Abstract
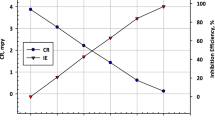
This article investigates the impact of cinnamaldehyde as an eco-friendly inhibitor in mitigating corrosion detriment on mild steel in aerated NaCl (3% w/w) using weight loss and potentiodynamic polarization methods. The results indicate moderate inhibition efficiency of cinnamaldehyde reaching around 70% at an optimum level of 0.5 g/L or 500 ppm by establishing an adsorption film on metal surface. Adsorption of the cinnamaldehyde seemed to adhere to the Langmuir isotherm. The corrosion rate decreased with cinnamaldehyde dose up to the optimum level while increased slowly with the medium temperature. The activation energy (Ea) achieved with cinnamaldehyde was found to be lower than that of without cinnamaldehyde. The polarization curves revealed that the inhibitor performs as a mixed-type inhibitor since it diminishes both anodic and cathodic current densities. The calculated inhibition efficiencies using both corrosion monitoring techniques were found to be in good agreement. Additionally, the mild steel surfaces (inhibited and uninhibited) were examined by using SEM–EDX analysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
14 February 2020
In the original publication of this article the fourth author���s name was incorrectly published.
References
DNV GL – Report No. OAPUS310GKOCH (PP110272)-1, Rev. 3 – www.dnvgl.com Page A-2 December 23, 2015 (http://impact.nace.org/documents/appendix-a.pdf) (n.d.)
Tian, W.; Du, N.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, Q.: Metastable pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 85, 372–379 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.033
Zhong, P.; Sun, M.; Xiao, K.; Hu, Y.B.; Li, X.G.; Dong, C.F.: Effects of solution pH and Cl − on electrochemical behaviour of an Aermet100 ultra-high strength steel in acidic environments. Corros. Sci. 53, 4159–4165 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.08.024
Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; McRae, G.A.; Cu, G.P.: Electrochemical investigation of chloride-induced depassivation of black steel rebar under simulated service conditions. Corros. Sci. 52, 1649–1659 (2010)
Cicolin, D.; Trueba, M.; Trasatti, S.P.: Effect of chloride concentration, pH and dissolved oxygen, on the repassivation of 6082-T6 Al alloy. Electrochim. Acta 124, 27–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.09.003
Zaid, B.; Saidi, D.; Benzaid, A.; Hadji, S.: Effects of pH and chloride concentration on pitting corrosion of AA6061 aluminum alloy. Corros. Sci. 50, 1841–1847 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2008.03.006
Mohammed, M.S.H.S.; Raghavan, R.S.; Knight, G.M.S.; Murugesan, V.: Macrocell corrosion studies of coated rebars. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39, 3535–3543 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1006-x
Cao, C.; Cheung, M.M.S.: Non-uniform rust expansion for chloride-induced pitting corrosion in RC structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 51, 75–81 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.10.042
Raja, V.S.; Padekar, B.S.: Role of chlorides on pitting and hydrogen embrittlement of Mg-Mn wrought alloy. Corros. Sci. 75, 176–183 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.05.030
Abd El-Haleem, S.M.; Abd El-Wanees, S.: Chloride induced pitting corrosion of nickel in alkaline solutions and its inhibition by organic amines. Mater. Chem. Phys. 128, 418–426 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.03.023
Klapper, H.S.; Goellner, J.; Burkert, A.; Heyn, A.: Environmental factors affecting pitting corrosion of type 304 stainless steel investigated by electrochemical noise measurements under potentiostatic control. Corros. Sci. 75, 239–247 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.06.005
Goyal, A.; Pouya, H.S.; Ganjian, E.; Claisse, P.: A review of corrosion and protection of steel in concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 5035–5055 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3303-2
Alhumade, H.; Abdala, A.; Yu, A.; Elkamel, A.; Simon, L.: Corrosion inhibition of copper in sodium chloride solution using polyetherimide/graphene composites. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 94, 896–904 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22439
Duan, Z.; Sun, R.; Liu, R.; Zhu, C.: Accurate thermodynamic model for the calculation of H2S solubility in pure water and brines. Energy Fuels 21, 2056–2065 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1021/ef070040p
Duan, Z.; Sun, R.: An improved model calculating CO2 solubility in pure water and aqueous NaCl solutions from 273 to 533 K and from 0 to 2000 bar. Chem. Geol. 193, 257–271 (2003)
Ating, E.I.; Umoren, S.A.; Udousoro, I.I.; Ebenso, E.E.; Udoh, A.P.: Leaves extract of ananas sativum as green corrosion inhibitor for aluminium in hydrochloric acid solutions. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 3, 61–68 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/17518250903505253
Abdel Hameed, R.S.: Ranitidine drugs as non-toxic corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in hydrochloric acid medium. Port. Electrochim. Acta. 29, 273–285 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.201104273
