Abstract
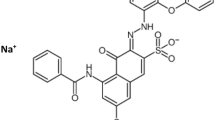
This study examines the decolourization of Reactive Black 5 (RB5) dye in aqueous solution and textile wastewater treatment by sono-electro-chemical method to obtain synergistic effect. The electrolytic cell equipped with stainless steel anode and graphite cathode was used for this study. Sodium persulphate (NaS) and manganese sulphate (MnS) are used as electrolytes to facilitate the process. The effects of various operational parameters such as initial solution pH, NaS concentration, MnS concentration, ultrasound power and voltage on the sono-electro-chemical treatment were investigated. The results have demonstrated that the enhanced colour removal efficiency was achieved at pH 2 for electro-chemical process; however, better efficiency was reached by synergistic effect of sono-electro-chemical treatment in the presence of less amount of electrolytes with the short reaction time than the individual sono-chemical and electro-chemical process. The maximum decolourization achieved was 89% under the condition: 100 ppm RB5, 50 ppm NaS, 75 ppm MnS, solution pH and 44 W ultrasound power, 20 V. When the similar methodology was adopted to real textile effluent, 90% of TOC removal was observed and it indicates the employment of studied process for industrial wastewater treatment purposes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robinson, T.; McMullan, G.; Marchant, R.; Nigam, P.: Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 77, 247–255 (2001)
Wang, X.J.; Gu, X.Y.; Lin, D.X.; Dong, F.; Wan, X.F.: Treatment of acid rose dye containing waste-water by ozonizing-biological aerated filter. Dyes Pigments 74(3), 736–740 (2007)
Baban, A.; Yediler, A.; Ciliz, N.K.: Integrated water management and CP implementation for wool and textile blend processes. Clean 38(1), 84–90 (2010)
Pinheiro, H.M.; Touraud, E.; Thomas, O.: Aromatic amines from azo dye reduction: status review with emphasis on direct UV spectrophotometric detection in textile industry wastewaters. Dyes Pigments 61, 121–139 (2004)
Börnick, H.; Schmidt, T.C.: Amines. In: Reemtsma, T., Jekel, M. (eds.) Organic Pollutants in the Water Cycle: Properties, Occurrence, Analysis and Environmental Relevance of Polar Compounds, pp. 181–208. Wiley, Weinheim (2006). ISBN 978-3-527-31297-9
Puvaneswari, N.; Muthukrishnan, J.; Gunasekaran, P.: Toxicity assessment and microbial degradation of azo dyes. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 144, 618–626 (2006)
Forgacs, E.; Cserhati, T.; Oros, G.: Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ. Int. 30, 953–971 (2004)
Demir, H.; Deveci, M.A.: Comparison of ultrasound and conventional technique for removal of methyl orange by luffa cylindrica fibers. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 43, 5881–5889 (2018)
Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B.: A review of imperative technologies for wastewater treatment I: oxidation technologies at ambient conditions. Adv. Environ. Res. 8, 501–551 (2004)
Saravanan, S.; Sivasankar, T.: Ultrasound assisted Fenton’s treatment of Reactive Black 5 dye: effect of system parameters, kinetics and mechanism. Desalin. Water Treat. 56, 492–501 (2015)
Eren, Z.; Acar, F.N.: Effect of Fenton’s reagent on the degradability of CI Reactive Yellow 15. Color. Technol. 122(5), 259–263 (2006)
López-Grimau, V.; Gutiérrez, M.C.: Decolourisation of simulated reactive dyebath effluents by electro-chemical oxidation assisted by UV light. Chemosphere 62, 106–112 (2006)
Kariyajjanavar, P.; Jogttappa, N.; Nayaka, Y.A.: Studies on degradation of reactive textile dyes solution by electro-chemical Method. J. Hazard. Mater. 190, 952–961 (2011)
Riera-Torres, M.; Gutiérrez, M.-C.: Colour removal of three reactive dyes by UV light exposure after electrochemical treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 156, 114–120 (2010)
Wang, K.-S.; Chen, H.-Y.; Huang, L.-C.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, S.-H.: Degradation of Reactive Black 5 using combined electro-chemical degradation-solar light/immobilized TiO2 film process and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere 72, 299–305 (2008)
Suslick, K.S.; Bang, J.H.: Applications of ultrasound to the synthesis of nano-structured materials. Adv. Mater. 22, 1039–1959 (2010)
Mishra, S.K.; Deymier, P.A.; Muralidharan, K.; Frantziskonis, G.; Pannala, S.; Simunovic, S.: Modeling the coupling of reaction kinetics and hydrodynamics in a collapsing cavity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 258–265 (2010)
Mishra, S.K.; De, A.: Coupling of reaction and hydrodynamics around a reacting block modeled by Lattice Boltzmann Method (LBM). Comput. Fluids 71, 91–97 (2013)
Keswani, M.; Raghavan, S.; Deymier, P.: Electrochemical investigations of stable cavitation from bubbles generated during reduction of water. Ultrason. Sonochem. 21, 1893–1899 (2014)
