Abstract
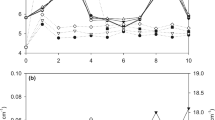
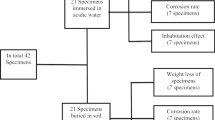
Corrosion is one of the most significant problems in irrigation systems, and fertigation may increase its damage. One of the solutions to mitigate this phenomenon would be using cathodic protection combined with piping coating, so it is essential to evaluate the type of sacrificial anodes and the cathode/anode area ratio, variables that change the performance of cathodic protection and its application cost. Thus, this study aimed to validate the effect of Al anodes on the protection against the mass loss of galvanized steel used in fertigation with white KCl solution at 10 g L−1 and verify the influence of the cathode/anode area ratio on the galvanized steel protection and anode consumption. Thus, we conducted immersion tests by simulating 10 years of fertigation to determine the mass loss of the galvanized steel and Al anodes. The results showed that Al anodes significantly reduce the mass loss in galvanized steel exposed to KCl solution, but there is no significant difference in its mass loss with the increase in the cathode/anode area ratio. Regarding the Al anodes, there was also no significant difference in mass loss with the increase in the cathode/anode area ratio.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Adeli, A.; Yan, H.: Effects of application methods and urea rates on ammonia volatilization, yields and fine root biomass of alfalfa. Field Crop Res 218, 115–125 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.01.011
Zhao, W.; Shan, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Y.: Effects of fertigation splits through center pivot on the nitrogen uptake, yield, and nitrogen use efficiency of winter wheat grown in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 240, 106291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106291
Larue, J.: How can fertigation and chemigation with a center pivot improve sustainability of irrigation corn? In: ASABE Annual International Meeting, Paper Number: 2200208, Minneapolis, Minnesota (2022)
Rodrigues, K.V.; Lima, L.A.; Thebaldi, M.S.: Effects of fertigation on corrosion in galvanized steel used in center pivot systems. Water Supply 20(4), 1189–1194 (2020). https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2020.029
Tayyab, M.; Abbas, Y.; Hussain, M.W.: Management options for large metropolitans on the verge of a water stress. J. Hum. Earth Future. 3(3), 333–344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.28991/HEF-2022-03-03-06
Delaunois, F.F.; Vitry, T.V.: Corrosion behaviour and biocorrosion of galvanized steel water distribution systems. Bioelectrochemistry 97, 110–119 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2014.01.003
LaRue, J.: A review of center pivot pipeline solutions for various water qualities. In: ASABE Meeting Presentation, Paper Number 072286. Minneapolis, Minnesota (2007)
Corrêa, F.V.; Lima, L.A.; Thebaldi, M.S.; Rodrigues, K.V.: Corrosion caused by fertigation with urea and potassium chloride solutions resembles that generated by irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 72, 1–12 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2819
Maraveas, C.: Durability issues and corrosion of structural materials and systems in farm environment. Appl. Sci. 10, 990 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030990
Amer, B.A.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; El-Ashtoukly, E.S.Z.; Amin, N.K.: Galvanic corrosion of steel in agitated vessels used in fertilizer industry. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 53(2), 280–291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579519020015
Francis, R.; Turnbull, A.; Hinds, G.: Bimetallic corrosion, guides for good practice in corrosion control, No. 5. National Physical Laboratory—NPL (2020)
Saji, V.S.: Review—photoelectrochemical cathodic protection in the dark: a review of nanocomposite and energy-storing photoanodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 121505 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abad70
Harvey, D.W.: Cathodic protection, guides to good practice in corrosion control, No. 1. National Physical Laboratory—NPL (2019)
Gentil, V.: Corrosão, 7th edn. LTC, Rio de Janeiro (2022)
Farh, H.M.H.; Seghier, M.E.A.B.; Zayed, T.: A comprehensive review of corrosion protection and control techniques for metallic pipelines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 43, 106885 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106885
Kleiner, Y.; Rajani, B.: Quantifying effectiveness of cathodic protection in water mains: theory. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 10, 43–51 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1076-0342(2004)10:2(43)
Gurrapa, I.: Cathodic protection of cooling water systems and selection of appropriate materials. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 166, 256–267 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2004.09.074
Xi, Y.; Jia, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D.; Sun, L.: Evaluating the performance of aluminum sacrificial anodes with different concentration of gallium in artificial sea water. Coatings 12(1), 53 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12010053
Pourgharibshahi, M.; Lambert, P.: The role of Indium in the activation of aluminum alloy galvanic anodes. Mater. Corros. 67, 857–866 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/maco.201508685
Pryor, M.J.; Keir, D.S.: Galvanic corrosion: II effect of pH and dissolved oxygen concentration on the aluminum-steel couple. J. Electrochem. Soc. 105(11), 629–635 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2428681
Standish, T.E.; Braithwaite, L.J.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Noël, J.J.: Influence of area ratio and chloride concentration on the galvanic coupling of copper and carbon steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166(11), C3448–C3455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0521911jes
