Abstract
Fast pyrolysis was used to convert waste biomass into bio-oil, which has a benefit of storage and transportation with the potential as a fossil oil substitute. Pakistani cotton stalk was pyrolyzed in a bench-scale bubbling fluidized bed reactor. The effect of reaction conditions such as temperature and feed size on the bio-oil, char and gas yields was investigated. The optimal pyrolysis temperature for the production of bio-oil was 490 °C which gave the maximum yield (36 wt%) of product at feed size of 1.0 mm. Bio-oil yield increased with the increase in temperature, while the yield of char decreased. The various properties of bio-oil attained under these pyrolysis conditions were defined. Chemical composition of bio-oil was determined using FTIR and GC–MS analysis, and major chemical compounds were phenols, carboxylic acids, ketones, aldehydes, furans and sugars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gokmen A., Temiz D.: The importance and impact of fossil and renewable energy sources in Turkey on business and the economy. Energy Sourc. Part B Econ. Plann. Policy 10(1), 14–20 (2015)
Panwar N.L., Kaushik S.C., Kothari S.: Role of renewable energy sources in environmental protection: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(3), 1513–1524 (2011)
Hall, D.O.; Barnard, G.W.; Moss, P.A.: Biomass for energy in the developing countries: current role, potential, problems, prospects. Elsevier, (2013)
Bridgewater A.V.: Biomass fast pyrolysis. Thermal Sci. 8(2), 21–50 (2004)
Bioenergy I.E.A.: Bioenergy,IEA Bioenergy-a Sustainable and Reliable Energy Source. International Energy Agency Bioenergy, Paris (2009)
Garcia-Parez M., Chaala A., Roy C.: Vacuum pyrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 65(2), 111–136 (2002)
Bentsen N.S., Felby C.: Biomass for energy in the European Union—a review of bioenergy resource assessments. Biotech. Biofuels 5(1), 25 (2012)
Carpenter D., Westover T.L., Czernik S., Jablonski W.: Biomass feedstocks for renewable fuel production: a review of the impacts of feedstock and pretreatment on the yield and product distribution of fast pyrolysis bio-oils and vapors. Green Chem. 16(2), 384–406 (2014)
Khan R.A., Khan A.N., Ahmed M., Khan M.R., Shah M.S., Azam N., Sadullah F., Dian F., Ullah S., Khan N.: Bioethanol sources in Pakistan: a renewable energy resource. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10(86), 19850–19854 (2014)
Koopmans, A.; Koppejan, J.: Agricultural and forest residues-generation, utilization and availability. In: Paper Presented at the Regional Consultation on Modern Applications of Biomass Energy, vol. 6:10 (1997)
Farooq M.K., Kumar S.: An assessment of renewable energy potential for electricity generation in Pakistan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 20, 240–254 (2013)
Bridgwater A.V.: Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenergy 38, 68–94 (2012)
Demirbas A.: Biomass resources for energy and chemical industry. Energy Edu. Sci. Technol 5(1), 21–45 (2000)
Bridgwater A.V., Bridge S.A: A Review of Biomass Pyrolysis and Pyrolysis Technologies. Biomass Pyrolysis Liquids Upgrading and Utilization, pp. 11–92. Springer, Berlin (1991)
Goyal H.B., Seal D., Saxena R.C.: Bio-fuels from thermochemical conversion of renewable resources: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 12(2), 504–517 (2008)
Jahirul M.I., Rasul M.G., Chowdhury A.A., Ashwath N.: Biofuels production through biomass pyrolysis—a technological review. Energies 5(12), 4952–5001 (2012)
Meier D., van de Beld B., Bridgwater A.V., Elliott D.C., Oasmaa A., Preto F.: State-of-the-art of fast pyrolysis in IEA bioenergy member countries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 20, 619–641 (2013)
Meier D., Faix O.: State of the art of applied fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic materials-a review. Bioresour. Technol. 68(1), 71–77 (1999)
Alper K., Tekin K., Karag S.: Pyrolysis of agricultural residues for bio-oil production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 17(1), 211–223 (2015)
