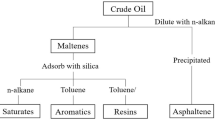
Abstract
Steam injection is a thermal recovery process that positively influences the properties changes of heavy crude oil, where the viscosity reduction is the one that is mostly modified. This method can be optimized with the addition of catalysts, allowing to increase the recovery factor. In the present investigation, the effects of the carrier fluid with two metal ion-based catalysts, Fe and Mo, were evaluated. The catalytic performance was analyzed from fluid–fluid tests in a Batch reactor, at a temperature of 270 °C, pressure of 440 psi and a reaction time of 66 h. The variables of the tests were the concentration and method of catalyst placement (directly or with naphtha as the carrier substance). The product was characterized by physical tests such as viscosity and density, where reductions of up to 75% in viscosity and increases in API gravity of almost 2 degrees were obtained. In addition, the characterization by 1H NMR spectroscopy and UV–VIS showed that the change in the physicochemical properties of the improved crude oil is mainly attributed to compositional variation. Finally, there was a synergy effect between catalyst and naphtha in the oil upgrading and it was reflected as a good option by using this substance as a carrier fluid.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeletsky, P.M.; Zaikina, O.O.; Sosnin, G.A.; Kukushkin, R.G.; Yakovlev, V.A.: Heavy oil cracking in the presence of steam and nanodispersed catalysts based on different metals. Fuel Process. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106239
Nares Ochoa, R.; Schacht Hernández, P.; Cabrera Reyes, M.C.; Ramírez Garnica, M.A.; Castrejón Vacio, F.; Ramírez López R.J.: Liquid ionic catalyst for improvement of heavy and super heavy oil, pp. 1–30 (2009)
Babadagli, T.: Philosophy of EOR. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 188, 1–24 (2020)
Pérez, R.; Sandoval, J.; Barbosa, C.; Delgadillo, C.; Trujillo, M.; Osma, L., et al.: Comparación de alternativas para mejora de la inyección cíclica de vapor mediante simulación numérica. Revista Fuentes el Reventón Energético 16, 91–107 (2018)
Arboleda, J.; Castillo, Á.; Muñoz, S.: Estudio de la acuatermólisis catalítica en procesos de upgrading de crudos pesados como método complementario en el recobro térmico de hidrocarburos. Revista Fuentes el Reventón Energético 16, 57–69 (2018)
Hyne, J.B.: Aquathermolysis: a synopsis of work on the chemical reaction between water (steam) and heayy oil sands during simulated steam stimulation. AOSTRA Publication Series. Calgary: AOSTRA Publication Series (1986)
Suwaid, M.A.; Varfolomeev, M.A.; Al-Muntaser, A.A.; Yuan, C.; Starshinova, V.L.; Zinnatullin, A., et al.: In-situ catalytic upgrading of heavy oil using oil-soluble transition metal-based catalysts. Fuel 281, 1–13 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118753
Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Xia, F.: Laboratory experiments and field tests of an amphiphilic metallic chelate for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Energy Fuels 22, 1502–1508 (2008)
Lakhova, A.; Petrov, S.; Ibragimova, D.; Kayukova, G.; Safiulina, A.; Shinkarev, A., et al.: Aquathermolysis of heavy oil using nano oxides of metals. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 153, 385–390 (2017)
Razavian, M.; Fatemi, S.: Catalytic evaluation of metal azolate framework-6 in pristine and metal doped modes in upgrading heavy residual fuel oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 156, 105093 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105093
Nares, H.R.; Schacht-Hernandez, P.; Cabrera-Reyes, M.C.; Ramirez-Garnica, M.; Cazarez-Candia, O.: Upgrading of heavy crude oil with supported and unsupported transition metals. In Canadian International Petroleum Conference. Calgary, pp. 1–10 (2006) Available from: https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/PETSOC-2006-060
