Abstract
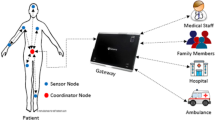
The burgeoning advances in wireless communications, healthcare facilities, and sensor technologies bring a lot of transformation in businesses, the global economy, and convenience to people’s life. To this, Wireless Body Area Networks (WBAN) has transpired as a low-cost, simple and effective solution for Smart E-Healthcare Systems. However, the mobility and open communication channel pose a significant risk of unapproved access, leakage of sensitive E-health data, and various attacks from the adversary, which remarkably impacts the large-scale adoption of the technology. To deal with such issues related to security and privacy in WBANs, many authentication schemes were suggested by the researchers in the past few years claiming to be secure, privacy-preserving, and efficient. Unfortunately, the existing schemes present security and privacy shortcomings which bring about the issues such as threats from adversaries and abuse of services. In this paper, we have propounded a secure and anonymous mutual authentication scheme for WBANs (SAMAKA). In particular, SAMAKA preserves all the desired security features and guards from various security attacks from an adversary. Besides, the formal security proof for SAMAKA is given using BAN Logic and AVISPA. Moreover, SAMAKA is proved to be provably secure in the RoR Model. More importantly, a detailed informal security analysis demonstrates the robustness of SAMAKA against well-known security attacks. Finally, a comparative performance analysis reveals that SAMAKA achieves superior performance and shows promising results while providing more robust security and privacy.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zimmerman, T.G.: Personal area networks: near-field intrabody communication. IBM Syst. J. 35, 609–617 (1996)
Mohammed, K.I.; Zaidan, A.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; Albahri, O.S.; Alsalem, M.A.; Albahri, A.S.; Hashim, M.: Real-time remote-health monitoring systems: a review on patients prioritisation for multiple-chronic diseases, taxonomy analysis, concerns and solution procedure. J. Med. Syst. 43(7), 223 (2019)
Narwal, B.; Mohapatra, A.K.: A Review on authentication protocols in wireless body area networks (WBAN). In: 2018 3rd International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Gurgaon, India (2018)
Sammoud, A.; Chalouf, M.A.; Hamdi, O.; Montavont, N.; Bouallegue, A.: A new biometrics-based key establishment protocol in WBAN: energy efficiency and security robustness analysis. Comput. Secur. 96, 101838 (2020)
Arfaoui, A.; Boudia, O.R.M.; Kribeche, A.; Senouci, S.M.; Hamdi, M.: Context-aware access control and anonymous authentication in WBAN. Comput. Secur. 88, 101496 (2020)
Hussain, M.; Mehmood, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, Z.: A Survey on Authentication Techniques for Wireless Body Area Networks. J. Syst. Architect. 101, 101655 (2019)
Narwal, B.; Mohapatra, A.K.: A survey on security and authentication in wireless body area networks. J. Syst. Architect. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sysarc.2020.101883
Ibrahim, M.H.; Kumari, S.; Das, A.K.; Wazid, M.; Odelu, V.: Secure anonymous mutual authentication for star two-tier wireless body area networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 135, 37–50 (2016)
Gahlot, S.; Reddy, S.R.N.; Kumar, D.: Review of smart health monitoring approaches with survey analysis and proposed framework. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(2), 2116–2127 (2018)
Ingestible biomedical Sensor, Available: https://www.azosensors.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=183. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Intraocular Pressure Sensor, Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5428792/. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Middle Ear MEMS Microphone, Available: https://archive.unews.utah.edu/news_releases/a-middle-ear-microphone/. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Microneedle Drug Delivery System, Available: https://www.purdue.edu/newsroom/research/2010/100831ZiaiePatches.html. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