De, A.; Mishra, S.K.: Simulation of chemical reactions induced by droplet in a phase separating media using Lattice Boltzmann-kinetic Monte-Carlo framework. Comput. Fluids 89, 133–142 (2014)
Martín de Vidales, M.J.; Millán, M.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.: Irradiated-assisted electrochemical processes for the removal of persistent pollutants from real wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 175, 428–434 (2017)
Rivera, M.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á.: Development of an electro-chemical cell for the removal of Reactive Black 5. Desalination 274, 39–43 (2011)
Nazari, R.; Rajić, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, W.; Alshawabkeh, A.N.: Degradation of 4-chlorophenol in aqueous solution by sono-electro-Fenton process. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 13, 9214–9230 (2018)
Steter, J.R.; Barros, W.R.P.; Lanza, M.R.V.; Motheo, A.J.: Electro-chemical and sonoelectro-chemical processes applied to amaranth dye degradation. Chemosphere 117, 200–207 (2014)
Martínez, S.S.; Uribe, E.V.: Enhanced sonochemical degradation of azure B dye by the electroFenton process. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19, 174–178 (2012)
Thokchom, B.; Pandit, A.B.; Qiu, P.; Park, B.; Choi, J.; Khim, J.: A review on sonoelectrochemical technology as an upcoming alternative for pollutant degradation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 27, 210–234 (2015)
Poza-Nogueiras, V.; Rosales, E.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á.: Current advances and trends in electro-Fenton process using heterogeneous catalysts—a review. Chemosphere 201, 399–416 (2018)
Cherepanov, P.V.; Ashokkumar, M.; Andreeva, D.V.: Ultrasound assisted formation of Al–Ni electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. Ultrason. Sonochem. 23, 142–147 (2015)
Thokchom, B.; Qiu, P.; Cui, M.; Park, B.; Pandit, A.B.; Khim, J.: Magnetic Pd@Fe3O4 composite nanostructure as recoverable catalyst for sonoelectrohybrid degradation of Ibuprofen. Ultrason. Sonochem. 34, 262–272 (2017)
American Public Health Association (APHA): Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington (1998)
Sivasankar, T.; Moholkar, V.S.: Physical insights into the sonochemical degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutants with cavitation bubble dynamics. Ultrason. Sonochem. 16(6), 769–781 (2009)
Bechtold, T.; Mader, C.; Mader, J.: Cathodic decolourization of textile dyebaths: tests with full scale plant. J. Appl. Electrochem. 32, 943–950 (2002)
Dinesh, G.K.; Anandan, S.; Sivasankar, T.: Sonophotocatalytic treatment of Bismarck Brown G dye and real textile effluent using synthesized novel Fe(0) doped TiO2 catalyst. RSC Adv. 5, 10440–10451 (2015)
Ramachandran, R.; Saraswathi, R.: Sonoelectrochemical studies on mass transport in some standard redox systems. Russ. J. Electrochem. 47, 15–25 (2011)
Babuponnusami, A.; Muthukumar, K.: Advanced oxidation of phenol: a comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem. Eng. J. 183, 1–9 (2012)
Vajnhandl, S.; Marechal, A.M.L.: Case study of the sonochemical decolourization of textile azo dye Reactive Black 5. J. Hazard. Mater. 141, 329–335 (2007)
Song, P.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.: Investigation of influencing factors and mechanism of antimony and arsenic removal by electrocoagulation using Fe − Al electrodes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 53, 12911–12919 (2014)
Georgiou, D.; Melidis, P.; Aivasidis, A.; Gimouhopoulos, K.: Degradation of azo-reactive dyes by ultraviolet radiation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. Dyes Pigments 52, 69–78 (2002)
Kurukutla, A.B.; Satishkumar, P.; Anandan, S.; Sivasankar, T.: Intensification of sonochemical degradation of rhodamine B using oxidants, hydrogen peroxide/peroxydisulphate/peroxymonosulphate with Fe2+ ion: proposed pathway and kinetics. Environ. Eng. Sci. 32(2), 129–140 (2015)
Sauer, T.; Neto, G.C.; José, H.J.; Moreira, R.F.P.M.: Kinetics of photocatalytic degradation of reactive dyes in a TiO2 slurry reactor. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 149, 147–154 (2002)
Tallec, A.: Electrochimie Organique: Synthéses et Mecanismes, pp. 95–97. Ed Masson, Paris (1985)
Lane, B.S.; Vogt, M.; DeRose, V.J.; Burgess, K.J.: Manganese-catalyzed epoxidations of alkenes in bicarbonate solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124, 11946–11954 (2002)
Reddy, B.R.; Sivasankar, T.; Sivakumar, M.; Moholkar, V.S.: Physical facets of ultrasonic cavitational synthesis of zinc ferrite particles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 17, 416–426 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johin, J., Nidheesh, P.V. & Sivasankar, T. Sono-electro-chemical Treatment of Reactive Black 5 Dye and Real Textile Effluent Using MnSO4/Na2S2O8 Electrolytes. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 9987–9996 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04159-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04159-0