Kudryashov, S.I.; Afanasiev, I.S.; Petrashov, O.V.; Vakhin, A.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Akhmadiayrov, A.A. et al.: Catalytic heavy oil upgrading by steam injection with using of transition metals catalysts. Neftyanoe Khozyaystvo - Oil Ind 30–34 (2017)
Clark, P.D.; Kirk, M.J.: Studies on the upgrading of bituminous oils with water and transition metal catalysts. Energy Fuels 8, 380–387 (1994)
Aliev, F.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Sitnov, S.A.; Ziganshina, M.R.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Sharifullin, A.V., et al.: In-situ heavy oil aquathermolysis in the presence of nanodispersed catalysts based on transition metals. Processes. 9, 1–22 (2021)
Mohammad, A.A.; Mamora, D.D.: Insitu upgrading of heavy oil under steam injection with tetralin and catalyst. In SPE/PS/CHOA International Thermal Operations and Heavy Oil Symposium. Calgary pp. 1–11 (2008)
Hendraningrat, L.; Souraki, Y.; Torsater, O.: Experimental investigation of decalin and metal nanoparticles-assisted bitumen upgrading during catalytic aquathermolysis. In SPE/EAGE European Unconventional Resources Conference and Exhibition. pp. 1–11 (2014) Available from: http://www.onepetro.org/doi/10.2118/167807-MS
Yusuf, A.; Al-Hajri, R.S.; Al-Waheibi, Y.M.; Jibril, B.Y.: In-situ upgrading of Omani heavy oil with catalyst and hydrogen donor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 121, 102–112 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2016.07.010
Liu, Y.; Fan, H.: The effect of hydrogen donor additive on the viscosity of heavy oil during steam stimulation. Energy Fuels 16, 842–846 (2002)
Ovalles, C.; Vallejos, C.; Vásquez, T.; Martinis, J.; Perez-Perez, A.; Cotte, E. et al.: Extra-heavy crude oil downhole upgrading process using hydrogen donors under steam injection conditions. In International Thermal Operations and Heavy Oil Symposium. Porlamar; pp. 1–6 (2001)
Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ha, S.; Li, S.: Additives on hydrogen donor catalytic upgrading for viscosity reduction of heavy oil under the conditions of steam injection. Appl. Mech. Mater. 55, 57–62 (2011)
Zhong, L.G.; Liu, Y.J.; Fan, H.F.; Jiang, S.J.: Liaohe extra-heavy crude oil underground aquathermolytic treatments using catalyst and hydrogen donors under steam injection conditions. In SPE International Improved Oil Recovery Conference in Asia Pacific. Kuala Lumpur. pp. 1–6 (2003) Available from: http://www.onepetro.org/doi/10.2118/84863-MS
Zhang, Z.: Experimental study of in-situ upgrading for heavy oil using hydrogen donors and catalyst under steam injection condition (2011)
Ovalles, C.; Rodríguez, H.: Extra heavy crude oil downhole upgrading using hydrogen donors under cyclic steam injection conditions: Physical and numerical simulation studies. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 47, 43–51 (2008)
Maity, S.K.; Ancheyta, J.; Marroquín, G.: Catalytic aquathermolysis used for viscosity reduction of heavy crude oils: a review. Energy Fuels 24, 2809–2816 (2010)
Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.: Influences on the aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalyzed by two catalysts with different ligands. Pet. Sci. Technol. 33, 1246–1252 (2015)
Yeletsky, P.M.; Zaikina, O.O.; Sosnin, G.A.; Kukushkin, R.G.; Yakovlev, V.A.: Heavy oil cracking in the presence of steam and nanodispersed catalysts based on different metals. Fuel Process. Technol. 199, 106239 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106239
Yusuf, A.; Al-Hajri, R.S.; Al-Waheibi, Y.M.; Jibril, B.Y.: Upgrading of Omani heavy oil with bimetallic amphiphilic catalysts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 67, 45–53 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.07.020
Vakhin, A.V.; Aliev, F.A.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Afanasiev, I.S.; Petrashov, O.V.; Sitnov, S.A., et al.: Aquathermolysis of heavy oil in reservoir conditions with the use of oil-soluble catalysts: part I-changes in composition of saturated hydrocarbons. Pet. Sci. Technol. 36, 1829–1836 (2018)
Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, L.: In situ upgrading heavy oil by aquathermolytic treatment under steam injection conditions. In SPE International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry. Houston, p. 8 (2005)
Wen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, S.: A study on catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy crude oil during steam stimulation. In International Symposium on Oilfield Chemistry [Internet]. Houston; 2007. pp. 1–5. Available from: http://www.onepetro.org/doi/10.2118/106180-MS
Dong, L.; Liu, Y.J.; Xu, K.M.; Zhao, F.J.; Liu, W.W.; Kong, X.W.: Laboratory experiment research and field tests on catalyst of aquathermolysis of heavy oils. Adv Mat Res. 773, 298–303 (2013)
Xu, H.; Pu, C.: Mechanism of underground heavy oil catalytic aquathermolysis. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 53, 913–921 (2018)
Chao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.: Laboratory experiments and field test of a difunctional catalyst for catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil. Energy Fuels 26, 1152–1159 (2012)
Kapadia, P.R.; Kallos, M.S.; Gates, I.D.: A review of pyrolysis, aquathermolysis, and oxidation of Athabasca bitumen. Fuel Process. Technol. 131, 270–289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.11.027
Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, J.; Li, P.; Yang, C.: Mechanism of catalytic aquathermolysis: Influences on heavy oil by two types of efficient catalytic ions: Fe3+ and Mo6+. Energy Fuels 24, 1502–1510 (2010)
Salas-Chia, L.M.; Naranjo, P.A.; Diaz, V.E.; Gambús-Ordaz, M.; Bermúdez, A.Y.: Influencia de parámetros operacionales de la inyección de vapor sobre las propiedades de crudos pesados sometidos a reacciones de acuatermólisis. 21, 65–81 (2023) Available from: https://doi.org/10.18273/revfue.v21n1-2023005
Zhong, L.G.; Liu, Y.J.; Fan, H.F.; Jiang, S.J.: Liaohe extra-heavy crude oil underground aquathermolytic treatments using catalyst and hydrogen donors under steam injection conditions. In SPE International Improved Oil Recovery Conference in Asia Pacific. Kuala Lumpur; p. 6. (2003) Available from: http://www.onepetro.org/doi/10.2118/84863-MS
Núñez-Méndez, K.S.; Salas-Chia, L.M.; Molina, V.D.; Muñoz, S.F.; León, P.A.; León, A.Y.: Effect of the catalytic aquathermolysis process on the physicochemical properties of a colombian crude oil. Energy Fuels 35, 5231–5240 (2021)
Fan, H.: The effects of reservoir minerals on the composition changes of heavy oil during steam stimulation. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 42, 11–14 (2003)
Fan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.: The catalytic effects of minerals on aquathermolysis of heavy oils. Fuel 83, 2035–2039 (2004)
Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Che, H.: Effects of reservoir minerals and chemical agents on aquathermolysis of heavy oil during steam injection. Chin. Pet. Process Pe. Technol. 12, 25–31 (2010)
Mecón Méndez, S.G.; Salas-Chia, L.M.; Martínez Vertel, J.J.; Velasco, D.R.M.; León, A.Y.; León, P.A.: Effect of mineralogy on the physicochemical properties of a heavy crude oil in hybrid steam injection technologies using 1H NMR. Energy Fuels 36, 10315–10326 (2022)
Alade, O.S.; Al Shehri, D.A.; Mahmoud, M.; Olusegun, S.; Lawal, L.O.; Kamal, M.S., et al.: Viscosity models for bitumen–solvent mixtures. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. 1505–20 (2021)
Xu, L.; Abedini, A.; Qi, Z.B.; Kim, M.; Guerrero, A.; Sinton, D.: Pore-scale analysis of steam-solvent coinjection: azeotropic temperature, dilution and asphaltene deposition. Fuel 220, 151–158 (2018)
León, A.Y.; Guerrero, N.A.; Muñoz, S.; Sandoval, M.; Pérez, R.; Molina, V.D.: Naphtha co-injection with steam effects on Colombian heavy crude oils quality by FTIR and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Fuel 366 (2024)
León, A.Y.; Guzman, A.; Laverde, D.; Chaudhari, R.V.; Subramaniam, B.; Bravo-Suárez, J.J.: Thermal cracking and catalytic hydrocracking of a colombian vacuum residue and its maltenes and asphaltenes fractions in toluene. Energy Fuels 31, 3868–3877 (2017)