MEMS Drug Delivery devices, Available: http://web.mit.edu/cprl/www/research.shtml. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Nanoparticle based Cancer Biomarker Sensor, Available: http://web.mit.edu/cprl/www/research.shtml. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Non Invasive Blood Monitor, Available: https://ucsdnews.ucsd.edu/pressrelease/clinical_trial_tests_tattoo_sensor_as_needleless_glucose_monitor_for_diabet. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Pressure Sensor for Damaged Nerves, Available: https://www.imedicalapps.com/2012/07/orpyx-body-sensor-diabetics-prevent-foot-ulcers/. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Smart Contact Lens, Available: https://labiotech.eu/features/contact-lens-glucose-diabetes/. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Wearable Skin sensor, Available: https://www.kth.se/en/aktuellt/nyheter/hudnara-elektronisk-doktor-ar-framtiden-1.382668. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Wearable UV Exposure, Available: https://www.wearable-technologies.com/2018/08/stay-safe-in-the-sun-smart-wearables-to-monitor-uv-radiation/. [Accessed On: 3, April, 2020]
Mwitende, G.; Ye, Y.; Ali, I.; Li, F.: Certificateless authenticated key agreement for blockchain-based WBANs. J. Syst. Archit. 110, 101777 (2020)
Khan, K.; Mehmood, A.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Mashwani, W.K.: A survey on intrusion detection and prevention in wireless ad-hoc networks. J. Syst. Archit. 105, 101701 (2020)
Razaque, A.; Rizvi, S.S.: Secure data aggregation using access control and authentication for wireless sensor networks. Comput. Secur. 70, 532–545 (2017)
Odelu, V.; Saha, S.; Prasath, R.; Sadineni, L.; Conti, M.; Jo, M.: Efficient privacy preserving device authentication in WBANs for industrial e-health applications. Comput. Secur. 83, 300–312 (2019)
Davis, J.J.; Clark, A.J.: Data preprocessing for anomaly based network intrusion detection: A review. Comput. Secur. 30(6–7), 353–375 (2011)
Djelouat, H.; Amira, A.; Bensaali, F.; Boukhennoufa, I.: Secure compressive sensing for ECG monitoring. Comput. Secur. 88, 101649 (2020)
Huang, H.; Zhu, P.; Xiao, F.; Sun, X.; Huang, Q.: A Blockchain-based Scheme for Privacy-Preserving and Secure Sharing of Medical Data. Comput. Secur. 99, 102010 (2020)
Li, X.; Ibrahim, M.H.; Kumari, S.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Gupta, V.; Choo, K.K.R.: Anonymous mutual authentication and key agreement scheme for wearable sensors in wireless body area networks. Comput. Net. 129, 429–443 (2017)
Chen, C.-M.; Xiang, B.; Wu, T.-Y.; Wang, K.-H.: An anonymous mutual authenticated key agreement scheme for wearable sensors in wireless body area networks. Appl. Sci. 8(7), 1074 (2018)
Koya, A.M.: Anonymous hybrid mutual authentication and key agreement scheme for wireless body area network. Comput. Net. 140(2018), 138–151 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.05.006
Gupta, A.; Tripathi, M.; Sharma, A.: A provably secure and efficient anonymous mutual authentication and key agreement protocol for wearable devices in WBAN. Comput. Commun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.06.010
Wu, F.; Xu, L.; Kumari, S.; Li, X.: An improved and anonymous two-factor authentication protocol for healthcare applications with wireless medical sensor networks. Multimedia Syst. 23(2), 195–205 (2017)
Amin, R.; Islam, S.H.; Biswas, G.; Khan, M.K.; Kumar, N.: A robust and anonymous patient monitoring system using wireless medical sensor networks. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 80, 483–495 (2018)
Farash, M.S.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Heydari, M.; Sadough, S.; Mohammad, S.; Kumari, S., et al.: A lightweight anonymous authentication scheme for consumer roaming in ubiquitous networks with provable security. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 30(4), e3019 (2017)
Wu F, Li X, Sangaiah AK, Xu L, Kumari S, Wu L, et al. A lightweight and robust twofactor authentication scheme for personalized healthcare systems using wireless medical sensor networks. Future Generation Computer Systems 2018.
