Abstract
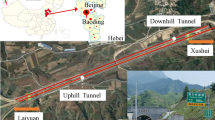
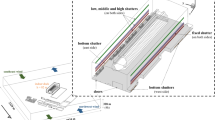
Construction ventilation runs through the entire construction process of large underground caverns and is the key to ensuring construction progress and project safety. For the specific underground cavern group of pumped-storage power plants, a three-dimensional model is constructed, and the CFD method based on fluid mechanics theory is used to simulate the ventilation flow field of the underground cavern group. Through the comparison of the airflow in the main caverns and the air velocity distribution law, Quantitative analysis of the influence of the diameter of the ventilation shaft and the inclination of the shaft on the ventilation flow field shows that when the diameter of the ventilation shaft is 8 m and the inclination of the shaft is 80°, the ventilation effect in the underground cavern group is the best. Applying this scheme to engineering practice and conducting on-site tests, the average relative error of the measuring points is 11.32% by comparing the measured data and the simulation results, which verifies the correctness of the CFD method used. It provides reference value for studying the construction ventilation of underground caverns.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, Y.L.; Yin, Q.; Mo, Z.Y.; Tang, C.Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.G.: Optimization of construction ventilation scheme for large-scale underground cavern group of Xiangjiaba hydropower station based on numerical simulation. J. Sichuan Univ. (Eng. Sci. Edition). 42(04), 1–6 (2010)
Li, M.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Wu, C.: Numerical simulation of air ventilation in super-large underground developments. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 52, 38–43 (2016)
Tong, Y.; Shi, M.H.; Gong, Y.F.; He, J.P.: Full-scale experimental study on smoke flow in natural ventilation road tunnel fires with shafts. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 24(6), 627–633 (2009)
Zhong, M.; Shi, C.; He, L.; Shi, J.; Fu, T.: Full-scale experimental research on fire fume refluence of sloped long and large curved tunnel. SCIENCE CHINA Technol. Sci. 54(S1), 89–94 (2011)
Zhong, M.; Shi, C.; He, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Tian, X.: Smoke development in full-scale sloped long and large curved tunnel fires under natural ventilation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 108, 857–865 (2016)
Sun, J.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.: Full-scale experiment of longitudinal ventilation smoke control system and central smoke exhaust system in city underwater tunnel. Procedia Engineering. 52, 330–335 (2013)
Pflitsch, A.; Bruene, M.; Steiling, B.; Killing-Heinze, M.; Agnew, B.; Irving, M.; Lockhart, J.: Air flow measurements in the underground section of a UK light rail system. Appl. Therm. Eng. 32, 22–30 (2012)
Musto, M.; Rotondo, G.: Numerical comparison of performance between traditional and alternative jet fans in tiled tunnel in emergency ventilation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 42, 52–58 (2014)
Nan, C.; Ma, J.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.: Numerical study on the mean velocity distribution law of air backflow and the effective interaction length of airflow in forced ventilated tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 46, 104–110 (2015)
Lee, S.C.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.: CFD analysis on ventilation characteristics of jet fan with different pitch angle. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 18(3), 812–818 (2014)
Diego, I.; Torno, S.; Toraño, J.; Menéndez, M.; Gent, M.: A practical use of CFD for ventilation of underground works. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 26(1), 189–200 (2011)
Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, H.: Numerical simulation of TBM construction ventilation in a long diversion tunnel. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 26(4), 560–572 (2011)
Sa, Z.; Li, F.; Qin, B.; Pan, X.: Numerical simulation study of dust concentration distribution regularity in cavern stope. Saf. Sci. 50(4), 857–860 (2012)
Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Lin, F.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.: Optimization scheme for construction ventilation in large-scale underground oil storage caverns. Appl. Sci. 8(10), 1652 (2018)
Lin, F.: Construction network ventilation system for underground lpg storage cavern. Civil Eng. J. 4(7), 1521–1541 (2018)
Hua, T.B.; Wang, Y.S.; Yao, Q.; Yang, X.G.; Li, H.T.: Numerical simulation and detection feedback of ventilation in the surge-chamber of a hydropower station. Adv. Eng. Sci. 49(03), 29–36 (2017)
Zhang, H.; Lin, F.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.S.; Chen, S.G.: Establishment of a ventilation network and the shaft ventilation effect in a large underground cavern group. Modern Tunn. Technol. 55(01), 203–209 (2018)
Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y.; Ma, W.; Ma, Y.: Numerical simulation and experimental study on ventilation system for powerhouses of deep underground hydropower stations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 105, 151–158 (2016)
Liu, Z.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, A.L.: Construction ventilation scheme optimization of underground main powerhouse based on CFD. Appl. Mech. Mater. 368–370, 619–623 (2013)
Lateb, M.; Masson, C.; Stathopoulos, T.; Bédard, C.: Comparison of various types of k–ε models for pollutant emissions around a two-building configuration. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 115, 9–21 (2013)
Nan, C.Z.; Zhang, W.H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.L.; Ma, J.M.: Numerical simulations of ventilation to remove noxious gases during excavation of complicated tunnels. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.). 54(08), 993–998 (2014)
Qiao, L.: Optimization of structural setting based on forced ventilation method in tunnel under construction. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 53(06), 1245–1252 (2018)
Zhang, H.; Lin, F.; Sun, J.C.; Zhou, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Lin, F.: CFD analysis of ventilation effect of tunnel construction based on typical wall rough model. China Railway Sci. 37(5), 58–65 (2016)
Shao, S.; Yang, X.G.; Zhou, J.W.: Numerical analysis of different ventilation schemes during the construction process of inclined tunnel groups at the Changheba Hydropower Station, China. Tunn. Underground Space Technol. incorporating Trenc. Technol. Res. 59, 157–169 (2016)
Li, A.; Ren, T.; Yang, C.; Xiong, J.; Tao, P.: Numerical simulation, PIV measurements and analysis of air movement influenced by nozzle jets and heat sources in underground generator hall. Build. Environ. 131, 16–31 (2017)
Tao, P.; Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.: Scaling model study of the air distribution in a powerhouse under different ventilation conditions. Build. Simul. 7(4), 389–400 (2014)
Li, A.; Tao, P.; Bao, X.; Zhao, Y.: PIV measurements of air distribution in a reduced-scale model - ventilation of a busbar corridor in a hydropower station. Int. J. Vent. 12(1), 81–98 (2013)
Shao, S.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.: Numerical analysis of different ventilation schemes during the construction process of inclined tunnel groups at the Changheba Hydropower Station. China. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology. 59, 157–169 (2016)
Wu, Y.; Shi, X.C.; Han, H.; Gao, X.Q.: Numerical simulation for contaminant dispersion induced by human-walking at the gateway of civil protection engineering. J. Saf. Environ. 14(02), 208–213 (2014)
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51905550), the Science and Technology Major Project of Changsha, China (No. kq1703022) and the independent exploration and innovation project of Central South University (No. 2020zzts100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Y., Xiao, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Numerical Simulation of Ventilation Performance for Large-scale Underground Cavern Group Considering Effect of Ventilation Shaft Structure. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 4093–4104 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05914-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05914-y