Santos, R.G,; Loh, W.; Bannwart, A.C.; Trevisan, O.V.: An overview of heavy oil properties and its recovery and transportation methods. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. Assoc. Brasiliera de Eng. Quimica/Braz. Soc. Chem. Eng. 571–590 (2014)
ASTM. Standard test method for boiling point distribution of samples with residues such as crude oils and atmospheric and vacuum residues by high temperature gas chromatography. Available from: www.astm.org,
Behrenbruch, P.; Dedigama, T.: Classification and characterisation of crude oils based on distillation properties. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 57, 166–180 (2007)
León, P.A.; Bottía, H.; Molina, V.D.; Martínez Vertel, J.J.; Muñoz, S.F.; León, A.Y.: Catalytic upgrading evaluation under steam injection conditions with spectroscopy 1H-NMR. Pet. Sci. Technol. 40, 1622–1639 (2022)
ASTM International. Standard Test Method for Density of Semi-Solid Bituminous Materials (Pycnometer Method). 2010. Available from: www.epa.gov/
ASTM International. Standard test methods for rheological properties of non-Newtonian materials by rotational viscometer. (2020)
ASTM. Standard test method for determination of asphaltenes (heptane insolubles) in crude petroleum and petroleum products. Available from: www.astm.org
ASTM. Standard Test Method for Characteristic Groups in Rubber Extender and Processing Oils and Other Petroleum-Derived Oils by the Clay-Gel Absorption Chromatographic Method. Available from: www.astm.org,
León, A.Y.; Guzman, A.; Laverde, D.; Chaudhari, R.V.; Subramaniam, B.; Bravo-Suaréz, J.J.: Thermal cracking and catalytic hydrocracking of a colombian vacuum residue and its maltenes and asphaltenes fractions in toluene. Energy Fuels 31, 3868–3877 (2017)
Silverstein, R.; Webster, F.; Kiemle, D.; Bryce, D.: Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 8th edn. Wiley (2014)
Poveda, J.C.; Molina, D.R.: Average molecular parameters of heavy crude oils and their fractions using NMR spectroscopy. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 84–85, 1–7 (2012)
Daniel Molina, V.; Uribe, U.N.; Murgich, J.: Partial least-squares (PLS) correlation between refined product yields and physicochemical properties with the 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of Colombian crude oils. Energy Fuels 21, 1674–1680 (2007)
Fergoug, T.; Bouhadda, Y.: Determination of Hassi Messaoud asphaltene aromatic structure from 1H & 13C NMR analysis. Fuel 115, 521–526 (2014)
Mecón Méndez, S.G.; Salas-Chia, L.M.; Martínez Vertel, J.J.; Molina Velasco, D.R.; León, A.Y.; León, P.A.: Effect of mineralogy on the physicochemical properties of a heavy crude oil in hybrid steam injection technologies using 1H NMR. Energy Fuels 36, 10315–10326 (2022)
Bayestehparvin, B.; Farouq Ali, S.M.; Abedi, J.: Use of solvents with steam-state-of-the-art and limitations. In SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia. pp. 1–31 (2016) Available from: http://onepetro.org/SPEOGWA/proceedings-pdf/16OGWA/2-16OGWA/D021S014R001/1426778/spe-179829-ms.pdf/1
Castro, Y.E.; Veliz, A.M.; Sanchez, D.A.; Rodriguez, M.M.; Rondon, N.G.; Rivero, S., et al.: Cyclic steam injection with solvents as method of thermal recovery for heavy and extraheavy oils: laboratory tests. In Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference. pp. 1–15 (2010) Available from: http://onepetro.org/SPEURCC/proceedings-pdf/10CURIPC/All-10CURIPC/SPE-137547-MS/1751852/spe-137547-ms.pdf/1
Hart, A.; Lewis, C.; White, T.; Greaves, M.; Wood, J.: Effect of cyclohexane as hydrogen-donor in ultradispersed catalytic upgrading of heavy oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 138, 724–733 (2015)
Rodriguez, F., Delamaide, E., Rousseau, D., Bekri, S.: Which is the most attractive IOR method to produce the venezuelan highly viscous oil resources in the energy transition era? A comprehensive review of research and field applications. ADIPEC. pp. 1–22 (2022) Available from: http://onepetro.org/SPEADIP/proceedings-pdf/22ADIP/1-22ADIP/D011S014R004/3043200/spe-211344-ms.pdf/1
