Abstract
Flow past four side-by-side identical square cylinders arranged normal to the flow have been found to show interesting and important flow features which are very difficult to get through experiments. Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is used for numerical simulations of two-dimensional (2D) flow around four side-by-side arranged cylinders. In this study, the Reynolds number (Re) is chosen to be 60, 80, 100, 120 and 140 and the spacing ratio g* (= g/D, where D is the size of cylinder and g is the distance between the cylinders) is set at 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.25, 1.5, 1.75, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5 and 4. Based on the flow characteristics, seven distinct and unique flow regimes are identified for different ranges of Re and g*. Physical features of each flow regime such as wake structures, vortex dynamics, gap flow behavior, time histories of lift coefficients, shedding frequencies and hydrodynamic forces are thoroughly discussed. The Reynolds numbers strongly affect the flow, especially at 0 ≤ g* ≤ 2, in terms of vortex-shedding frequency. A significant secondary frequency is also found other than the primary frequency in the base-bleed and flip-flopping flow regimes. It is observed that for g* ≥ 2.5 primary shedding frequency strongly affects the flow dynamics and the mutual interaction of the wakes behind the cylinders decreases with an increase in the Reynolds number. The Strouhal value is same for the outer and inner cylinders in inphase–antiphase weak interaction flow regime and different for base-bleed and flip-flopping flow regimes. In inphase asynchronous weak interaction flow regime, the Strouhal number is same for all four cylinders.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C 1 :
-
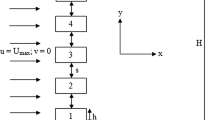
First cylinder from bottom to top
- C 2 :
-
Second cylinder from bottom to top
- C 3 :
-
Third cylinder from bottom to top
- C 4 :
-
Fourth cylinder from bottom to top
- c :
-
Speed of sound
- C D :
-
Drag coefficient
- C L :
-
Lift coefficient
- C Dmean :
-
Mean drag coefficient
- C D1mean :
-
Mean drag coefficient of first cylinder
- C D2mean :
-
Mean drag coefficient of second cylinder
- C D3mean :
-
Mean drag coefficient of third cylinder
- C D4mean :
-
Mean drag coefficient of fourth cylinder
- C Drms :
-
Root mean square of drag coefficient
- C D1rms :
-
First cylinder rms of drag coefficient
- C D2rms :
-
Second cylinder rms of drag coefficient
- C D3rms :
-
Third cylinder rms of drag coefficient
- C D4rms :
-
Fourth cylinder rms of drag coefficient
- C Lrms :
-
Root mean square of lift coefficient
- C L1rms :
-
First cylinder rms of lift coefficient
- C L2rms :
-
Second cylinder rms of lift coefficient
- C L3rms :
-
Third cylinder rms of lift coefficient
- C L4rms :
-
Fourth cylinder rms of lift coefficient
- D :
-
Size of the cylinder
- f i :
-
Particle distribution function
- f (eq) i :
-
Equilibrium distribution function
- f s :
-
Vortex-shedding frequency
- g* :
-
Dimensionless separation ratio
- g :
-
Distance between the cylinders
- L x :
-
Length of the computational domain
- L y :
-
Height of the computational domain
- Ma:
-
Mach number
- Re:
-
Reynolds number
- St:
-
Strouhal number
- St1:
-
First cylinder Strouhal number
- St2:
-
Second cylinder Strouhal number
- St3:
-
Third cylinder Strouhal number
- St4:
-
Fourth cylinder Strouhal number
- t :
-
Dimensionless time
- U ∞ :
-
Uniform inflow velocity
- u :
-
Velocity components
- v :
-
Kinematic viscosity of fluid
- ω i :
-
Weighting coefficients
- x :
-
Position of particles
- ρ :
-
Density of fluid
- τ :
-
Single-relaxation-time parameter
- e i :
-
Velocity particles
References
Zdravkovich, M.M.: Review of flow interference between two circular cylinders normal to a stream. J. Fluids Eng. 99, 618–633 (1977)
Bearman, P.W.; Wadcock, A.J.: The interaction between a pair of circular cylinders normal to a stream. J. Fluids Mech. 61, 499–511 (1973)
Meneghini, J.R.; Saltara, F.: Numerical simulation of flow interference between two circular cylinders in tandem and side-by-side arrangements. J. Fluids Struct. 15, 327–350 (2001)
Kumada, M.; Hiwada, M.; Ito, M.; Mabuchi, I.: Wake interference between three circular cylinders arranged side-by-side normal to a flow. Trans. JSME 50, 1699–1707 (1984). (in Japanese)
Alam, M.M.; Zheng, Q.; Hourigan, K.: The wake and thrust by four side-by-side cylinders at a low Re. J. Fluids Struct. 70, 131–144 (2017)
Williamson, C.H.K.: Evolution of a single wake behind a pair of bluff bodies. J. Fluids Mech. 159, 1–18 (1985)
Kang, S.: Numerical study on laminar flow over three side-by-side cylinders. KSME Int. J. 18, 1869–1879 (2004)
Shengwei, M.; Kang, C.W.; Lim, T.B.A.; Wu, C.H.; Tutty, O.: Wake of two side-by-side square cylinders at low Reynolds numbers. Phys. Fluids 29, 1–23 (2017)
