Abstract
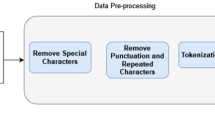
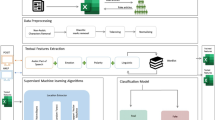
The quick spread of fake news in different languages on social platforms has become a global scourge threatening societal security and the government. Fake news is usually written to deceive readers and convince them that this false information is correct; therefore, stopping the spread of this false information becomes a priority of governments and societies. Building fake news detection models for the Arabic language comes with its own set of challenges and limitations. Some of the main limitations include 1) lack of annotated data, 2) dialectal variations where each dialect can vary significantly in terms of vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, 3) morphological complexity with complex word formations and root-and-pattern morphology, 4) semantic ambiguity that make models fail to accurately discern the intent and context of a given piece of information, 5) cultural context and 6) diacrasy. The objective of this paper is twofold: first, we design a large corpus of annotated fake new data for the Arabic language from multiple sources. The corpus is collected from multiple sources to include different dialects and cultures. Second, we build fake detection by building machine learning models as model head over the fine-tuned large language models. These large language models were trained on Arabic language, such as ARBERT, AraBERT, CAMeLBERT, and the popular word embedding technique AraVec. The results showed that the text representations produced by the CAMeLBERT transformer are the most accurate because all models have outstanding evaluation results. We found that using the built deep learning classifiers with the transformer is generally better than classical machine learning classifiers. Finally, we could not find a stable conclusion concerning which model works well with each text representation method because each evaluation measure has a different favored model.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nasir, J.A.; Khan, O.S.; Varlamis, I.: Fake news detection: a hybrid CNN-RNN based deep learning approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 1(1), 100007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JJIMEI.2020.100007
Zhou, X.; Zafarani, R.: A survey of fake news. ACM Comput. Surv.Comput. Surv. 53, 5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3395046
El Ballouli, R.; El-Hajj, W.; Ghandour, A.; Elbassuoni, S.; Hajj, H.; Shaban, K: CAT: Credibility analysis of arabic content on twitter. In: Proceedings of the third Arabic natural language processing workshop. pp. 62–71. (2017). https://doi.org/10.18653/V1/W17-1308
Shu, K.; Sliva, A.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Liu, H.: Fake news detection on social media: a data mining perspective. ACM SIGKDD Explor. newslett. 19(1), 22–36 (2017)
Mehta, D.; Dwivedi, A.; Patra, A.; Anand Kumar, M.: A transformer-based architecture for fake news classification. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min.Netw. Anal. Min. 11, 1–12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13278-021-00738-Y
Nassif, A.B.; Darya, A.M.; Elnagar, A.: Empirical evaluation of shallow and deep learning classifiers for arabic sentiment analysis. Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3466171
Nassif, A.B.; Elnagar, A.; Elgendy, O.; Afadar, Y.: Arabic fake news detection based on deep contextualized embedding models. Neural Comput. Appl.Comput. Appl. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-022-07206-4/TABLES/6
Najadat, H.; Tawalbeh, M.; Awawdeh, R.: Fake news detection for Arabic headlines-articles news data using deep learning. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 12(4), 3951–3959 (2022). https://doi.org/10.11591/IJECE.V12I4.PP3951-3959
Al-Laith, A.; Mahlous, A.R.: Fake news detection in arabic tweets during the covid-19 pandemic common words in arabic and urdu languages view project fake news detection in arabic tweets during the covid-19 pandemic. Artic. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 12(6), 2021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0120691
Sahoo, S.R.; Gupta, B.B.: Multiple features based approach for automatic fake news detection on social networks using deep learning. Appl. Soft Comput.Comput. 100, 106983 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2020.106983
Hadj Ameur, M.S.; Aliane, H.: AraCOVID19-MFH arabic COVID-19 multi-label fake news & hate speech detection dataset. Proced. Comput. Sci. 189, 232–241 (2021)
Jardaneh, G.; Abdelhaq, H.; Buzz, M.; Johnson, D.: "Classifying Arabic tweets based on credibility using content and user features," in:2019 IEEE Jordan international joint conference on electrical engineering and information technology, JEEIT 2019 – Proceedings, pp. 596–601. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/JEEIT.2019.8717386.