Chen, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.: An improved three-factor user authentication and key agreement scheme for wireless medical sensor networks. IEEE Access 7, 85440–85451 (2019)
Kompara, M.; Islam, S.H.; Hlbl, M.: A robust and efficient mutual authentication and key agreement scheme with untraceability for wbans. Comput. Netw. 148, 196–213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.11.016
Xu, Z.; Xu, C.; Chen, H.; Yang, F.: A lightweight anonymous mutual authentication and key agreement scheme for WBAN. Concurrency and Comput.: Pract. Exp. 31(14), e5295 (2019)
Ostad-Sharif, A.; Nikooghadam, M.; Abbasinezhad-Mood, D.: Design of a lightweight and anonymous authenticatedkey agreement protocol for wireless body area networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 32(12), e3974 (2019)
Alzahrani, B.A.; Irshad, A.; Albeshri, A.; Alsubhi, K.: A Provably Secure and Lightweight Patient-Healthcare Authentication Protocol in Wireless Body Area Networks. Wireless Pers. Commun. 117, 1–23 (2020)
Shuai, M.; Liu, B.; Yu, N.; Xiong, L.; Wang, C.: Efficient and privacy-preserving authentication scheme for wireless body area networks. J. Inform. Security Appl. 52, 102499 (2020)
Narwal, B.; Mohapatra, A.K.: SEEMAKA: secured energy-efficient mutual authentication and key agreement scheme for wireless body area networks. Wireless Pers. Commun. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07304-3
Fotouhi, M.; Bayat, M.; Das, A.K.; Far, H.A.N.; Morteza Pournaghi, S.; Doostari, M.A.: A lightweight and secure two-factor authentication scheme for wireless body area networks in healthcare IoT. Comput. Net. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107333
Hussain SJ, Irfan M, Jhanjhi NZ, Hussain K, & Humayun M (2020). Performance Enhancement in Wireless Body Area Networks with Secure Communication. Wireless Personal Communications, 1–22.
Dolev, D.; Yao, A.: On the security of public key protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 29(2), 198–208 (1983)
Burrows, M.; Abadi, M.; Needham, R.: A logic of authentication. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. 8(1), 18–36 (1990)
A. Armando, D. Basin, Y. Boichutet al., 2005 The avispa tool for the automated validation of internet security protocols and applications,” inInternational Conference on Computer Aided Verification. Springer, Heidelberg.
Kumar, M.; Chand, S.: A lightweight cloud-assisted identity-based anonymous authentication and key agreement protocol for secure wireless body area network. IEEE Syst. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2020.2990749
Jabeen T, Ashraf H, & Ullah A (2021). A survey on healthcare data security in wireless body area networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 1–14.
Almuhaideb, A.M.; Alqudaihi, K.: A lightweight three-factor authentication scheme for WHSN architecture. Sensors 20(23), 6860 (2020)
Hajar MS, Al-Kadri MO, & Kalutarage HK (2021). A Survey on Wireless Body Area Networks: Architecture, Security Challenges and Research Opportunities. Computers & Security, 102211.
Almuhaideb, A.M.; Alqudaihi, K.S.: A lightweight and secure anonymity preserving protocol for WBAN. IEEE Access 8, 178183–178194 (2020)
Mwitende, G.; Ali, I.; Eltayieb, N., et al.: Authenticated key agreement for blockchain-based WBAN. Telecommun. Syst. 74, 347–365 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-020-00662-0
Azees, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Karuppiah, M., et al.: An efficient anonymous authentication and confidentiality preservation schemes for secure communications in wireless body area networks. Wireless Netw (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02560-y
Yang, X., Yi, X., Nepal, S., Khalil, I., Huang, X., & Shen, J. (2021). Efficient and Anonymous Authentication for Healthcare Service with Cloud based WBANs. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing.
Hussain, S.J.; Irfan, M.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Hussain, K.; Humayun, M.: Performance enhancement in wireless body area networks with secure communication. Wireless Pers. Commun. 116(1), 1–22 (2021)
Narwal, B.; Mohapatra, A.K.; Usmani, K.A.: Towards a taxonomy of cyber threats against target applications. J. Stat. Manage. Syst. 22(2), 301–325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/09720510.2019.1580907
Narwal, B.: Security analysis and verification of authenticated mobile payment protocols. In: 2019 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), pp. 202–207 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCON47742.2019.9036151
Dhawan, S.; Shah, S.; Narwal, B.: A walkthrough of blockchain technology and its potential applications. In: Batra, U., Roy, N., Panda, B. (eds.) Data Science and Analytics. REDSET 2019. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol. 1230. Springer, Singapore (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-5830-6_2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narwal, B., Mohapatra, A.K. SAMAKA: Secure and Anonymous Mutual Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for Wireless Body Area Networks. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 9197–9219 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05707-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05707-3