Abstract
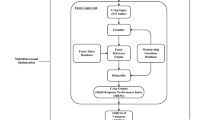
The current study explores the precision enhancement of AISI420 Martensitic Stainless Steel (MSS) using sinking-electrical discharge machining (S-EDM) with Copper electrodes, which is a unique combination of materials and machining process and conducts a comprehensive multivariate analysis to investigate the correlation between machine control variables (MCV) and measured machining performance (MMP) in the context of AISI420 Martensitic Stainless Steel and Sinking-Electrical Discharge Machining. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) establishes the hierarchy of machine control variables influence: Pulse current (B) > Gap voltage (A) > Pulse on Time (C). Remarkably, Pulse current (B) emerges as the paramount parameter, thus constituting a cornerstone of this study's findings. This research article utilizes the RSM–GRA–PCA methodology, which combines response surface methodology (RSM), grey relational analysis (GRA), and principal component analysis (PCA) to optimize the machining process. Using traditional RSM–GRA technique and RSM–GRA–PCA methodology, the experimental Grey Relational Grade (GRGexperiment) are achieved 0.8048 and 0.9817, respectively. The validation test has been performed to confirm the fittest method positions. The percentage significance of significant factor is also improved from 64.63 to 79.71% and error is reduced from 5.22 to 1.68% using RSM–GRA–PCA methodology with improved GRG of 0.068. This integrated approach improves the grey relational grade (GRG) and reduces errors, leading to more accurate and efficient machining.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isfahany, A.N., et al.: The effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AISI420 martensitic stainless steel. J. Alloy. Compd. 509(9), 3931–3936 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.12.174
Puertas, I.; Luis, C.J.A.: Study of optimization of machining parameters for electrical discharge machining of boron carbide. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 19, 1041–1070 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1081/AMP-200035200
Maciel, D.T., et al.: Characteristics of machined and formed external threads in titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 79, 779–792 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6858-z
Torres, A., et al.: Modelling of surface finish, electrode wear and material removal rate in electrical discharge machining of hard-to-machine alloys. Precis. Eng. 40, 33–45 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.10.001
Yildiz, Y.: Prediction of white layer thickness and material removal rate in electrical discharge machining by thermal analyses. J. Manuf. Process. 23, 47–53 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.05.01
Kumar, N.M., et al.: An investigation of mechanical properties and material removal rate, tool wear rate in EDM machining process of AL2618 alloy reinforced with Si3N4, AlN and ZrB2 composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 650, 318–327 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.292
Pradhan, M.K.: Estimating the effect of process parameters on MRR, TWR and radial overcut of EDMed AISI D2 tool steel by RSM and GRA coupled with PCA. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 68, 591–605 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-4780-9
Aggarwal, V., et al.: Parametric modeling and optimization for wire electrical discharge machining of Inconel 718 using response surface methodology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 79, 31–47 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-6797-8
Singh, B., et al.: Influences of process parameters on MRR improvement in simple and powder-mixed EDM of AA6061/10%SiC composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 30, 303–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.930888
Hourmand, M., et al.: Investigating the electrical discharge machining (EDM) parameter effects on Al–Mg2Si metal matrix composite (MMC) for high material removal rate (MRR) and less EWR–RSM approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 77, 831–838 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6491-2
Mogilicharla, A., et al.: Kriging surrogate based multi-objective optimization of bulk vinyl acetate polymerization with branching. Mater. Manuf. Process. 30, 394–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2014.921709
Mandal, A., et al.: Modeling and optimization of machining nimonic C-263 superalloy using multicut strategy in WEDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 31, 860–868 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1048462
Mandaloi, G., et al.: Effect on crystalline structure of AISI M2 steel using tungsten–thorium electrode through MRR, EWR, and surface finish. Measurement 90, 74–84 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.04.041
Rajmohan, K.; Kumar, A.S.: Experimental investigation and prediction of optimum process parameters of micro-wire-cut EDM of 2205 DSS. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 93, 187–204 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8615-3
Pantula, P.D., et al.: KERNEL: Enabler to build smart surrogates for online optimization and knowledge discovery. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32, 1162–1171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2016.1269918