Yeletsky, P.M.; Zaikina, O.O.; Sosnin, G.A.; Kukushkin, R.G.; Yakovlev, V.A.: Heavy oil cracking in the presence of steam and nanodispersed catalysts based on different metals. Fuel Process. Technol. 199, 106239 (2020)
Yusuf, A.; Al-Hajri, R.S.; Al-Waheibi, Y.M.; Jibril, B.Y.: Upgrading of Omani heavy oil with bimetallic amphiphilic catalysts. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 67, 45–53 (2016)
Foss, L.; Petrukhina, N.; Kayukova, G.; Amerkhanov, M.; Romanov, G.; Ganeeva, Y.: Changes in hydrocarbon content of heavy oil during hydrothermal process with nickel, cobalt, and iron carboxylates. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 169, 269–276 (2018)
Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Vakhin, A.V.; Ivanova, A.G.; Voronina, E.V.: Composition of aquathermolysis catalysts forming in situ from oil-soluble catalyst precursor mixtures. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 169, 44–50 (2018)
Lin, D.; Zhu, H.; Wu, Y.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X., et al.: Morphological insights into the catalytic aquathermolysis of crude oil with an easily prepared high-efficiency Fe3O4-containing catalyst. Fuel 245, 420–428 (2019)
Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, F.: Influences on the aquathermolysis of heavy oil catalyzed by two different catalytic ions: Cu2+ and Fe3+. Energy Fuels 27, 2555–2562 (2013)
Galukhin, A.V.; Erokhin, A.A.; Gerasimov, A.V.; Eskin, A.A.; Nurgaliev, D.K.: Influence of iron pentacarbonyl on catalytic aquathermolysis of heavy oil: Changes of oil’s parameters and formation of magnetic nanoparticles. In Society of Petroleum Engineers - SPE Russian Petroleum Technology Conference. (2015)
Vakhin, A.V.; Sitnov, S.A.; Mukhamatdinov, I.I.; Onishchenko, Y.V.; Feoktistov, D.A.: Aquathermolysis of high-viscosity oil in the presence of an oil-soluble iron-based catalyst. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 53, 666–674 (2017)
Bej, R.; Dey, P.; Ghosh, S.: Disulfide chemistry in responsive aggregation of amphiphilic systems. Soft Matter. R. Soc. Chem. 16(1), 11–26 (2019)
Korneev, D.S.; Pevneva, G.S.; Golovko, A.K.: Thermal transformations of asphaltenes at a temperature of 120 °C. J. Sib. Fed. Univ. Chem. 12, 101–117 (2019)
Douda, J.; Alvarez, R.; Bolaños, J.N.: Characterization of Maya asphaltene and maltene by means of pyrolysis application. Energy Fuels 22, 2619–2628 (2008)
Varfolomeev, M.A.; Galukhin, A.; Nurgaliev, D.K.; Kok, M.V.: Thermal decomposition of Tatarstan Ashal’cha heavy crude oil and its SARA fractions. Fuel 186, 122–127 (2016)
Poutsma, M.: Free-radical thermolysis and hydrogenolysis of model hydrocarbons relevant to processing of coal. Energy Fuels 4, 113–131 (1990)
Akah, A.; Al-Ghrami, M.; Saeed, M.; Siddiqui, M.A.B.: Reactivity of naphtha fractions for light olefins production. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 8, 221–233 (2017)
Banda-Cruz, E.; Padrón-Ortega, S.; Gallardo-Rivas, N.; Páramo-García, U.; Díaz-Zavala, N.; Melo-Banda, A.: Physicochemical characterization of heavy oil and the precipitated asphaltenes fraction using UV spectroscopy and dynamic light scattering. J. Eng. Technol. 6, 49–58 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Universidad Industrial de Santander (UIS) and their professionals’ staff according under projects Nos. 3914 and 3910 (Programa estratégico de investigación aplicada interdisciplinar).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Brenda Juliana Pineda Galvis and Sergio Fernando Castellanos Amador. Paola Andrea León Naranjo, Luis Miguel Salas Chia, Adan Yovani León Bermúdez and Daniel Ricardo Molina Velasco worked in the research supervision. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Luis Miguel Salas Chia, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Salas-Chia, L.M., Pineda, B.J., Castellanos, S.F. et al. Influence of Organic Catalysts in Naphtha Solution on the Heavy Colombian Crude Oil Upgrading During Steam Injection. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09117-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-09117-z