Abstract
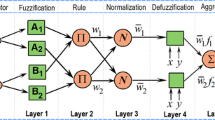
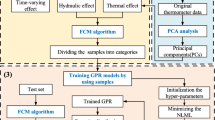
The concrete dam displacement monitoring model is an essential part of dam health. Due to the complicated nonlinear mapping relationship between concrete dam displacement and various environmental quantities, as well as conventional statistical models, neural networks, and machine learning methods fail to consider each input's fuzzy uncertainty factors. Therefore, the model's prediction accuracy is usually affected by selecting impact factors and modeling methods. This paper uses the Copula theory to perform nonlinear correlation tests on displacement influencing factors for the above problems. Furthermore, on this basis, this paper proposes a hybrid model, which uses an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) to establish a regression model and uses the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm to find the optimal parameters of the model. This paper takes a roller-compacted concrete gravity dam as an example. It explores the effect of two clustering methods (subtractive clustering and fuzzy C-means clustering) on the ANFIS model's performance based on the dam's measured data. The results show that the MAPE in the subtractive clustering is about 26% less than the fuzzy C-means clustering in the test stage. Finally, this paper compares the prediction results of the Copula-ANFIS-PSO model with the other five conventional methods. The analysis of the results of six models with four error indicators shows that the error in the Copula-ANFIS-PSO model is about 46% less than other models. It provides a new method for concrete dam displacement monitoring.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, S.H.: Hydraulic Structures. CRC Press, London (2015) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-47331-3
Akpinar, U.; Binici, B.; Arici, Y.: Earthquake stresses and effective damping in concrete gravity dams. Earthq. Struct. 6(3), 251–266 (2014). https://doi.org/10.12989/eas.2014.6.3.251
Mehdi, H.J.; Abolghasem, A.: Application of Froude dynamic similitude in anaerobic baffled reactors to prediction of hydrodynamic characteristics of a prototype reactor using a model reactor. Water Sci. Eng. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2017.03.002
Zheng, D.J.; Li, X.Q.; Yang, M.; Su, H.Z.; Gu, C.S.: Copula entropy and information diffusion theory-based new prediction method for high dam monitoring. Earthq. Struct. 14(2), 143–153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.12989/eas.2018.14.2.143
Shao, C.; Gu, C.; Yang, M.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.: A novel model of dam displacement based on panel data. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 25(1), e20371–e22037 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2037
Mei, Y.T.; Xu, H.L.; Wang, F.; Wu, B.B.; Wan, L.L.: Time-varying prediction model of dam monitoring data based on principal component analysis. Water Power 37(10), 100–103 (2011)
Shen, W.W.; Ren, J.M.: Multiple stepwise regression analysis crack open degree data in gravity dam. Appl. Mech. Mater. 477–478, 888–891 (2013)
Su, H.Z.; Wen, Z.P.; Wu, Z.R.: Study on an intelligent inference engine in early-warning system of dam health. Water Resour. Manage 25(6), 1545–1563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9760-3
Wen, H.Y., Zhou, L., Chen, G.Y., Hu, J.Y., He, M.L.: Research on dam displacement analysis model considering multi-factors. Appl. Mech. Mater. 351, 13l8–1324 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.351-352.1318
Mt, O.L.: Application of fuzzy sets method to identify seepage path through dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 129(7), 546–548 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2003)129:7(546)
Liu, H.C.; Liu, L.; Bian, Q.H.; Lin, Q.L.; Dong, N.; Xu, P.C.: Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy evidential seasoning approach and grey theory. Expert Syst. Appl. 338(4), 4403–4415 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.09.110
Liu, S.F.; Lin, Y.: Grey Systems: Theory and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Sortis, A.D.; Paoliani, P.: Statistical analysis and structural identification in concrete dam monitoring. Eng. Struct. 29(1), 110–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2006.04.022
Mata, J.: Interpretation of concrete dam behaviour with artificial neural network and multiple linear regression models. Eng. Struct. 33(8), 903–910 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2010.12.011
Bayrak, T.: Modelling the relationship between water level and vertical displacements on the Yamula Dam. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci 7(2), 289–297 (2007). https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-7-289-2007
Tabari, M.R.; M. : Prediction of river runoff using fuzzy theory and direct search optimization algorithm coupled model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 41(10), 4039–4051 (2016)
Zhong, D.H.; Shi, M.N.; Cui, B.; Wang, J.J.; Guan, T.: Research progress of the intelligent construction of dams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 50(1), 38–52 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13243/j.cnki.slxb.20181131
Li, Y.; Bao, T.; Gong, J.; Shu, X.; Zhang, K.: The prediction of dam displacement time series using STL, extra-trees, and stacked LSTM neural network. IEEE Access 99, 1–1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2995592
Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, G.: Multi-step wind speed forecasting based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition, long short term memory network and error correction strategy. Energies 10(12), 1–22 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12101822
Bruce, A.; Donoho, D.; Gao, H.Y.: Wavelet analysis for signal processing. IEEE Spectr. 33(10), 26–35 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/6.540087
Li, B.; Yang, J.; Hu, D.X.: Dam monitoring data analysis methods: a literature review. Struct. Control. Health Monit. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.2501
Kao, C.Y.; Loh, C.H.: Monitoring of long-term static displacement data of Fei-Tsui arch dam using artificial neural network-based approaches. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 20(3), 282–303 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1002/stc.492
Rankovi, V.; Grujovi, N.; Divac, D., et al.: Modelling of dam behaviour based on neuro-fuzzy identification. Eng. Struct. 35, 107–113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.11.011
Salaza, F.; Rafael, M.; Miguel, Á.T.; Eugenio, O.: Data-based models for the prediction of dam behaviour: a review and some methodological considerations. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-015-9157-9
Tabari, M.M.R.; Zarif, S.H.R.: Prediction of the intermediate block displacement of the dam crest using artificial neural network and support vector regression models. Soft. Comput. 23, 9629–9645 (2019)
Salleh, M.; Hussain, K.: A review of training methods of ANFIS for applications in business and economics. Int. J. U & E Serv. Sci. Technol. 9(7), 165–172 (2016)
Nourani, V.; Partoviyan, A.: Hybrid denoising-jittering data pre-processing approach to enhance multi-step-ahead rainfall-runoff modeling. Stochast. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 32(2), 545–562 (2018)
Ehsanzadeh, B.; Ahangari, K.: A novel approach in estimation of the soilcrete columns diameter and optimization of the high pressure jet grouting using adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Open J. Geol. 4(8), 386–398 (2014). https://doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2014.48030
Li, X.D.; Zhong, R.B., et al.: Prediction of curtain grouting efficiency based on ANFIS. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 78, 281–309 (2020)
Adedeji, P.A.; Akinlabi, S.; Madushele, N.: Wind turbine power output short-term forecast: a comparative study of data clustering techniques in a PSO-ANFIS model. J. Clean. Prod. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120135
Seyedpoor, S.M.; Salajegheh, J.; Salajegheh, E.: Optimum shape design of arch dams for earthquake loading using a fuzzy inference system and wavelet neural networks. Eng. Optim. 41(5), 473–493 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1080/03052150802596076
Bui, K.T.T.; Bui, D.T.; Zou, J.; Doan, C.; Revhaug, I.: A novel hybrid artificial intelligent approach based on neural fuzzy inference model and particle swarm optimization for horizontal displacement modeling of hydropower dam. Neural Comput. Appl. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-016-2666-0
Sklar, A.: Random variables, joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetik-Praha 9(6), 449–460 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.2009.0502
Nelsen, R.B.: An introduction to copulas. Technometrics (2000). https://doi.org/10.2307/1271100
Jang, J.S.R.: ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 23(3), 665–685 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1109/21.256541
Chahkoutahi, F.; Khashei, M.: A seasonal direct optimal hybrid model of computational intelligence and soft computing techniques for electricity load forecasting. Energy (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.009
Ratrout, N.T.: Subtractive clustering-based K-means technique for determining optimum time-of-day breakpoints. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 25(5), 380–387 (2011)
Khalil, B.; Ali, C.: Clustered ANFIS network using fuzzy c-means, subtractive clustering, and grid partitioning for hourly solar radiation forecasting. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 137, 1–13 (2018)
Nayak, J.; Naik, B.; Behera, H.S.: Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) Clustering Algorithm: A Decade Review from 2000 to 2014. Springer, India (2015)
Zhang, Z.J.: A PSO-ANFIS based hybrid approach for short term PV power prediction in microgrids. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 36, 95–103 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the project Funded by the Key projects of natural science basic research program of Shaanxi province (Grant No. 2018JZ5010), The joint fund project of Natural science basic research program of Shaanxi province and Hanjiang to Weihe River Water Diversion Project Construction Co. Ltd., Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2019JLM-55) and the water science plan project of Shaanxi province (Grant No. 2018SLKJ-5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, F., Yang, J., Ma, C. et al. The Prediction of Concrete Dam Displacement Using Copula-PSO-ANFIS Hybrid Model. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 4335–4350 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06100-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-06100-w