Abstract
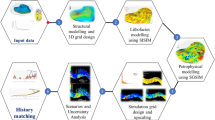
Sequential indicator simulation algorithm is one of the popular stochastic simulation algorithms for reservoir geomodelling. It has been used to model delineated lithofacies and depofacies units within the OPO field, western Niger Delta. This simulation algorithm was chosen because of its ability to honour the well logs as local conditioning data using the global histogram, areal and vertical geological trends of the data, as well as the patterns of correlation. Three lithofacies were identified and modelled, namely sand, shaly sand and shale units. Vertical succession of the depositional facies within the field reveals five major facies which are basal shelf shale facies, heterolithic (sand–shale) facies, lower shoreface sand facies, upper shoreface sand facies and shoreface channel systems. The general environment of deposition is interpreted to be shoreline–shelf systems where the shoreface channel units, upper shoreface sand, lower shaly sand and heterolithic units constitute the parallic reservoir sequences, while the shale units within the shoreface and coastal environments act as potential source rocks and caprocks for hydrocarbon accumulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 April 2018
The original version of this article unfortunately contained mistakes.
20 April 2018
The original version of this article unfortunately contained mistakes.
20 April 2018
The original version of this article unfortunately contained mistakes.
References
Edigbue, P.; Olowookere, M.T.; Adetokunbo, P.; Jegede, E.: Integration of sequence stratigraphy and geostatistics in 3-D reservoir modelling: a case study of Otumara field, onahore Niger Delta. Arab. J. Geosci. 8(10), 8615–8631 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-1821-8
Mikes, D.; Geel, C.: Standard facies models to incorporate all heterogeneity levels in a reservoir model. Marin Pet. Geol. 23, 943–959 (2006)
Cao, R.; Zee, M.Y.; Gomez, E.: Geostatistical applications in petroleum reservoir modelling. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 114, 625–630 (2014)
Cosentino, R.L. (ed.): Integrated Reservoir Studies. Editions Technip, Paris (2001)
Matheron, G. (ed.): Éléments pour une théorie des milieu poreux. Masson, Paris (1967)
Stoyan, D.S.; Kendal, W.S.; Mecke, J. (eds.): Stochastic Geometry and Its Application, 2nd edn. Wiley, Chichester (1995)
Deutsch, C.V.; Journel, A.G. (eds.): GSLIB. Geostatistics Software Library and User’s Guide, New York (1998)
Liu, Y.; Harding, A.; Abriel, W.; Strebelle, S.: Multiple-point simulation integrating wells, three-dimensional seismic data, and geology. AAPG Bull. 88(7), 905–921 (2004)
Hu, L.Y.; Le Ravalec-Dupin, M.: Elements for an integrated geostatistical modelling of heterogeneous reservoirs. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 59(2), 141–155 (2004)
Zhang, T.: Incorporating geological conceptual models and interpretations into reservoir modelling using multiple-point geostatistics. Earth Sci. Front. 15(1), 26–35 (2008)
Al-Mudhafar, W.A.: Geostatistical lithofacies modelling of the upper sandstone member/Zubair formation in south Rumaila oil field, Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 10, 153–167 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2951-y
Mohammadmoradi, P.: Facies and fracture network modelling by a novel image processing based method. Geomaterials 3, 156–164 (2013)
Jacod, J.; Joathon, O.: Use of random genetic models in the study of sedimentary processes. Math. Geol. 3, 265–279 (1971)
Hu, L.Y.; Joseph, P.; Dubrule, O.: Random genetic simulation of the internal geometry of deltaic sand bodies. SPE Formation Eval. 9(4), 245–250 (1994)
Lopez, S.; Galli, A.; Cojan, I.: Fluvial meandering channelized reservoirs: a stochastic and process-based approach. In: Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Association of Mathematical Geology, 6–12 September, Cancun Mexico (2001)
Guardiano, F.; Srivastava, M.: Multivariate geostatistics: beyond bivariate moments. In: Soares, A. (ed.) Geostatistics Troia’92, vol. 1, pp. 133–144 (1993)
Strebelle, S.; Journel, A.: Sequential simulation drawing structures from training images. In: Kleingeld and Krige (eds.) Geostatistics 2000 Cape Town, vol. 1, pp. 381–392 (2000)
Patrick, D.D.; Gerilyn, S.S.; John, P.C.: Outcrop-base reservoir characterization: a composite phylloid-algal mound, western Orogrande Basin (New Mexico). AAPG Bull 86(5), 779–795 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1306/61EEDB98-173E-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Damuth, J.E.: Neogene gravity tectonics and depositional processes on the deep Niger Delta Continental margin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 11(3), 320–346 (1994)