Goyal H.B., Saxena R.C., Seal D.: Thermochemical Conversion of Biomass to Liquids and Gas. Monograph communicated to Haworth Press, Philadelphia (2006)
Mohan D., Pittman C.U., Steele P.H.: Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: a critical review. Energy Fuels 20(3), 848–889 (2006)
Balat M., Balat M., Kirtay E., Balat H.: Main routes for the thermo-conversion of biomass into fuels and chemicals. Part 1: Pyrolysis systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 50(12), 3147–3157 (2009)
Bridgwater A.V.: Principles and practice of biomass fast pyrolysis processes for liquids. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 51(1), 3–22 (1999)
Daim T.U., Honnappa L., Murthy M., Rusnac C., Pornsatit C.: Technological Assessment of Emerging Technologies in Conversion of Municipal Solid Waste to Energy. Policies and Programs for Sustainable Energy Innovations, pp. 83–105. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Westerhof R.J.M., Brilman D.W.F., van Swaaij W.P.M., Kersten S.R.A.: Effect of temperature in fluidized bed fast pyrolysis of biomass: oil quality assessment in test units. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49(3), 1160–1168 (2009)
Heo H.S., Park H.J., Yim J.-H., Sohn J.M., Park J., Kim S.-S., Ryu C., Jeon J.-K., Park Y.-K.: Influence of operation variables on fast pyrolysis of Miscanthus sinensis var. purpurascens. Bioresour. Technol. 101(10), 3672–3677 (2010) doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.078
Pattiya A., Suttibak S.: Production of bio-oil via fast pyrolysis of agricultural residues from cassava plantations in a fluidised-bed reactor with a hot vapour filtration unit. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 95(0), 227–235 (2012) doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2012.02.010
Mourant D., Lievens C., Gunawan R., Wang Y., Hu X., Wu L., Syed-Hassan S.S.A., Li C.-Z.: Effects of temperature on the yields and properties of bio-oil from the fast pyrolysis of mallee bark. Fuel 108, 400–408 (2013)
Kim S.-S., Agblevor F.A., Lim J.: Fast pyrolysis of chicken litter and turkey litter in a fluidized bed reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 15(2), 247–252 (2009)
Montoya, J.I.; Valdés C.; Chejne, F.; Gómez C.A.; Blanco A.; Marrugo, G.; Osorio, J.; Castillo, E.; Aristóbulo, J.; Acero, J.: Bio-oil production from Colombian bagasse by fast pyrolysis in a fluidized bed: An experimental study. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 112, 379–387 (2015)
Scott D.S., Piskorz J.: The flash pyrolysis of aspen poplar wood. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 60(5), 666–674 (1982)
Raja S.A., Kennedy Z.R., Pillai B.C., Lee C.L.R.: Flash pyrolysis of jatropha oil cake in electrically heated fluidized bed reactor. Energy 35(7), 2819–2823 (2010)
Heidari A., Stahl R., Younesi H., Rashidi A., Troeger N., Ghoreyshi A.A.: Effect of process conditions on product yield and composition of fast pyrolysis of Eucalyptus grandis in fluidized bed reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 2594–2602 (2014)
Park H.J., Dong J.-I., Jeon J.-K., Park Y.-K., Yoo K.-S., Kim S.-S., Kim J., Kim S.: Effects of the operating parameters on the production of bio-oil in the fast pyrolysis of Japanese larch. Chem. Eng. J. 143(1), 124–132 (2008)
Choi H.S., Choi Y.S., Park H.C.: Fast pyrolysis characteristics of lignocellulosic biomass with varying reaction conditions. Renew. Energy 42, 131–135 (2012)
Garcia-Perez M., Wang X.S., Shen J., Rhodes M.J., Tian F., Lee W.-J., Wu H., Li C.-Z.: Fast pyrolysis of oil mallee woody biomass: effect of temperature on the yield and quality of pyrolysis products. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 47(6), 1846–1854 (2008)
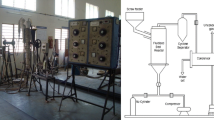
Ali, N.; Saleem, M.; Shahzad, K.; Chughtai, A.; Khan, W.A.: Fast pyrolysis of Pakistani cotton stalks in fluidized bed reactor: design and preliminary results. Life Sci. J. 11(7), 137–144 (2014)
Kunni, D.; Levenspiel, O.: Fluidization Engineering., Edit. Wiley, EE UU, (1969)
