Abstract
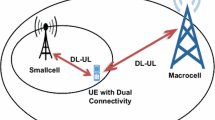
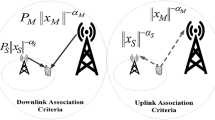
Cell association policies in present-day heterogeneous networks (HetNets) cannot promise fairness and high capacity to all network users. To optimize this cell association, concept of downlink (DL)–uplink (UL) decoupling (DUDe) has been introduced where uplink and downlink channels can be associated with two different base stations (BSs) instead of existing policy of being associated with same BS. For this decoupled access, a number of theoretical uplink or downlink analysis frameworks have been proposed. However, these frameworks do not fully take into account the practical realization aspects. In these preceding works, all network users are assumed to employ decoupled access despite the fact that it is not preferred by all users. These models also ignore noise to get simplified solutions which can result into practical inaccuracies. In this paper, we propose a realistic user association technique in which both coupled access and decoupled access are permissible to users, depending upon their location and benefits. Therefore, the goal of the present paper is to present K-tier uplink analysis framework for network devices that prefer decoupled access. Simple closed-form solutions without ignoring noise are presented, which relate user performance to number of HetNet tiers, base-station densities and power levels. Moreover, derived distributions are also employed to compare performance of DUDe case with existing process of coupled access. Finally, decoupling impacts on K-tier network design have been presented. Based on conducted analysis, it can be concluded that decoupling is beneficial and can be easily realized in 5G K-tier HetNets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boccardi, F.; Heath, R.W.; Lozano, A.; Marzetta, T.L.; Popovski, P.: Five disruptive technology directions for 5G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 52(2), 74–80 (2014)
Jo, H.S.; Sang, Y.J.; Xia, P.; Andrews, J.G.: Heterogeneous cellular networks with flexible cell association: a comprehensive downlink SINR analysis. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 11(10), 3484–3495 (2012)
Gavrilovska, L.; Rakovic, V.; Atanasovski, V.: Visions towards 5G: technical requirements and potential enablers. Wireless Pers. Commun. 87(3), 731–757 (2016)
Andrews, J.G.; Ganti, R.K.; Haenggi, M.; Jindal, N.; Weber, S.: A primer on spatial modeling and analysis in wireless networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48(11), 156–163 (2010)
Ghosh, A.; Mangalvedhe, N.; Ratasuk, R.; Mondal, B.; Cudak, M.; Visotsky, E.; Thomas, T.; Andrews, J.G.; Xia, P.; Jo, H.S.; et al.: Heterogeneous cellular networks: from theory to practice. IEEE Commun. Mag. 50(6), 54–64 (2012)
Damnjanovic, A.; Montojo, J.; Wei, Y.; Ji, T.; Luo, T.V.M.Y.T.; Song, O.; Malladi, D.: A survey on 3GPP heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 18(3), 10–21 (2011)
Rost, P.; Maeder, A.; Pérez-Costa, X.: Asymmetric uplink–downlink assignment for energy-efficient mobile communication systems. In: IEEE 75th Vehicular Technology Conference, pp. 1–5 (2012)
Document TR 36.842, 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), Study on Small cell Enhancements for E-UTRA and E-UTRAN; Higher Layer Aspects (2013). http://www.3gpp.org/dynareport/36842.htm. Accessed 20 Jan 2017
Boccardi, F.; Andrews, J.G.; Elshaer, H.; Dohler, M.; Parkvall, S.; Popovski, P.; Singh, S.: Why to decouple the uplink and downlink in cellular networks and how to do it. IEEE Commun. Mag. 54(3), 110–117 (2016)
Singh, S.; Zhang, X.; Andrews, J.G.: Joint rate and SINR coverage analysis for decoupled uplink–downlink biased cell associations in HetNets. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(10), 5360–5373 (2015)
Elshaer, H.; Boccardi, F.; Dohler, M.; Irmer, R.: Downlink and uplink decoupling: a disruptive architectural design for 5G networks. In: IEEE Global Communications Conference, pp. 1798–1803 (2014)
Smiljkovikj, K.; Popovski, P.; Gavrilovska, L.: Analysis of the decoupled access for downlink and uplink in wireless heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 4(2), 173–176 (2015)
Smiljkovikj, K.; Gavrilovska, L.; Popovski, P.: Efficiency analysis of decoupled downlink and uplink access in heterogeneous networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.1652 (2014)
Chiu, S.N.; Stoyan, D.; Kendall, W.S.; Mecke, J.: Stochastic geometry and its applications. John Wiley & Sons (2013)
Smiljkovikj, K.; Elshaer, H.; Popovski, P.; Boccardi, F.; Dohler, M.; Gavrilovska, L.; Irmer, R.: Capacity analysis of decoupled downlink and uplink access in 5G heterogeneous systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.7270 (2014)
ElBamby, M.S.; Bennis, M.; Latva-aho, M.: UL/DL decoupled user association in dynamic TDD small cell networks. In: International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems, pp. 456–460. IEEE (2015)
Sekander, S.; Tabassum, H.; Hossain, E.: Matching with externalities for decoupled uplink–downlink user association in full-duplex small cell networks. In: IEEE International WIE Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, pp. 411–414. IEEE (2015)
Sui, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.: Energy efficiency analysis of heterogeneous cellular networks with downlink and uplink decoupling. In: IEEE GLOBECOM, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2015)
Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Elkashlan, M.; Wong, K.; Schober, R.; Hanzo, L.: User association in 5G networks: a survey and an outlook. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 18(2), 1018–1044 (2016)
Bao, W.; Liang, B.: Stochastic analysis of uplink interference in two-tier femtocell networks: open versus closed access. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(11), 6200–6215 (2015)
Lin, Y.; Bao, W.; Yu, W.; Liang, B.: Optimizing user association and spectrum allocation in HetNets: a utility perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 33(6), 1025–1039 (2015)
Singh, S.; Zhang, X.; Andrews, J.G.: Uplink rate distribution in heterogeneous cellular networks with power control and load balancing. In: 2015 ICCW, pp. 1275–1280 (2015)
Novlan, T.D.; Dhillon, H.S.; Andrews, J.G.: Analytical modeling of uplink cellular networks. Trans. Wirel. Commun. 12(6), 2669–2679 (2013)
Baccelli, F.; Blaszczyszyn, B.: Stochastic geometry and wireless networks. NOW Found. Trends Netw. 4, 1–312 (2010)
Dhillon, H.S.; Andrews, J.G.: Downlink rate distribution in heterogeneous cellular networks under generalized cell selection. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 3(1), 42–45 (2014)
Document TR 136.213, 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), LTE: Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access E-UTRA; Physical Layer Procedures (2009). http://www.3gpp.org/dynareport/136213.htm. Accessed 29 July 2016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sial, M.N., Ahmed, J. A Realistic Uplink–Downlink Coupled and Decoupled User Association Technique for K-tier 5G HetNets. Arab J Sci Eng 44, 2185–2204 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3339-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3339-3