Yang Y, Tsukahara K, Sawayama S (2008) Biodegradation and methane production from glycerol-containing synthetic wastes with fixed-bed bioreactor under mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic conditions. Process Biochem 43:362–367
Chang M, Wang Y, Pan Y, Zhang K, Lyu L, Wang M, Zhu T (2019) Nitrogen removal from wastewater via simultaneous nitrification and denitrification using a biological folded non-aerated filter. Bioresource Technol 289:121696
Vandieken V, Pester M, Finke N, Hyun JH, Friedrich MW, Loy A, Thamdrup B (2012) Three manganese oxide-rich marine sediments harbor similar communities of acetate-oxidizing manganese-reducing bacteria. ISME J 6:2078–2090
Dyksma S, Jansen L, Gallert C (2020) Syntrophic acetate oxidation replaces acetoclastic methanogenesis during thermophilic digestion of biowaste. Microbiome 8:1–14
Narihiro T, Nobu MK, Kim NK, KamagataY LWT (2015) The nexus of syntrophy-associated microbiota in anaerobic digestion revealed by long-term enrichment and community survey. Environ Microbiol 17:1707–1720
Thauer RK, Jungermann K, Decker K (1977) Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 41:100
Fotidis I, Karakashev D, Angelidaki I (2014) The dominant acetate degradation pathway/methanogenic composition in full-scale anaerobic digesters operating under different ammonia levels. Int J Environ Sci Te 11:2087–2094
Rajagopal R, Massé DI, Singh G (2013) A critical review on inhibition of anaerobic digestion process by excess ammonia. Bioresource Technol 143:632–641
Müller B, Sun L, Westerholm M, Schnürer A (2016) Bacterial community composition and fhs profiles of low-and high-ammonia biogas digesters reveal novel syntrophic acetate-oxidising bacteria. Biotechnol Biofuels 9:1–18
Xu R, Zhang K, Liu P, Khan A, Xiong J, Tian F, Li X (2018) A critical review on the interaction of substrate nutrient balance and microbial community structure and function in anaerobic co-digestion. Bioresource Technol 247:1119–1127
Romero-Güiza M, Vila J, Mata-Alvarez J, Chimenos J, Astals S (2016) The role of additives on anaerobic digestion: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 58:1486–1499
Ryue J, Lin L, Kakar FL, Elbeshbishy E, Al-Mamun A, Dhar BR (2020) A critical review of conventional and emerging methods for improving process stability in thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Energ Sust Develop 54:72–84
Ghanimeh S, El-Fadel M, Saikaly PE (2018) Performance of thermophilic anaerobic digesters using inoculum mixes with enhanced methanogenic diversity. J Chem Technol Biot 93:207–214
Schmidt J, Ahring B (1993) Effects of magnesium on thermophilic acetate-degrading granules in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Enzyme Microb Tech 15:304–310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 181 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menon, A., Lyng, J. & Giannis, A. Higher bacterial diversity in two-phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste after micronutrient supplementation. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 13, 5187–5195 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01704-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01704-6