Abstract
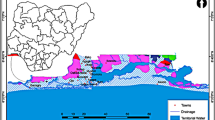
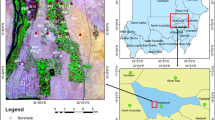
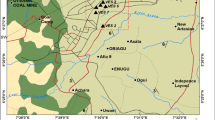
Groundwater of the Quaternary shallow alluvial aquifer is the only safe and reliable water resource in Yenagoa and environs, Southern Nigeria. The determination of the aquifer hydrogeophysical parameters is thus critical and constitutes the basic foundation for optimizing the short- and long-term groundwater utilization strategies. In this study, 29 Schlumberger vertical electrical soundings, borehole data, pump test, hydrochemical analysis, and measured and/or calculated hydrogeophysical parameters were integrated to reconnaissance the local aquifer conditions. Aquifer qualitative and quantitative properties in terms of electric and hydraulic conditions were also investigated. The freshwater aquifer was delineated with true resistivity and thickness ranges of 134–664 Ωm and 6.7–41.4 m respectively. Transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity values vary between 189–2609 m2/day and 28–118 m/day, respectively. Porosity ranges between 0.40 and 0.45 and tortuosity ranges between 1.28 and 1.31. Correlation of the results of the geochemical analysis of the groundwater samples with the layer resistivities shows that in the locations where the aquifer is overlain by clay layer (ρ ∼ 10 Ωm) have higher concentrations of dissolved iron (Fe > 0.1 mg/L), whereas the iron concentrations are remarkably low (Fe < 0.1 mg/l) in areas the aquifer is underneath relatively thin silty sand layer (ρ ∼ 349 Ωm). The near-surface lithology acts as a controlling factor for spatial distribution of groundwater iron within the very shallow depths (<20 m). The geochemistry of the groundwater was observed to be controlled mainly by weathering of silicate group of minerals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akujieze C.N., Coker S.J.L., Oteze G.E.: Groundwater in Nigeria—a millennium experience—distribution, practice, problems and solutions. Hydrogeol. J. 11, 259–274 (2013)
Masch F.D., Denny K.J.: Grain size distribution and its effects on the hydraulic conductivity of unconsolidated sands. Water Resour. Res. 2, 665–677 (1996)
Amadi P.A., Ofoegbu C.O., Morrison T.: Hydrogeochemical assessment of groundwater quality in parts of the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 14, 195–202 (1987)
Offodile, M.E.: An Approach to Groundwater Study and Development in Nigeria. Mecon Services Ltd, Jos, pp. 224–227 (1992)
Okiongbo K.S., Ogobiri G.: Geoelectric investigation of groundwater resources in parts of Bayelsa State, Nigeria. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 3, 620–624 (2011)
Okiongbo K.S., Douglas R.K.: Rock–water interaction and its control on the chemical composition of groundwater in an alluvial aquifer in Yenagoa City and environs, Southern Nigeria. Ife J. Sci. 15(3), 489–507 (2013)
Akpokodje E.U., Etu-Efeotor J.O.: The occurrence and Economic potential of clean sand deposits of the Niger Delta. J. Afri. Earth Sci. 6(1), 61–65 (1987)
Short K.C., Stauble A.J.: Outline of geology of Niger Delta. AAPG Bull. 51, 761–779 (1967)
Allen J.R.L.: Late Quaternary Niger Delta and adjacent areas: sedimentary environments and lithofacies. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. Bull. 49, 549–600 (1965)
Abam, T.K.S.: Dynamics and quality of water resources in the Niger Delta. Impacts of urban growth on surface water and groundwater quality. In: Preceedings of IUGG Symposium, Birmigham, publication no. 259 (1999)
Mbonu P.D.C., Ebeniro J.O., Ofoegbu C.O., Ekine A.S.: Geoelectric sounding for the determination of aquifer characteristics in parts of Umuahia area of Nigeria. Geophysics 56, 284–291 (1991)
Ekine, A.S.; Osobonye, G.T.: Surface geoelectric sounding for the determination of aquifer characteristics in part of Bonny Local Government Area of Rivers State. Nig. J. Phys. 85 (1996)
APHA: Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water (17th ed.). American Public Health Association, Washington (1998)
Fetter, C.W.: Applied Hydrogeology. C.E. Merril (ed), Columbus, pp. 170–173 (1994)
Niwas S., Singhal D.C.: Estimation of aquifer transmissvity from Dar-Zarrouk parameters in a porous media. J. Hydrol. 50, 393–399 (1981)
Mazac O., Kelly W.E., Landa I.: A hydrogeophysical model for relations between electrical and hydraulic properties of aquifers. J. Hydrol. 79, 1–19 (1985)
Alyamani M.S., Sen Z.: Determination of hydraulic conductivity from grain size distribution curves. Groundwater 31, 551–555 (1993)
Vukovic, M.; Soro, A.: Determination of Hydraulic Conductivity of Porous Media from Grain Size Composition. Water Resources Publication, Littleton
Maxwell, J.C.A.: Treatise on electricity and magnetism, vol.1. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Amajor L.C.: Aquifers in the Benin Formation (Miocene—Recent), Eastern Niger Delta, Nigeria. Lithostratigraphy, Hydraulics and water quality. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 17, 85–101 (1991)
Frohlick R.K., Kelly W.E.: The relation between hydraulic transmissivity and transverse resistance in a complicated aquifer of glacial outwash deposits. J. Hydrol. 79, 215–229 (1985)
Salem H.S.: Determination of fluid transmissivity and electric transverse resistance for shallow aquifers and deep reservoirs from surface and well-log measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 3, 421–428 (1991)
Hem, J.D.: Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water, U.S Geological Survey water-supply paper 1473, 2nd ed. (1970)
Nath B., Berner Z., Chatterjee D., Mallik S.B., Stuben D.: Mobility of arsenic in the West Bengal aquifers conducting low and high groundwater arsenic: part II: comparative geochemical profile and leaching study. Appl. Geochem. 23, 996–1011 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okiongbo, K.S., Akpofure, E. Hydrogeophysical Characterization of Shallow Unconsolidated Alluvial Aquifer in Yenagoa and Environs, Southern Nigeria. Arab J Sci Eng 41, 2261–2270 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1827-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1827-2