Pramanik, A., et al.: Processing of duplex stainless steel by WEDM. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 1559–1567 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1453165
Pilligrin, C.J., et al.: Effects of electrode materials on performance measures of electrical discharge micro-machining. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33, 606–615 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1364757
Payla, A., et al.: Investigations on power consumption in WEDM of EN31 steel for sustainable production. Mater. Manuf. Process. 34, 1855–1865 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1683577
Balasubramanian, K., et al.: Machinability analysis and application of response surface approach on CNC turning of LM6/SiCp composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 34, 1389–1400 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1660787
Hanif, M., et al.: Investigating the effects of electric discharge machining parameters on material removal rate and surface roughness on AISI D2 steel using RSM–GRA integrated approach. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 101, 1255–1265 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-3019-1
Li, C., et al.: Deformation mechanism and force modelling of the grinding of YAG single crystals. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf 143, 23–37 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2019.05.003
Singh, G., et al.: Analysis of electrical discharge machining parameters for H13 steel using OVAT technique. Eng. Res. Express. 1, 025031 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ab52dc
Tiwari, T., et al.: Investigations on bending of micro-thin sheets using spark discharges. Mater. Manuf. Process. 35, 1362–1371 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1772488
Aldrinraj, J., et al.: Experimental investigations on WEDM process for machining high Manganese steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 35, 1612–1621 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1779941
Miriyala, S.S.; Mitra, K.: Multi-objective optimization of iron ore induration process using optimal neural networks. Mater. Manuf. Process. 35, 537–544 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2019.1643476
Chaudhari, R., et al.: Multi-response optimization of WEDM parameters using an integrated approach of RSM–GRA analysis for pure titanium. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. D 101, 117–126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-020-00204-7
Ahuja, N., et al.: Experimental investigation and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining for surface characteristics and corrosion rate of biodegradable Mg alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 29, 4117–4129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04905-8
Rouniyar, A.K.; Shandilya, P.: Experimental investigation on recast layer and surface roughness on aluminum 6061 alloy during magnetic field assisted powder mixed electrical discharge machining. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 29, 7981–7992 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05244-4
Kumar, S., et al.: Multi-variable optimization in die-sinking EDM process of AISI420 stainless steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 36, 572–582 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1843678
Zhu, C., et al.: A titanium alloys design method based on high-throughput experiments and machine learning. J. Market. Res. 11, 2336–2353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.055
Le, V.T.: Influence of processing parameters on surface properties of SKD61 steel processed by powder mixed electrical discharge machining. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 30, 3003–3023 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05584-9
Hou, S.; Bai, J.; Tian, B., et al.: Experimental investigation to improve the efficiency and surface integrity of deep micro-hole machined by micro-EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 123, 2249–2259 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10272-6
Vakharia, V., et al.: Experimental investigations and prediction of WEDMed surface of nitinol SMA using SinGAN and DenseNet deep learning model. J. Market. Res. 18, 325–337 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.02.093
Karthik Pandiyan, G.; Prabaharan, T.; Jafrey Daniel James, D., et al.: Machinability analysis and optimization of electrical discharge machining in AA6061-T6/15wt.% SiC composite by the multi-criteria decision-making approach. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 31, 3741–3752 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06511-8
Haja Syeddu Masooth, P., et al.: Analysis of machining characteristics in electrical discharge machining of SiC and Al2O3 reinforced AA6061 hybrid metal matrix composites using Taguchi and ANOVA techniques. Mater. Res. Express. 9, 046521 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ac672d
Meng, Z., et al.: PINN-FORM: a new physics-informed neural network for reliability analysis with partial differential equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 414, 116172 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2023.116172
