Abstract
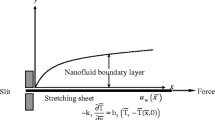
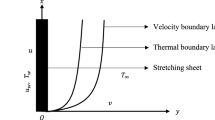
An incompressible three-dimensional hydromagnetic Bödewadt flow of Casson nanofluid above a stationary stretching disk is studied. Water is taken as the base fluid containing nanoparticles namely copper (Cu), copper oxide (CuO) and silver (Ag). Appropriate transformation variables are used to reduce the governing flow model into a system consisting of nonlinear ordinary differential equations. Numerical results are calculated by shooting method. Numerical values of skin-friction coefficient and local-Nusselt number for various quantities are calculated. A statistical method, namely Bayesian approach, is implemented in order to measure the correlation among the physical parameters and variables to determine the intensity of linear association. Multipurpose graphs are also plotted to understand the posterior distribution features along with the strength and direction of relationship. Graphical results are plotted against the obtained physical parameters. Two-dimensional and three-dimensional plots are generated for the visualization of flow analysis. The results indicated that the Nusselt number is enhanced against the increasing Biot number and Prandtl number values for Ag-water nanofluid. The 100% probability of the positive correlation among magnetic parameter and skin-friction coefficient is observed, while 100% probability of the negative correlation is noticed between magnetic parameter and axial velocity at the infinity. The radial velocity field is enhanced against the increased Casson parameter and is reduced by the imposed magnetic field.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, C.Y.: Stretching a surface in a rotating fluid. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 39, 177–185 (1988)
Turkyilmazoglu, M.: Bödewadt flow and heat transfer over a stretching stationary disk. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 90, 246–250 (2015)
Mustafa, M.; Pop, I.; Naganthran, K.; Nazar, R.: Entropy generation analysis for radiative heat transfer to Bödewadt slip flow subject to strong wall suction. Eur. J. Mech.–B/Fluids 72, 179–188 (2018)
Rafiq, T.; Mustafa, M.; Farooq, M.A.: Numerical assessment of Bödewadt flow and heat transfer over a permeable disk with variable fluid properties. Physica A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 534, 122138 (2019)
Muhammad, K.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Ahmad, B.: Numerical study of entropy production minimization in Bödewadt flow with carbon nanotubes. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 550, 123966 (2020)
Abbas, Z.; Rafiq, M.Y.; Hasnain, J.; Nadeem, A.: Thermally developed generalized Bödewadt flow containing nanoparticles over a rotating surface with slip condition. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 122, 105143 (2021)
Rafiq, T.; Mustafa, M.: Bödewadt flow of Bingham fluids over a non-isothermal permeable disk with viscous dissipation effects. Alex. Eng. J. 60, 2857–2864 (2021)
Hayat, T.; Asad, S.; Alsaedi, A.: Flow of Casson fluid with nanoparticles. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 37, 459–470 (2016)
Rehman, K.U.; Qaiser, A.; Malik, M.Y.; Ali, U.: Numerical communication for MHD thermally stratified dual convection flow of Casson fluid yields by stretching cylinder. Chin. J. Phys. 55, 1605–1614 (2017)
Liu, C.; Zheng, L.; Lin, P.; Pan, M.; Liu, F.: Anomalous diffusion in rotating Casson fluid thorough a porous medium. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 528, 121431 (2019)
Aneja, M.; Chandra, A.; Sharma, S.: Natural convection in a partially heated porous cavity to Casson fluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 114, 104555 (2020)
Goud, B.S.; Kumar, P.P.; Malga, B.S.: Effect of heat source on an unsteady MHD free convection flow of Casson fluid past a vertical oscillating plate in porous medium using finite element analysis. Partial Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 2, 100015 (2020)
Kumar, R.; Kumar, R.; Vajravelu, K.; Sheikholeslami, M.: Three dimensional stagnation flow of Casson nanofluid through Darcy-Forchheimer space: a reduction to Blasius/Sakiadis flow. Chin. J. Phys. 68, 874–885 (2020)
Verma, V.K.; Mondal, S.: A brief review of numerical methods for heat and mass transfer of Casson fluids. Partial Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 3, 100034 (2021)
Choi, S.U.S.; Eastman, J.A.: Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles, p. 6699–7105. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition, San Francisco, CA (1995)
Eastman, J.A.; Choi, S.U.S.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; Thompson, L.J.: Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivities of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 718–720 (2001)
Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K.: Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2002–2018 (2007)
Animasaun, I.L.; Yook, S.; Muhammad, T.; Mathew, A.: Dynamics of ternary-hybrid nanofluid subject to magnetic flux density and heat source or sink on a convectively heated surface. Surf. Interfaces 28, 101654 (2022)
