Abstract
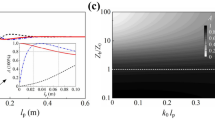
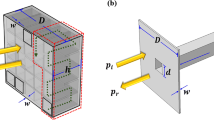
In this work, an acoustic metasurface composed of pie-sliced resonator segments is proposed and its attenuation characteristics in ultra-low-frequency regime are examined using analytical, numerical, and experimental means. This metasurface absorber is systematically designed and realized with inhomogeneous unit cells in the shape of sliced pie to accomplish ultra-low-frequency (<100 Hz) noise cancellation. Firstly, a sound absorber with four unit cells having deep sub-wavelength thickness (\(\lambda \)/39) is fabricated and it exhibited a sound wave mitigation of more than 80% throughout the low-frequency range of 212–276 Hz. For enhancing the broadband absorption in the ultra-low-frequency regime, an acoustic absorber with eight pie-sliced unit cells is designed, realized and tested. Thereafter, a compact absorber with very-low vertical (\(\lambda /34\)) and lateral (\(\lambda /52\)) dimensions is considered and it accomplished more than 85% sound absorption in the ultra-low-frequency domain of 66–100 Hz. It is further demonstrated that, by tailoring the geometrical features such as cavity depth, resonator diameter, neck length, sector angle and number of unit cells of the metastructure, the bandwidth and frequency of the absorption peak can be modified as per the requirement. Owing to the compactness, ease of production and high absorption capacity over a wide band in the ultra-low-frequency regime, the introduced acoustic metasurface is a potential candidate for noise control applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tyagi, V.; Kumar, K.; Jain, V.K.: A study of the spectral characteristics of traffic noise attenuation by vegetation belts in Delhi. Appl. Acoust. 67(9), 926–935 (2006)
Ekici, I.; Bougdah, H.: A review of research on environmental noise barriers. Build. Acoust. 10(4), 289–323 (2003)
Tang, X.; Yan, X.: Acoustic energy absorption properties of fibrous materials: a review. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 101, 360–380 (2017)
Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.: Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 10, 25–35 (2018)
Ingard, U.: On the theory and design of acoustic resonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 25(6), 1037–61 (1953)
Prydz, R.; Wirt, L.; Kuntz, H.; Pope, L.: Transmission loss of a multilayer panel with internal tuned Helmholtz resonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 87(4), 1597–1602 (1990)
Kim, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Jang, J.H.: A theoretical model to predict the low-frequency sound absorption of a Helmholtz resonator array. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 119(4), 1933–1936 (2006)
Mahesh, K.; Mini, R.S.: Investigation on the acoustic performance of multiple Helmholtz resonator configurations. Acoust. Aust. 49(2), 355–369 (2021)
Huang, S.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Assouar, B.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y.: Acoustic perfect absorbers via Helmholtz resonators with embedded apertures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 145(1), 254–262 (2019)
Zhu, J.; Qu, Y.; Gao, H.; Meng, G.: Nonlinear sound absorption of Helmholtz resonators with serrated necks under high-amplitude sound wave excitation. J. Sound Vib. 537, 117197 (2022)
Ma, G.; Yang, M.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Z.; Sheng, P.: Acoustic metasurface with hybrid resonances. Nat. Mater. 13(9), 873–878 (2014)
Mei, J.; Ma, G.; Yang, M.; Yang, Z.; Wen, W.; Sheng, P.: Dark acoustic metamaterials as super absorbers for low-frequency sound. Nat. Commun. 3(1), 1–7 (2012)
Sampaio, L.Y.; Cerântola, P.C.; de Oliveira, L.P.: Lightweight decorated membranes as an aesthetic solution for sound insulation panels. J. Sound Vib. 532, 116971 (2022)
Maa, D.Y.: Microperforated-panel wideband absorbers. Noise Control Eng. J. 29(3), 77 (1987)
Maa, D.Y.: Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 104(5), 2861–2866 (1998)
Rafique, F.; Wu, J.H.; Waqas, M.; Lushuai, X.; Ma, F.: A thin double-layer multiple parallel-arranged inhomogeneous microperforated panel absorber for wideband low-frequency sound absorption. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 44(1), 1–18 (2022)
Tan, W.-H.; Ripin, Z.M.: Optimization of double-layered micro-perforated panels with vibro-acoustic effect. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 38(3), 745–760 (2016)
Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Kang, L.; Liu, B.: Design of multiple parallel-arranged perforated panel absorbers for low frequency sound absorption. Materials 12(13), 2099 (2019)
Mi, Y.; Yu, X.: Attenuation of low-frequency sound in u-shaped duct with membrane coupled acoustic resonator: modeling and analysis. J. Sound Vib. 489, 115679 (2020)
Sakagami, K.; Nagayama, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Yairi, M.: Pilot study on wideband sound absorber obtained by combination of two different microperforated panel (MPP) absorbers. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 30(2), 154–156 (2009)
Wang, C.; Cheng, L.; Pan, J.; Yu, G.: Sound absorption of a micro-perforated panel backed by an irregular-shaped cavity. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 127(1), 238–246 (2010)
Li, D.; Chang, D.; Liu, B.: Enhanced low-to mid-frequency sound absorption using parallel-arranged perforated plates with extended tubes and porous material. Appl. Acoust. 127, 316–323 (2017)
Shen, X.; Bai, P.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; To, S.: Low frequency sound absorption by optimal combination structure of porous metal and microperforated panel. Appl. Sci. 9(7), 1507 (2019)
Boulvert, J.; Humbert, T.; Romero-García, V.; Gabard, G.; Fotsing, E.R.; Ross, A.; Mardjono, J.; Groby, J.-P.: Perfect, broadband, and sub-wavelength absorption with asymmetric absorbers: realization for duct acoustics with 3d printed porous resonators. J. Sound Vib. 523, 116687 (2022)
Guo, J.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.: Acoustic characterizations of Helmholtz resonators with extended necks and their checkerboard combination for sound absorption. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 53(50), 505504 (2020)
Gai, X.L.; Xing, T.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.J.: Sound absorption of microperforated panel mounted with Helmholtz resonators. Appl. Acoust. 114, 260–265 (2016)
Park, S.H.: Acoustic properties of micro-perforated panel absorbers backed by Helmholtz resonators for the improvement of low-frequency sound absorption. J. Sound Vib. 332(20), 4895–4911 (2013)
Langfeldt, F.; Hoppen, H.; Gleine, W.: Broadband low-frequency sound transmission loss improvement of double walls with Helmholtz resonators. J. Sound Vib. 476, 115309 (2020)
Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Z.: Wideband low-frequency sound absorption by inhomogeneous multi-layer resonators with extended necks. Compos. Struct. 260, 113538 (2021)
Liu, X.; Yu, C.; Xin, F.: Gradually perforated porous materials backed with Helmholtz resonant cavity for broadband low-frequency sound absorption. Compos. Struct. 263, 113647 (2021)
Mahesh, K.; Mini, R.S.: Theoretical investigation on the acoustic performance of Helmholtz resonator integrated microperforated panel absorber. Appl. Acoust. 178, 108012 (2021)
Mahesh, K.; Ranjith, S.K.; Mini, R.S.: Inverse design of a Helmholtz resonator based low-frequency acoustic absorber using deep neural network. J. Appl. Phys. 129(17), 174901 (2021)
Assouar, B.; Liang, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.C.; Jing, Y.: Acoustic metasurfaces. Nat. Rev. Mater. 3(12), 460–472 (2018)
Liu, H.; Wu, J.H.; Ma, F.: High-efficiency sound absorption by a nested and ventilated metasurface based on multi-slit synergetic resonance. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54(20), 205304 (2021)
Liu, H.; Wu, J.H.; Ma, F.: Dynamic tunable acoustic metasurface with continuously perfect sound absorption. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54(36), 365105 (2021)
Liu, L.; Chang, H.; Zhang, C.; Hu, X.: Single-channel labyrinthine metasurfaces as perfect sound absorbers with tunable bandwidth. Appl. Phys. Lett. 111(8), 083503 (2017)
Xu, Z.; Qin, L.; Xu, W.; Fang, S.; Wang, J.: Design approach of perforated labyrinth-based acoustic metasurface for selective acoustic levitation manipulation. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 1–11 (2021)
Li, M.; Wu, J.H.; Yuan, X.Y.: Metasurface zero-impedance matching mechanism for aerodynamic noise reduction. J. Sound Vib. 536, 117147 (2022)
Zhu, Y.; Assouar, B.: Multifunctional acoustic metasurface based on an array of Helmholtz resonators. Phys. Rev. B 99(17), 174109 (2019)
