Abstract
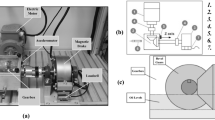
Condition monitoring plays a vital role in predictive maintenance of machinery in today’s world. It is very important to detect the faults in the machinery as early as possible in order to stop the propagation of faults which may lead to heavy damages. The objective of our study is to investigate the vibration analysis of bevel gearbox to detect the faults. An experimental setup was developed to carry out the vibration analysis. Various types of faults were induced in the gearbox. The vibration analysis was carried out for different types of faults with different lubrication levels in the gearbox. MATLAB toolbox was used for signal processing in which Coiflet wavelet was used for denoising the signal. An artificial neural network (ANN) and a deep neural network (DNN) were used to detect the faults in the bevel gearbox automatically. The results were promising in detecting the faults with high accuracy.





























Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- DNN:
-
Deep neural network
- HP:
-
Horsepower
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- GMF:
-
Gear mesh frequency
- MSE:
-
Mean squared error
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- PSNR:
-
Peak signal-to-noise ratio
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- RPM:
-
Revolution per minute
- Hz:
-
Hertz
- kHz:
-
Kilo Hertz
- Max:
-
Maximum
- Min:
-
Minimum
- Eq.:
-
Equation
- Sec.:
-
Section
- ∑:
-
Summation
- + ∞:
-
Positive infinity
- − ∞:
-
Negative infinity
- σ:
-
Standard deviation
References
Barbieri, N.; Barbieri, G.S.A.V.; Martins, B.M.; Barbieri, L.S.A.V.; Lima, K.F.: Analysis of automotive gearbox faults using vibration signal. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 129(1), 148–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.04.028
Hartono, D.; Halim, D.; Widodo, A.; Roberts, G.: Bevel gearbox fault diagnosis using vibration measurements. MATEC Web Confer. 59(06002), 5 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/20165906002
Narendiranath Babu, T.; Himamshu, H.S.; Prabin Kumar, N.; Rama Prabha, D.; Nishant, C.: Journal bearing fault detection based on Daubechies wavelet. Arch. Acoust. 42(3), 401–414 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/aoa-2017-0042
Sharma, S.; Tiwari S.K., Singh S.: Diagnosis of gear tooth fault in a bevel gearbox using discrete wavelet transform and autoregressive modeling. Life Cycle Reliab. Saf. Eng. 8(1), 21–32 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41872-018-0061-9
Huang, W.; Kong, F.; Zhao, X.: Spur bevel gearbox fault diagnosis using wavelet packet transform and rough set theory. J. Intell. Manuf. 29(1), 1257–1271 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1174-x
Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Teng, W.; Jiang, R.: Crack fault detection for a gearbox using discrete wavelet transform and an adaptive resonance theory neural network. J. Mech. Eng. 61(1), 63–73 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5545/sv-jme.2014.1769
Heidari, M.; Homaei, H.; Golestanian, H.; Heidari, A.: Fault diagnosis of gearboxes using wavelet support vector machine, least square support vector machine and wavelet packet transform. J. Vibroeng. 18(2), 860–875 (2016)
Wang, J.; Kong, D.; Dong, S.; Wang, C.: The gearbox fault diagnosis based on wavelet transform. Int. Ind. Inf. Comput. Eng. Confer. 12(1), 1973–1976 (2015). https://doi.org/10.2991/iiicec-15.2015.430
Parey, A.; Singh, A.: Gearbox fault diagnosis using acoustic signals, continuous wavelet transform and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Appl. Acoust. 147(1), 133–140 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2018.10.013
Chen, R.; Huang, X.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.: Intelligent fault diagnosis method of planetary gearboxes based on convolution neural network and discrete wavelet transform. Comput. Ind. 106(3), 48–59 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2018.11.003
Liang, P.; Deng, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, Z.: Intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery via wavelet transform, generative adversarial nets and convolutional neural network. Measurement 159(4), 107768 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107768
Teng, W.; Ding, X.; Cheng, H.; Han, C.; Liu, Y.; Mu, H.: Compound faults diagnosis and analysis for a wind turbine gearbox via a novel vibration model and empirical wavelet transform. Renew. Energy 136(9), 393–402 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.12.094
Xin, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; An, Z.; Wang, J.: Adaptive reinforced empirical Morlet wavelet transform and its application in fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. IEEE Access 7(1), 65150–65162 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917042
Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Jiang, Y.: Overfitting and underfitting analysis for deep learning based end-to-end communication systems. In: 2019 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, pp 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/WCSP.2019.8927876
Han, B.; Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Lan, W.: Comparisons of different deep learning-based methods on fault diagnosis for geared system. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 15(11), 1–17 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1550147719888169
Srivastava, A.; Singh, A.; Sugumaran, V.; Amarnath, M.: Fault diagnosis of helical gear box using vibration signals through random tree and wavelet features. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 9(33), 1–11 (2016). https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i33/101330
Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, J.; Xiao, M.; Sun, G.; He, J.: Fault diagnosis of a rolling bearing using wavelet packet denoising and random forests. IEEE Sens. J. 17(17), 5581–5588 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2017.2726011