Al-Yahya, M.; Al-Khalifa, H.; Al-Baity, H.; Alsaeed, D.; Essam, A.: Arabic fake news detection: comparative study of neural networks and transformer-based approaches. Complexity (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5516945
Himdi, H.; Weir, G.; Assiri, F.; Al-Barhamtoshy, H.: Arabic fake news detection based on textual analysis. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47(8), 10453–10469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/S13369-021-06449-Y/FIGURES/7
Kaliyar, R.K.; Goswami, A.; Narang, P.: FakeBERT: fake news detection in social media with a BERT-based deep learning approach. Multimed. Tools Appl. 80(8), 11765–11788 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/S11042-020-10183-2/TABLES/22
Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J.: "Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space," 1st Int. Conf. Learn. Represent. ICLR 2013 - Work. Track Proc., (2013). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1301.3781.
Bojanowski, P.; Grave, E.; Joulin, A.; Mikolov, T.: Enriching word vectors with subword information. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 5, 135–146 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1162/TACL_A_00051/43387/ENRICHING-WORD-VECTORS-WITH-SUBWORD-INFORMATION
Shaalan, K.; Siddiqui, S.; Alkhatib, M.; Abdel Monem, A.: Challenges in arabic natural language processing. Comput. Linguist. Speech Image Process. Arab. Lang. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789813229396_0003
Assaf, R.; Saheb, M.; “Dataset for arabic fake news”, 15th IEEE Int. Conf. Appl. Inf. Commun. Technol. AICT, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/AICT52784.2021.9620228.
Khalil, A.; Jarrah, M.; Aldwairi, M.; Jaradat, M.: AFND: arabic fake news dataset for the detection and classification of articles credibility. Data Br. 42, 108141 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIB.2022.108141
Antoun W; Baly F; Hajj H: "AraBERT Transformer-based Model for arabic language understanding," (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2003.00104.
Inoue, G.; Alhafni, B.; Baimukan, N.; Bouamor, H.; Habash, N.: "The interplay of variant, size, and task type in arabic pre-trained language models," (2021). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2103.06678.
Abdul-Mageed, M.; Elmadany, A. R.; Nagoudi, E. M. B.: "ARBERT & MARBERT: Deep bidirectional transformers for arabic," ACL-IJCNLP 2021 - 59th Annu. Meet. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 11th Int. Jt. Conf. Nat. Lang. Process. Proc. Conf., pp. 7088–7105, (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2101.01785.
Antoun, W.; Baly, F.; Hajj, H.: "AraELECTRA: Pre-training text discriminators for arabic language understanding," (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2012.15516.
Soliman, A.B.; Eissa, K.; El-Beltagy, S.R.: AraVec: a set of arabic word embedding models for use in arabic NLP. Proced. Comput. Sci. 117, 256–265 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2017.10.117
Moatez E.; et al.: "Machine generation and detection of arabic manipulated and fake news," in: Proceedings of the fifth arabic natural language processing workshop, pp. 69–84, Accessed: Aug. 19, (2022). [Online]. Available: https://aclanthology.org/2020.wanlp-1.7.
Saadany, H.; Mohamed, E.; Orasan, C.: “Fake or real? a study of arabic satirical fake news," (2020). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2011.00452.
Helwe, C.; Elbassuoni, S.; Al Zaatari, A.; El-Hajj, W.: "Assessing arabic weblog credibility via deep co-learning," in: proceedings of the fourth arabic natural language processing workshop, pp. 130–136, (2019). https://doi.org/10.18653/V1/W19-4614.
Rangel, F.; Rosso, P.; Charfi, A.; Zaghouani, W.: "Detecting deceptive tweets in arabic for cyber-security," in: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Security Informatics, ISI 2019, pp. 86–91, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISI.2019.8823378.
Haouari, F.; Sheikh Ali, Z.; Elsayed, T.: "bigIR at CLEF 2019: automatic verification of arabic claims over the web," Accessed: Aug. 30, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://reporterslab.org/fact-checking-triples-over-four-years/.