Atshan, A.A.; Hasan, B.O.; Ali, M.H.: Effect of anode type and position on the cathodic protection of carbon steel in sea water. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 3(5), 2017–2024 (2013)
Jafar, S.A.: The influence of area ratio, temperature and rotational speed on galvanic corrosion between law alloy steel–copper couple in 4%NaCl solution. Eng. Technol. J. 35(6), 617–623 (2017). https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.35.6A.9
Loto, C.A.; Popoola, A.P.I.: Effect of anode and size variations on the cathodic protection of mild steel in sea water and sulphuric acid. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 6(12), 2861–2868 (2011)
Refait, Ph.; Jeannin, M.; Sabot, R.; Antony, H.; Pineau, S.: Corrosion and cathodic protection of carbon steel in the tidal zone: products, mechanisms and kinetics. Corr. Sci. 90, 375–382 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.10.035
Loto, C.A.; Loto, R.T.; Popoola, A.P.: Performance evaluation of zinc anodes for cathodic protection of mild steel corrosion in HCl. Chem. Data Collect. 24, 100280 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2019.100280
Owoeye, F.T.; Adetunji, O.R.; Kuye, S.I.; Bada, B.S.: Cathodic protection of aluzinc coated, galvanized and stainless steels in Ijegun seawater using aluminum as sacrificial anode. United Int. J. Res. Technol. 2(2), 81–92 (2020)
Astuti, P.; Rafdinal, R.S.; Yamamoto, D.; Andriamisaharimanana, V.; Hamada, H.: Effective use of sacrificial zinc anode as a suitable repair method for severely damaged RC members due to chloride attack. Civ. Eng. J. 8(7), 1535–1548 (2022). https://doi.org/10.28991/CEJ-2022-08-07-015
Nezgoda, J.; Goudar, J.V.; Brasil, S.L.D.C.: Estudo das camadas calco-magnesianas formadas em superfícies metálicas sob proteção catódica. In: INTERCORR 2016, Associação Brasileira de Corrosão (ABRACO), Búzios (2016)
Rodrigues, K.V.; Lima, L.A.; Thebaldi, M.S.: Use of sacrificial anodes as protection of galvanized steel exposed to potassium chloride and urea fertigation solutions. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (In press) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08412-5
Tsujino, B.; Miyase, S.: On area ratio of anode to cathode for iron in neutral solution. Corrosion 37(9), 540–545 (1981). https://doi.org/10.5006/1.3580803
Dong, C.F.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.G.; Cheng, Y.F.: Galvanic corrosion of a carbon steel-stainless steel couple in sulfide solutions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 20(9), 1631–1637 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-011-9839-x
Pramanik, N.; Kumar, R.; Ray, A.; Chaudhary, V.K.; Ghosh, S.: Corrosion behavior of mild steel in the presence of urea, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, and glycine: a kinetic and potentiodynamic polarization study approach. J. Bio Tribo-Corros. 8, 112 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-022-00713-w
ABNT NBR 6323: Galvanização por imersão a quente de produtos de aço e ferro fundido – Especificação. Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas—ABNT, Rio de Janeio (2016)
Wu, Y.H.; Liu, T.M.; Luo, S.X.; Sun, C.: Corrosion characteristics of Q235 steel in simulated Yingtan soil solutions. Mat.-wiss. u. Werkstofftech. 41(3), 42–146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/mawe.201000559
Ferreira, D.F.: SISVAR: a computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Rev. Bras. de Biom. 37(4), 529–535 (2019). https://doi.org/10.28951/rbb.v37i4.450
Dong, C.F.; Xiao, K.; Li, X.G.; Cheng, Y.F.: Erosion accelerated corrosion of a carbon steel–stainless steel galvanic couple in a chloride solution. Wear 270, 39–45 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2010.09.004
Song, G.; Johannesson, B.; Hapugoda, S.; Stjohn, D.: Galvanic corrosion of magnesium alloy AZ91D in contact with an aluminium alloy, steel and zinc. Corros. Sci. 46, 955–977 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(03)00190-2
Nwoye, C.I.; Chinwuko, E.C.; Nwosu, I.E.; Onyia, W.C.; Amalu, N.I.; Nwosu, P.C.: Operational dependence of galvanized steel corrosion rate on its structural weight loss and immersion-point pH in sea water environment. Am. J. Min. Metall. 2(4), 81–87 (2014)
NACE SP 07-75: Preparation, installation, analyses, and interpretation of corrosion in oilfield operation. National Association of Corrosion Engineers—NACE, Houston (2013)
Kim, W.; Han, K.; Kim, J.; Yang, S.; Seok, H.; Han, H.; Kim, Y.: Effect of surface area on corrosion properties of magnesium for biomaterials. Met. Mater. Int. 19(5), 1131–1137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-013-5032-0
Yaro, A.S.; Hameed, K.W.; Khadom, A.A.: Study for prevention of steel corrosion by sacrificial anode cathodic protection. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 47(3), 266–273 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579513030147
Prayitno, D.; Irsyad, M.: Effect of ratio of surface area on the corrosion rate. SINERGI 22(1), 7–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.22441/sinergi.2018.1.002
Bilgic, S.: Galvanic corrosion. In: The Eurasia Proceedings of Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics (EPSTEM), vol. 4, pp. 259–262 (2018). http://www.epstem.net/en/download/article-file/598406
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), grant number 001, and by the Department of Water Resources of the Universidade Federal de Lavras (DRH-UFLA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, K.V., Lima, L.A., Thebaldi, M.S. et al. Cathode/Anode Area Ratio on the Sacrificial Cathodic Protection Against Mass Loss of Galvanized Steel Used in Potassium Chloride Fertigation. Arab J Sci Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08696-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08696-7