Mullen C.A., Boateng A.A., Goldberg N.M., Lima I.M., Laird D.A., Hicks K.B.: Bio-oil and bio-char production from corn cobs and stover by fast pyrolysis. Biomass Bioenergy 34(1), 67–74 (2010)
Park Y.-K., Yoo M.L., Lee H.W., Park S.H., Jung S.-C., Park S.-S., Kim S.-C.: Effects of operation conditions on pyrolysis characteristics of agricultural residues. Renew. Energy 42, 125–130 (2012)
Demiral Ä.I., Ayan E.A.: Pyrolysis of grape bagasse: effect of pyrolysis conditions on the product yields and characterization of the liquid product. Bioresour. Technol. 102(4), 3946–3951 (2011)
Sulaiman W.R.W., Lee E.S.: Pyrolysis of Eucalyptus wood in a fluidized-bed reactor. Res. Chem. Intermed. 38(8), 2025–2039 (2012)
Heidari A., Stahl R., Younesi H., Rashidi A., Troeger N., Ghoreyshi A.A.: Effect of process conditions on product yield and composition of fast pyrolysis of Eucalyptus grandis in fluidized bed reactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 20(4), 2594–2602 (2013)
Islam M.N., Ani F.N.: Liquid oil from fluidized bed pyrolysis of rice husk waste and its characterization. RERIC Int. Energy J. 20, 55–65 (1998)
Gercel H.F.: The effect of a sweeping gas flow rate on the fast pyrolysis of biomass. Energy Sources 24(7), 633–642 (2002)
Zhou L., Yang H., Wu H., Wang M., Cheng D.: Catalytic pyrolysis of rice husk by mixing with zinc oxide: characterization of bio-oil and its rheological behavior. Fuel Process. Technol. 106, 385–391 (2013)
Tsai W.T., Lee M.K., Chang Y.M.: Fast pyrolysis of rice straw, sugarcane bagasse and coconut shell in an induction-heating reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 76(1), 230–237 (2006)
Kim S.-J., Jung S.-H., Kim J.-S.: Fast pyrolysis of palm kernel shells: influence of operation parameters on the bio-oil yield and the yield of phenol and phenolic compounds. Bioresour. Technol. 101(23), 9294–9300 (2010)
Akhtar J., Amin N.A.S.: A review on process conditions for optimum bio-oil yield in hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(3), 1615–1624 (2011)
Wei L., Xu S., Zhang L., Zhang H., Liu C., Zhu H., Liu S.: Characteristics of fast pyrolysis of biomass in a free fall reactor. Fuel Process. Technol. 87(10), 863–871 (2006)
Di Blasi C.: Kinetic and heat transfer control in the slow and flash pyrolysis of solids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35(1), 37–46 (1996)
Gerdes C., Simon C.M., Ollesch T., Meier D., Kaminsky W.: Design, construction, and operation of a fast pyrolysis plant for biomass. Eng. Life Sci. 2(6), 167–174 (2002)
Shen J., Wang X.-S., Garcia-Perez M., Mourant D., Rhodes M.J., Li C.-Z.: Effects of particle size on the fast pyrolysis of oil mallee woody biomass. Fuel 88(10), 1810–1817 (2009)
Ridout A.J., Carrier M., Gorgens J.: Fast pyrolysis of low and high ash paper waste sludge: Influence of reactor temperature and pellet size. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 111, 64–75 (2015)
Zhou S., Garcia-Perez M., Pecha B., McDonald A.G., Westerhof R.J.M.: Effect of particle size on the composition of lignin derived oligomers obtained by fast pyrolysis of beech wood. Fuel 125, 15–19 (2014)
Heo H.S., Park H.J., Park Y.-K., Ryu C., Suh D.J., Suh Y.-W., Yim J.-H., Kim S.-S.: Bio-oil production from fast pyrolysis of waste furniture sawdust in a fluidized bed. Bioresour. Technol. 101(1, Supplement), S91–S96 (2010) doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.003
Mullen C.A., Boateng A.A.: Chemical Composition of Bio-oils Produced by Fast Pyrolysis of Two Energy Crops. Energy Fuels 22(3), 2104–2109 (2008)
Duman G., Okutucu C., Ucar S., Stahl R., Yanik J.: The slow and fast pyrolysis of cherry seed. Bioresour. Technol. 102(2), 1869–1878 (2010)
Radlein D.: Study of levoglucosan production—a review. Fast Pyrolysis Biomass: A Handbook 2, 205–241 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, N., Saleem, M., Shahzad, K. et al. Bio-Oil Production from Fast Pyrolysis of Cotton Stalk in Fluidized Bed Reactor. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 3019–3027 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1801-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1801-z