Ramezanzadeh, M.; Sanaei, Z.; Bahlakeh, G.; Ramezanzadeh, B.: Highly effective inhibition of mild steel corrosion in 3.5% NaCl solution by green Nettle leaves extract and synergistic effect of eco-friendly cerium nitrate additive: experimental, MD simulation and QM investigations. J. Mol. Liq. 256, 67–83 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.021
Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Hoseiny, F.S.; Jafari, Y.: Corrosion inhibition of copper by ephedra sarcocarpa plant extract as green corrosion inhibitor in strong acidic medium. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 6, 341–354 (2014)
Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Hoseiny, F.S.; Jafari, Y.: Green approach to corrosion inhibition of copper by the extract of calligonum comosum in strong acidic medium. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 46, 293–299 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2634-1
Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Ghandchi, M.S.: Santolina chamaecyparissus extract as a natural source inhibitor for 304 stainless steel corrosion in 3.5% NaCl. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 31, 231–237 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.06.028
Lebrini, M.; Robert, F.; Roos, C.: Alkaloids extract from Palicourea guianensis plant as corrosion inhibitor for C38 steel in 1 M hydrochloric acid medium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 6, 847–859 (2011)
El Ouariachi, E.; Bouyanzer, A.; Salghi, R.; Hammouti, B.; Desjobert, J.M.; Costa, J.; Paolini, J.; Majidi, L.: Inhibition of corrosion of mild steel in 1 M HCl by the essential oil or solvent extracts of Ptychotis verticillata. Res. Chem. Intermed. 41, 935–946 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1246-5
Lahhit, N.; Bouyanzer, A.; Desjobert, J.-M.; Hammouti, B.; Salghi, R.; Costa, J.; Jama, C.; Bentiss, F.; Majidi, L.: Fennel (Foeniculum Vulgare) essential oil as green corrosion inhibitor of carbon steel in hydrochloric acid solution. Port. Electrochim. Acta. 29, 127–138 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4152/pea.201102127
Halambek, J.; Berković, K.; Vorkapić-Furač, J.: Laurus nobilis L. oil as green corrosion inhibitor for aluminium and AA5754 aluminium alloy in 3% NaCl solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 137, 788–795 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.09.066
Rieger, K.A.; Schiffman, J.D.: Electrospinning an essential oil: cinnamaldehyde enhances the antimicrobial efficacy of chitosan/poly(ethylene oxide) nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 113, 561–568 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.06.075
Growcock, F.B.; Frenier, W.W.: Kinetics of steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid inhibited with trans-cinnamaldehyde. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 817–823 (1988)
Cabello, G.; Funkhouser, G.P.; Cassidy, J.; Kiser, C.E.; Lane, J.; Cuesta, A.: CO and trans-cinnamaldehyde as corrosion inhibitors of I825, L80-13Cr and N80 alloys in concentrated HCl solutions at high pressure and temperature. Electrochim. Acta 97, 1–9 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.03.011
Keleş, H.; Keleş, M.: Electrochemical investigation of a schiff base synthesized by cinnamaldehyde as corrosion inhibitor on mild steel in acidic medium. Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 193–209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0955-5
Negm, A.N.; Yousef, A.M.; Tawfik, M.S.: Impact of synthesized and natural compounds in corrosion inhibition of carbon steel and aluminium in acidic media. Recent Patents Corros. Sci. 3, 58–68 (2013)
Solmaz, R.: Investigation of the inhibition effect of 5-((E)-4-phenylbuta-1,3-dienylideneamino)-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol Schiff base on mild steel corrosion in hydrochloric acid. Corros. Sci. 52, 3321–3330 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.06.001
Jafferji, H.; Sharifi, N.P.; Schneider, E.M.; Sakulic, A.R.: Investigation of incorporating cinnamaldehyde into Lightweight Aggregate for potential corrosion reduction in cementitious materials. Cement Concr. Compos. 87, 1–9 (2018)
Jafferji, H.; Sakulich, A.R.; Schiffman, J.D.: Preliminary study on mitigating steel reinforcement corrosion with bioactive agent. Cement Concr. Compos. 69, 9–17 (2016)
Hossain, S.M.Z.; Al-Shater, A.; Kareem, S.A.R.: Cinnamaldehyde as a green inhibitor in mitigating AISI 1015 carbon steel corrosion in HCl. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 5489–5499 (2019)
Rekkab, S.; Zarrok, H.; Salghi, R.; Zarrouk, A.; Bazzi, L.; Hammouti, B.; Kabouche, Z.; Touzani, R.; Zougagh, M.: Green corrosion inhibitor from essential oil of eucalyptus globulus (Myrtaceae) for C38 steel in sulfuric acid solution. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 3, 613–627 (2012)
Emregül, K.C.; Abdülkadir Akay, A.; Atakol, O.: The corrosion inhibition of steel with Schiff base compounds in 2 M HCl. Mater. Chem. Phys. 93, 325–329 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.03.008