Liu, R.; Yang, B.; Zio, E.; Chen, X.: Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: a review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 108(1), 33–47 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.02.016
Rajakarunakarana, S.; Venkumara, P.; Devaraja, D.; Surya P.R.K.: Artificial neural network approach for fault detection in rotary system. Appl. Soft Comput. 8(1), 740–748 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2007.06.002
Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J.: Data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2015-0-02071-8
Baron, P.; Kocisko, M.; Blasko, L.; Szentivanyi, P.: Verification of the operating condition of stationary industrial gearbox through analysis of dynamic signal, measured on the pinion bearing housing. Measurement 96(1), 24–33 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.10.048
Jedlinski, L.; Jonak, J.: A disassembly-free method for evaluation of spiral bevel gear assembly. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 88(1), 399–412 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.11.005
Ramteke, D.S.; Parey, A.; Pachori, R.B.: Automated gear fault detection of micron level wear in bevel gears using variational mode decomposition. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 33(1), 5769–5777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-000-0000-0
Saravanan, N.; Cholairajan, S.; Ramachandran K.I.: Vibration-based fault diagnosis of spur bevel gear box using fuzzy technique. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(1), 3119–3135 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2008.01.010
Saravanan, N.; RAMACHANDRAN K.I.: Incipient gear box fault diagnosis using discrete wavelet transform (DWT) for feature extraction and classification using artificial neural network (ANN). Expert Syst. Appl. 37(1), 4168–4181 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.11.006
Sharma, V.; Parey, A.: Extraction of weak fault transients using variational mode decomposition for fault diagnosis of gearbox under varying speed. Eng. Fail. Anal. 107(1), 104–204 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2019.104204
Singh, A.; Parey, A.: Gearbox fault diagnosis under non-stationary conditions with independent angular re-sampling technique applied to vibration and sound emission signals. Appl. Acoust. 144(1), 11–22 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2017.04.015
Urbanek, J.; Barszcz, T.; Straczkiewicz, M.; Jablonski, A.: Normalization of vibration signals generated under highly varying speed and load with application to signal separation. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 82(1), 13–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.04.017
Ziani, R.; Hammami, A.; Chaari, F.; Felkaoui, A.; Haddar, M.: Gear fault diagnosis under non-stationary operating mode based on EMD, TKEO, and Shock Detector. Compt. Rend. Mecan. 347(1), 663–675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crme.2019.08.003
Zuber, N.; Bajric, R.: Application of artificial neural networks and principal component analysis on vibration signals for automated fault classification of roller element bearings. Maint. Reliab. 18(2), 299–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.17531/ein.2016.2.19
Zhang, D.; Yu, D.: Multi-fault diagnosis of gearbox based on resonance-based signal sparse decomposition and comb filter. Measurement 103(1), 361–369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2017.03.006
Magsi, H., Sodhro, A.H., Chachar, F.A., Abro, S.A.K.: Analysis of signal noise reduction by using filters. In: 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies, pp. 1–6 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOMET.2018.8346412
Merry, R.J.E.: Wavelet theory and applications: a literature study. DCT Reports, Vol. 2005.053. Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven (2005)
Barat, V.; Borodin, Y.; Kuzmin, A.: Intelligent AE signal filtering methods. J. Acoust. Emiss. 28(1), 109–119 (2010)
Kumar, D.; Kaur, J.; Sharma, V.: Analysis of various wavelets transform techniques. Int. J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. Technol. 5(5), 46–51 (2016)
Chourasia, V.S.; Mittra A. K.: Selection of mother wavelet and denoising algorithm for analysis of foetal phonocardiographic signals. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 33(6), 442–448 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/03091900902952618
Monzon, L.; Beylkin, G.; Hereman, W.: Compactly supported wavelets based on almost interpolating and nearly linear phase filters (Coiflets). Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 7(1), 184–210 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/acha.1999.0266
Maind, S.B.; Wankar, P.: Research paper on basic of artificial neural network. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2(1), 96–100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.17762/ijritcc.v2i1.2920
Sazli, M.H.: A brief review of feedforward neural networks. Commun. Fac. Sci. Univer. Ankara Ser. A2–A3 Phys. Sci. Eng. 50(1), 1–7 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1501/commua1-2_0000000026
Siddharth, S.; Simone, S.; Anidhya, A.: Activation functions in neural networks. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. Technol. 4(12), 310–316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.33564/IJEAST.2020.v04i12.054
Martin, F.M.: A scaled conjugate gradient algorithm for fast supervised learning. Neural Netw. 6(4), 525–533 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(05)80056-5
Sharma, P.; Singh, A.: Era of deep neural networks: a review. In: 8th international conference on computing, communication and networking technologies, pp 1–5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCNT.2017.8203938
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, T.N., Ali, P.S.N., Prabha, D.R. et al. Fault Diagnosis in Bevel Gearbox Using Coiflet Wavelet and Fault Classification Based on ANN Including DNN. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 15823–15849 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06767-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-022-06767-9