Gong, K.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, H.; Mo, J.: Tuneable gradient Helmholtz-resonator-based acoustic metasurface for acoustic focusing. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 52(38), 385303 (2019)
Mahesh, K.; Ranjith, S.K.; Mini, R.S.: Inverse design of a Helmholtz resonator-based acoustic metasurface for low-frequency sound absorption using deep neural network. In: Euronoise 2021, pp. 1369–1377 (2021)
Liu, C.R.; Wu, J.H.; Yang, Z.; Ma, F.: Ultra-broadband acoustic absorption of a thin microperforated panel metamaterial with multi-order resonance. Compos. Struct. 246, 112366 (2020)
Yang, M.; Chen, S.; Fu, C.; Sheng, P.: Optimal sound-absorbing structures. Mater. Horiz. 4(4), 673–680 (2017)
Li, Y.; Assouar, B.M.: Acoustic metasurface-based perfect absorber with deep subwavelength thickness. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108(6), 063502 (2016)
Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, G.; Tang, X.; Chen, T.: Low-frequency sound-absorbing metasurface with a channel of nonuniform cross section. J. Appl. Phys. 127(6), 064902 (2020)
Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Z.: A compact low-frequency sound-absorbing metasurface constructed by resonator with embedded spiral neck. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117(22), 221902 (2020)
Liu, Y.; Ren, S.; Sun, W.; Lei, Y.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.: Broadband low-frequency sound absorbing metastructures based on impedance matching coiled-up cavity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 119(10), 101901 (2021)
Ji, J.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Jing, Y.: Low-frequency broadband acoustic metasurface absorbing panels. Front. Mech. Eng. 6, 94 (2020)
Donda, K.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, S.-W.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Assouar, B.: Extreme low-frequency ultrathin acoustic absorbing metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115(17), 173506 (2019)
Zhang, X.; Qu, Z.; Wang, H.: Engineering acoustic metamaterials for sound absorption: from uniform to gradient structures. Iscience 23(5), 101110 (2020)
Stinson, M.R.: The propagation of plane sound waves in narrow and wide circular tubes, and generalization to uniform tubes of arbitrary cross-sectional shape. J. Acousti. Soc. Am. 89(2), 550–558 (1991)
Huang, S.; Zhou, E.; Huang, Z.; Lei, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.: Broadband sound attenuation by metaliner under grazing flow. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118(6), 063504 (2021)
Duan, M.; Yu, C.; Xu, Z.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J.: Acoustic impedance regulation of Helmholtz resonators for perfect sound absorption via roughened embedded necks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117(15), 151904 (2020)
Duan, M.; Yu, C.; He, W.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J.: Perfect sound absorption of Helmholtz resonators with embedded channels in petal shape. J. Appl. Phys. 130(13), 135102 (2021)
Dong, H.-W.; Zhao, S.-D.; Oudich, M.; Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.-S.; Fang, D.: Reflective metasurfaces with multiple elastic mode conversions for broadband underwater sound absorption. Phys. Rev. Appl. 17(4), 044013 (2022)
ISO 10534-2:1998(E), Determination of sound absorption coefficient and impedance in impedance tubes (1998)
ASTM E1050-12, Standard test method for impedance and absorption of acoustical materials using a tube, two microphones and a digital frequency analysis system (2012)
Romero-García, V.; Theocharis, G.; Richoux, O.; Pagneux, V.: Use of complex frequency plane to design broadband and sub-wavelength absorbers. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 139(6), 3395–3403 (2016)
Carbajo, J.; Ramis, J.; Godinho, L.; Amado-Mendes, P.; Alba, J.: A finite element model of perforated panel absorbers including viscothermal effects. Appl. Acoust. 90, 1–8 (2015)
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (K. Mahesh) gratefully acknowledges the research sponsorship under the AICTE Doctoral Fellowship (Government of India) scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahesh, K., Anoop, P.P., Damodaran, P. et al. Ultra-Low-Frequency Broadband Sound Absorption Characteristics of an Acoustic Metasurface with Pie-Sliced Unit Cells. Arab J Sci Eng 48, 12247–12257 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07734-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-07734-8