Sutanto, D.; M. G.-A. J. E. A. Sci; undefined 2015, "A benchmark of classification framework for non-communicable disease prediction: a review," arpnjournals.org, vol. 10, 2015, Accessed: Aug. 19, 2022. [Online]. Available: http://www.arpnjournals.org/jeas/research_papers/rp_2015/jeas_1115_2962.pdf.
Alkhair, M.; Meftouh, K.; Smaïli, K.; Othman, N.: An arabic corpus of fake news: collection, analysis and classification. Commun. Comput. Inform. Sci. 1108, 292–302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-32959-4_21/COVER
Bsoul, M.A.; Qusef, A.; Abu-Soud, S.: Building an optimal dataset for arabic fake news detection. Proced. Comput. Sci. 201, 665–672 (2022)
Ozbay, F.A.; Alatas, B.: Fake news detection within online social media using supervised artificial intelligence algorithms. Phys. A Stat. Mech. its Appl. 540, 123174 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PHYSA.2019.123174
Traylor, T.; Straub, J.; Gurmeet; Snell, N: "Classifying fake news articles using natural language processing to identify in-article attribution as a supervised learning estimator," in: Proceedings - 13th ieee international conference on semantic computing, ICSC 2019, pp. 445–449, (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOSC.2019.8665593.
Antoun, W.; Baly, F.; Achour, R.; Hussein, A.; Hajj, H.: "State of the art models for fake news detection tasks," in: 2020 IEEE international conference on informatics, IoT, and enabling technologies, ICIoT 2020, pp. 519–524, (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIOT48696.2020.9089487.
Abd Elminaam, D. S.; Abdelaziz, A.; Essam, G.; Mohamed, S. E: AraFake: A deep learning approach for Arabic fake news detection. In: 2023 international mobile, intelligent, and ubiquitous computing conference (MIUCC) (pp. 1–8). IEEE. (2023)
Harrag, F.; Djahli, M.K.: Arabic fake news detection: a fact-checking based deep learning approach. Trans. Asian Low Resour. Lang. Inform. Process. 21(4), 1–34 (2022)
Hawashin, B.; Althunibat, A.; Kanan, T.; AlZu'bi, S.; Sharrab, Y.: Improving arabic fake news detection using optimized feature selection. In: 2023 international conference on information technology (ICIT) (pp. 690–694). IEEE. (2023)
Shishah, W.: JointBert for detecting arabic fake news. IEEE Access 10, 71951–71960 (2022)
Wotaifi, T.A.; Dhannoon, B.N.: An effective hybrid deep neural network for arabic fake news detection. Baghdad Sci. J. 20(4), 1392–1392 (2023)
Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D.:"GloVe: global vectors for word representation," in: 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), (2014), pp. 1532–1543, Accessed: Aug 19, (2022).
Altszyler, E.; Sigman, M.; Ribeiro, S.; Slezak, D.F.: Comparative study of LSA vs Word2Vec embeddings in small corpora: a case study in dreams database. Conscious. Cogn.Cogn. 56, 178–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2017.09.004
Naili, M.; Chaibi, A.H.; Ben Ghezala, H.H.: “Comparative study of word embedding methods in topic segmentation.” Proced. Comput Sci. 112, 340–349 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2017.08.009
Santos, I.; Nedjah, N.; De Macedo Mourelle, L.: "Sentiment analysis using convolutional neural network with fasttext embeddings. In: 2017 IEEE Latin American conference on computational intelligence, LA-CCI - Proceedings, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/LA-CCI.2017.8285683.
Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K.: “BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding,.” Hum. Lang. Technol. Proc. Conf. 1, 4171–4186 (2018). https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1810.04805
Simko, J.; Racsko, P.; Tomlein, M.; Hanakova, M.; Moro, R.; Bielikova, M.: A study of fake news reading and annotating in social media context. New rev. hypermedia multimed. 27(1–2), 97–127 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/13614568.2021.1889691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Azzeh, M., Qusef, A. & Alabboushi, O. Arabic Fake News Detection in Social Media Context Using Word Embeddings and Pre-trained Transformers. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08959-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08959-x