Zheng, Q.; Alam, M.M.: Intrinsic features of flow past three square prisms in side-by-side arrangement. J. Fluids Mech. 826, 996–1033 (2017)
Inoue, O.; Suzuki, Y.: Beat of sound generated by flow past three side-by-side square cylinders. Phys. Fluids 19, 1–4 (2007)
Rahman, H.; Islam, S.U.; Zhou, C.Y.; Kiyani, T.; Saha, S.C.: On the effect of Reynolds number for flow past three side-by-side square cylinders for unequal gap spacings. KSCE J. Civil Eng. 19, 233–247 (2015)
Islam, S.U.; Rahman, H.; Zhou, C.Y.; Saha, S.C.: Comparison of wake structures and force measurements behind three side-by-side cylinders. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 38, 843–858 (2016)
Norberg, C.: Flow around rectangular cylinders: Pressure forces and wake frequencies. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerod 49, 187–196 (1993)
Robichuax, J.; Balachandara, S.; Vanka, S.P.: Three-dimensional Fouquet instability of the wake of square cylinder. Phys. Fluids 11, 560–578 (1999)
Williamson, C.V.H.K.: Vortex dynamics in the cylinder wake. Annurev. Fluid 28, 477–539 (1996)
Kumar, S.R.; Sharma, A.; Agrawal, A.: Simulation of flow around a row of square cylinders. J. Fluids Mech. 606, 369–397 (2008)
He, X.; Luo, L.-S.: Lattice Boltzmann model for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation. J. Stat. Phys. 88, 927–944 (1997)
Dazchi, Y.; Renwei, M.; Luo, L.-S.; Wei, S.: viscous flow computations with the method of lattice Boltzmann equation. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 39, 329–367 (2003)
Mohamad, A.A.: Lattice Boltzmann Method, Fundamentals and Engineering Applications with Computer Codes. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Succi, S.: Lattice Boltzmann Method for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2001)
Saha, A.K.; Biswas, G.; Muralidhar, K.: Three-dimensional study of flow past a square cylinder at low Reynolds numbers. Int. J. Heat Fluid Fl 24, 54–66 (2003)
Guo, Z.; Liu, H.; Luo, L.-S.; Xu, K.: A comparative study of the LBE and GKS methods for 2D near incompressible laminar flows. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 4955–4976 (2008)
Sukop, M.C.; Thorne, D.T.: Lattice Boltzmann Modeling: An Introduction for Geoscientists and Engineers, p. 172. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Shimizu, Y.; Tanida, Y.: Fluid forces acting on cylinders of rectangular cross section. Trans. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. 44, 2699–2706 (1978)
Sharma, A.; Eswaran, V.: Heat and fluid flow across a square cylinder in the two-dimensional laminar flow regime. Numer. Heat. Trans. A Appl. 45, 247–269 (2004)
Sohankar, A.; Norberg, C.; Davidson, L.: Numerical simulation of unsteady low-Reynolds number flow around rectangular cylinders at incidence. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerod. 69–71, 189–201 (1997)
Chatterjee, D.; Biswas, G.; Amiroudine, S.: Numerical simulation of flow past row of square cylinders for various separation ratios. Comput. Fluids 39, 49–59 (2010)
Rosenfeld, M.; Kwak, D.; Vinokur, M.: A fractional step solution method for the unsteady incompressible Navier-stokes equations in generalized coordinate systems. J. Comput. Phys. 94(1), 102–137 (1991)
Lele, S.K.: Compact finite difference scheme with spectral-like resolution. J. Comput. Phys. 103, 16–42 (1992)
Sengupta, T.K.; Sengupta, A.: Analysis and design of a new dispersion relation preserving alternate bi-diagonal compact scheme. J. Sci. Comput. 310, 92–115 (2015)
Levitas, V.I.; Roy, A.M.; Preston, D.L.: Multiple twinning and variant-variant transformations in martensite: Phase-field approach. Phys. Rev. B 88(5), 054113 (2013)
Levitas, V.I.; Roy, A.M.: Multiphase phase field theory for temperature- and stress-induced phase transformations. Phys. Rev. B 91(17), 174109 (2015)
Levitas, V.I.; Roy, A.M.: Multiphase phase field theory for temperature-induced phase transformations: Formulation and application to interfacial phases. Acta Mater. 105, 244–257 (2016)
Atmaca, M.; Cetin, B.; Yılmaz, E.: CFD analysis of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) moving in Flocks. Acta Phys. Polonica A 134, 694–694 (2004)
Atmaca, M.; Girgin, I.; Ezgi, C.: CFD modeling of a diesel evaporator used in fuel cell systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 41(14), 6004–6012 (2016)
Atmaca, M.; Ezgi. C. Three-dimensional CFD modeling of a steam ejector. Energy Source Part A, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1649326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shams-ul-Islam, Ullah, N. & Zhou, C.Y. Fluid Dynamics of Flow Around Side-by-Side Arranged Cylinders. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 5907–5923 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04603-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04603-6