Oke, A.S.; Animasaun, I.L.; Mutuku, W.N.; Kimathi, M.; Shah, N.A.; Saleem, S.: Significance of Coriolis force, volume fraction, and heat source/sink on the dynamics of water conveying 47 nm alumina nanoparticles over a uniform surface. Chin. J. Phys. 71, 716–727 (2021)
Sowmya, G.; Gireesha, B.J.; Animasaun, I.L.; Shah, N.A.: Significance of buoyancy and Lorentz forces on water-conveying ion(III) and silver nanoparticles in a rectangular cavity mounted with two heated fins: heat transfer analysis. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 144, 2369–2384 (2021)
Song, Y.; Obideyi, B.D.; Shah, N.A.; Animasaun, I.L.; Mahrous, Y.M.; Chung, J.D.: Significance of haphazard motion and thermal migration of alumina and copper nanoparticles across the dynamics of water and ethylene glycol on a convectively heated surface. Case Stud. Thermal Eng. 26, 101050 (2021)
Kumar, R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Seth, G.S.; Chamkha, A.J.: Transportation of magnetite nanofluid flow and heat transfer over a rotating porous disk with Arrhenius activation energy: Fourth order Noumerov’s method. Chin. J. Phys. 69, 172–185 (2021)
Saranya, S.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M.: Computational study on nanoparticle shape effects of Al2O3 -silicon oil nanofluid flow over a radially stretching rotating disk. Case Stud. Thermal Eng 25, 100943 (2021)
Iqbal, Z.; Azhar, E.; Maraj, E.N.: Performance of nano-powders SiO2 and SiC in the flow of engine oil over a rotating disk influenced by thermal jump conditions. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 565, 125570 (2021)
Nayak, M.K.; Shaw, S.; Khan, M.I.; Pandey, V.S.; Nazeer, M.: Flow and thermal analysis on Darcy-Forchheimer flow of copper-water nanofluid due to a rotating disk: a static and dynamic approach. J. Market. Res. 9, 7387–7408 (2020)
Xu, H.: Modelling unsteady mixed convection of a nanofluid suspended with multiple kinds of nanoparticles between two rotating disks by generalized hybrid model. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 108, 104275 (2019)
Qayyum, S.; Khan, M.I.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.: Comparative investigation of five nanoparticles in flow of viscous fluid with Joule heating and slip due to rotating disk. Physica B 534, 173–183 (2018)
Animasaun, I.L.: 47nm alumina-water nanofluid flow within boundary layer formed on upper horizontal surface of paraboloid of revolution in the presence of quartic autocatalysis chemical reaction. Alex. Eng. J. 55, 2375–2389 (2016)
Shahzad, F.; Haq, R.U.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M.: Water driven Cu nanoparticles between two concentric ducts with oscillatory pressure gradient. J. Mol. Liq. 224, 322–332 (2016)
Venables W.N. and Ripley B.D., Robust Statistics, 1986, 1994, 203–222
Kruschke, J.K.: Bayesian estimation supersedes the T test. J. Exp. Psychol. General 142, 573–588 (2013)
Sharma, K.; Vijay, N.; Makinde, O.D.; Bhardwaj, S.B.; Singh, R.M.; Mabood, F.: Boundary layer flow with forced convective heat transfer and viscous dissipation past a porous rotating disk, Chaos. Solitons Fractals 148, 111055 (2021)
Akolade, M.T.: Thermophysical impact on the squeezing motion of non-Newtonian fluid with quadratic convection velocity slip, and convective surface conditions between parallel disks. Partial Differ. Equ. Appl. Math. 4, 100056 (2021)
Abbasi, A.; Mabood, F.; Farooq, W.; Batool, M.: Bioconvective flow of viscoelastic nanofluid over a convective rotating stretching disk. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 119, 104921 (2020)
Jyothi, K.; Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, M.S.: Influence of magnetic field and thermal radiation on convective flow of SWCNTs-water and MWCNTs-water nanofluid between rotating disk with convective boundary conditions. Powder Technol. 331, 326–337 (2018)
Bååth R., Bayesian First Aid : A package that implements Bayesian alternatives to the classical test functions in R, Proc. UseR 2014, 33, 2014
Plummer M.M., Package rjags, 2019.
Mustafa, M.; Khan, J.A.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.: On Bödewadt flow and heat transfer of nanofluids over a stretching stationary disk. J. Mol. Liq. 211, 119–125 (2015)
Lange, K.L.; Little, R.J.A.; Taylor, J.M.G.: Robust Statistical Modeling Using the t Distribution. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 84, 881–896 (1989)
Hespanhol, L.; Vallio, C.S.; Costa, L.M.; Saragiotto, B.T.: Understanding and interpreting confidence and credible intervals around effect estimates. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 23, 290–301 (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hani, U., Khan, J.A., Rauf, A. et al. Bayesian and Numerical Techniques for Non-Newtonian Bödewadt Nanofluid Flow Above a Stretchable Stationary Disk. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 15931–15945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06773-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06773-x