Bilotti, F.; Shaw, J.H.: Deep-water Niger Delta fold and thrust belt modeled as a critical-taper wedge; the influence of elevated baal fluid pressure on structural styles. AAPG Bull. 89(11), 1475–1491 (2005)
Hosper, J.: The geology of the Niger Delta area. In: The Geology of the East Atlantic Continental Margin, Great Britain. Inst. Geological Sci. Report, vol. 70(16), pp. 121–147 (1971)
Merki, P.J.: Structural geology of the Cenozoic Niger Delta. In: 1st Conference on African Geology Proceedings. Ibadan University Press, Nigeria (1972)
Thomas, D.: Niger Delta oil production, reserves, field sizes assessed. Oil Gas J. 93(46), 101–104 (1995)
Lawrence, S.R.; Munday, S.; Bray, R.: Regional geology and geophysics of the eastern Gulf of Guinea (Niger Delta to Rio Muni). Lead Edge 21(11), 1112–1117 (2002)
Avbovbo, A.A.: Tertiary lithostratigraphy of Niger Delta. AAPG Bull. 62, 295–300 (1978)
Orife, J.M.; Avbovbo, A.A.: Stratigraphic and unconformity traps in the Niger Delta. AAPG Bull. 57, 251–262 (1981)
Serra, A.; Sulpice, L.: Sedimentological analysis of sand-shale series from well logs. In: 16th Annual Logging Symposium, Society of Petrophysicists and Well Log Analysts (SPWLA). Paper W (1975)
Rider, M.: Gamma-ray log shape used as a facies indicator: critical analysis of an oversimplified methodology. In: Hurst, A., Lovell, M.A., Morton, A.C. (eds.) Geological Application of Wireline Logs, pp. 27–37. Geological Society of London Special Publication, London (1990). https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1990.048.01.04
Ates, H.; Bahar, A.; El-Abd, S.; Charfeddine, M.; Kelkar, M.; Datta-Gupta, A.: Ranking and upscalling of geostatistical reservoir models by use of streamline simulation: a field case study. Soc. Pet. Eng. Reserv. Eval. Eng. 8(1), 22–32 (2005)
Sablok, R.; Aziz, K.: Upscaling and Discretization Errors in Reservoir Simulation. SPE Reservoir Simulation Symposium. Texas (2005). https://doi.org/10.2118/93372-MS
Lambers, J.V.; Gerritsen, M.G.; Mallison, B.T.: Accurate local upscaling with variable compact multipoint transmissible calculations. Comput. Geosci. 12, 399–416 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-007-9068-4
Gringarten, E.; Deutsch, CV.: Methodology for variogram interpretation and modelling for improved reservoir characterization. In: SPE Annual Technical Conference, pp. 1–13 (1999). https://doi.org/10.2118/56654-MS
Esfahani, N.M.; Asghari, O.: Fault detection in 3D by sequential Gaussian simulation of Rock Quality Designation (RQD) Case study: Gazestan phosphate ore deposit, Central Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 6(10), 3737–3747 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0633-3
Journel, A.G.; Alabert, F.G.: New method for reservoir mapping. J. Pet. Technol. 42(02), 212–218 (1990)
Journel, A.G.; Go’mez-Herna’ndez, J.J.: Stochastic imaging of the Wilmington clastic sequence. Soc. Pet. Eng. Formation Eval. 8(1), 33–40 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2118/19857-PA
Caers, J.: Direct sequential indicator simulation. In: The 6th International Geostatistics Congress, South Africa (2000)
Goovaerts, P.: Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation. Oxford University Press, New York (1997)
Pyrcz, M.J.; Deutsch, C.V.: Geostatistical Reservoir Modelling, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York (2014)
Van Wagoner, J.C.; Mitchum, R.M.; Campion, K.M.; Rahmanian, V.D.: Siliciclastic sequence stratigraphy in well logs, cores and outcrops: concepts for high-resolution correlations of time and facies. AAPG Methods Explor. Ser. 7, 55 (1990)
Boyd, R.; Dalrymple, R.; Zaitlin, B.A.: Classification of clastic coastal depositional environments. Sediment. Geol. 1978(80), 139–150 (1992)
Hosper, J.: The geology of the Niger Delta area. In: The Geology of the East Atlantic Continental Margin, Great Britain. Inst. Geological Sci. Report, vol. 70(16), pp. 121–147 (1971)
Reynolds, A.D.: Paralic reservoirs. In: Hampson, G.J., Reynolds, A.D., Kostic, B., Wells, M.R. (eds.) Sedimentology of Paralic Reservoirs: Recent Advances, pp. 1–28. Geological Society of London Special Publications, London (2016)
Weber, K.J.; Van Guens, L.C.: Framework for constructing clastic reservoir simulation models. J. Pet. Technol. 43, 1248–1253 (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original version of this article was revised: The authors’ family and given names had been interchanged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oyeyemi, K.D., Olowokere, M.T. & Aizebeokhai, A.P. Building 3D Lithofacies and Depositional Models Using Sequential Indicator Simulation (SISIM) Method: A Case History in Western Niger Delta. Arab J Sci Eng 43, 3775–3792 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3212-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3212-4