Anosri, Siwakorn, et al.: A comparative study of state-of-the-art metaheuristics for solving many-objective optimization problems of fixed wing unmanned aerial vehicle conceptual design. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 30, 3657–3671 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-023-09914-z
Cao, P.; Tong, H.; Li, Y., et al.: Interelectrode gas–liquid–solid three-phase flow analysis and simulation for drilling holes with high aspect ratio by micro-EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 128, 5261–5276 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-12220-4
Dikshit, M.K., et al.: Surface characteristics optimization of biocompatible Ti6Al4V with RCCD and NSGA II using die sinking EDM. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 24, 223–235 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.03.005
Mehrvar, A.; Mirak, A.: Comparative evaluation of surface integrity of CMSX-4 nickel-based superalloy after grinding, wire electrical discharge machining, and electrochemical machining processes. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-023-08194-9
Janardhana, K., et al.: Experimental investigation on microhardness, surface roughness, and white layer thickness of dry EDM. Eng. Res. Express. 5, 025022 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/acce8f/meta
Abbas, A.T., et al.: A machine learning perspective to the investigation of surface integrity of Al/SiC/Gr composite on EDM. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 7(5), 163 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp7050163
Mookam, N.; Sunasuan, P.; Madsa, T., et al.: Effects of graphite and boron carbide powders mixed into dielectric fluid on electrical discharge machining of SKD 11 tool steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 2553–2563 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05156-4
Shastri, R.K.; Mohanty, C.P.: Sustainable electrical discharge machining of nimonic C263 superalloy. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 7273–7293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05211-0
Alharbi, N.: Effect of electrical discharge machining on corrosion resistance of Inconel 718. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 15661–15671 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06713-9
Sundaresan, D.; Marappan, L.; Thangavelu, K., et al.: Machinability of nimonic alloy 90 in µ-Titanium carbide mixed electrical discharge machining. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 15223–15243 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06499-2
Bhosale, S.B.; Bhowmik, S.; Ray, A.: Evaluation of machinability and recast layer analysis of ferrous clay composite through electric discharge machining process. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 8523–8533 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06337-5
Kumar, S.; Goud, M.; Suri, N.M.: Grey relational analysis-based multi-response optimization of magnetic-field-assisted powder-mixed electric discharge machining of Inconel 706. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 8315–8833 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06204-3
Saha, S.; Maity, S.R.; Dey, S.: Machinability study of A286 superalloy for complex profile generation through wire electric discharge machining. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48, 3241–3253 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07028-5
Paswan, K.; Pramanik, A.; Chattopadhyaya, S., et al.: An analysis of machining response parameters, crystalline structures, and surface topography during EDM of die-steel using EDM oil and liquid-based viscous dielectrics: a comparative analysis of machining performance. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48, 11941–11957 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07626-x
Nahak, B.; Srivastava, A.: Non-destructive monitoring of electro-discharge machined die steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 47, 15153–15160 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06497-4
Nagabhooshanam, N.; Baskar, S.; Anitha, K., et al.: Sustainable machining of hastelloy in EDM using nanoparticle-infused biodegradable dielectric fluid. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 11759–11770 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05652-1
Ishfaq, K.; Rehman, M.; Wang, Y.: Toward the targeted material removal with optimized surface finish during EDM for the repair applications in dies and molds. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 48, 2653–2669 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-07006-x
Deng, J.L.: Introduction to grey system theory. J. Grey Syst. 1, 1–24 (1989). https://doi.org/10.5555/90757.90758
Lin, Z.C.; Ho, C.Y.: Analysis and application of grey relation and ANOVA in chemical–mechanical polishing process parameters. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 21, 10–14 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001700300001
Hotelling, H.: Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. J. Educ. Psychol. 24, 417–441 (1933). https://doi.org/10.1037/h0071325
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, S., Ghoshal, S.K., Arora, P.K. et al. Unlocking AISI420 Martensitic Stainless Steel's Potential: Precision Enhancement Via S-EDM with Copper Electrodes and Multivariate Optimization. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08711-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-024-08711-5