Messaadia, L.; Id El mouden, O.; Anejjar, A.; Messali, M.; Salghi, R.; Benali, O.; Cherkaoui, O.; Lallam, A.: Adsorption and corrosion inhibition of new synthesized pyridazinium-based ionic liquid on carbon steel in 05 M H2SO4. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 6, 598–606 (2015)
De Souza, F.S.; Gonçalves, R.S.; Spinelli, A.: Assessment of caffeine adsorption onto mild steel surface as an eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 25, 81–90 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20130270
Cristofari, G.; Znini, M.; Majidi, L.; Bouyanzer, A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Paolini, J.; Hammouti, B.; Costa, J.: Chemical composition and anti-corrosive activity of Pulicaria mauritanica essential oil against the corrosion of mild steel in 0.5 M H 2SO 4. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 6, 6699–6717 (2011)
Keleş, H.; Keleş, M.: Electrochemical investigation of a schiff base synthesized by cinnamaldehyde as corrosion inhibitor on mild steel in acidic medium. Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 193–209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-012-0955-5
Jafferji, H.; Sakulich, A.R.; Schiffman, J.D.: Preliminary study on mitigating steel reinforcement corrosion with bioactive agent. Cem. Concr. Compos. 69, 9–17 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.02.011
Zucchi, F.; Trabanelli, G.; Brunoro, G.: Iron corrosion inhibition in hot 4 M HCl solution by t-cinnamaldehyde and its structure-related compounds. Corros. Sci. 36, 1683–1690 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-938X(94)90123-6
Manssouri, M.; El Ouadi, Y.; Znini, M.; Costa, J.; Bouyanzer, A.; Desjobert, J.M.; Majidi, L.: Adsorption proprieties and inhibition of mild steel corrosion in HCl solution by the essential oil from fruit of Moroccan Ammodaucus leucotrichus. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 6, 631–646 (2015)
Reaction Rates. Retrieved from Tutorvista.com: http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/physical-chemistry/reaction-rates.html#activation-energy (n.d.)
Awad, M.I.: Eco friendly corrosion inhibitors: inhibitive action of quinine for corrosion of low carbon steel in 1 M HCl. J. Appl. Electrochem. 36, 1163–1168 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-006-9204-1
Guan, N.M.; Xueming, L.; Fei, L.: Synergistic inhibition between o-phenanthroline and chloride ion on cold rolled steel corrosion in phosphoric acid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 86, 59–68 (2004)
Noor, E.A.; Al-Moubaraki, A.H.: Thermodynamic study of metal corrosion and inhibitor adsorption processes in mild steel/1-methyl-4[4′(-X)-styryl pyridinium iodides/hydrochloric acid systems. Mater. Chem. Phys. 110, 145–154 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.01.028
Sankarapapavinasam, S.; Ahmed, M.F.: Benzenethiols as inhibitors for the corrosion of copper. J. Appl. Electrochem. 22, 390–395 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01092694
Andreani, S.; Znini, M.; Paolini, J.; Majidi, L.; Hammouti, B.; Costa, J.; Muselli, A.: Study of corrosion inhibition for mild steel in hydrochloric acid solution by Limbarda crithmoides (L.) essential oil of Corsica. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 7, 187–195 (2016)
Eduok, U.M.; Khaled, M.: Corrosion inhibition for low-carbon steel in 1 MH 2 SO 4 solution by phenytoin: evaluation of the inhibition potency of another “anticorrosive drug”. Res. Chem. Intermed. 41(9), 6309–6324 (2015)
Umoren, S.A.; Eduok, U.M.; Israel, A.U.; Obot, I.B.; Solomon, M.M.: Coconut coir dust extract: a novel eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for Al in HCl solutions. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 5, 303–313 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2011.625980
Singh, A.; Ansari, K.R.; Quraishi, M.A.; Lgaz, H.: Effect of electron donating functional groups on corrosion inhibition of J55 steel in a sweet corrosive environment: experimental, density functional theory, and molecular dynamic simulation. Materials (Basel). 12, (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010017
Cheng, S.; Chen, S.; Liu, T.; Chang, X.; Yin, Y.: Carboxymenthylchitosan as an ecofriendly inhibitor for mild steel in 1 M HCl. Mater. Lett. 61, 3276–3280 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.11.102
Acknowledgement
The author(s) would like to acknowledge the support provided by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals (KFUPM) for funding this work through project No. DF181018. The authors also would like to gratefully acknowledge the support provided by Deanship of Scientific Research, University of Bahrain, Kingdom of Bahrain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakir Hossain, S.M., Kareem, S.A., Alshater, A.F. et al. Effects of Cinnamaldehyde as an Eco-Friendly Corrosion Inhibitor on Mild Steel in Aerated NaCl Solutions. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 229–239 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04236-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04236-4