Abstract
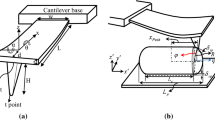
The manipulation of nanoparticles is a current topic of research in the nano world. This is an important subject, since by displacing the nanoparticles, a structure different from the one which is currently available can be obtained. To achieve such a purpose, the atomic force microscope (AFM) is employed as a manipulator to push or pull the target nanoparticles on a substrate and get them to the desired locations. The important point in this process is the amount of force which is necessary to move a particle to the intended spot. Also, to estimate the time for the onset of nanoparticle movement in the sliding mode, it becomes important to obtain the critical time as well. In this paper, through the dynamic simulation of a nanoparticle, its governing manipulation equations have been derived and simulated, so that they can be applied to determine the critical force and time for gold, yeast and platelet nanoparticles in gas, liquid, alcohol, and plasma mediums. Another important issue in the manipulation of nanoparticles is the control of the AFM probe. So, we propose to use an appropriate input such as the torque applied to the probe tip in order to control the probe deviation from its center and to observe the amount of probe displacement along its vertical direction so that, during the moving operation, the AFM probe always remains in contact with the nanoparticle being displaced. This control issue has been investigated for various liquid environments and with different biological and non-biological nanoparticles. Furthermore, the probe of the AFM has been controlled in water, alcohol, and plasma mediums by employing the sliding mode control approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Junno T., Deppert K., Montelius L., Samuelson L.: Controlled manipulation of nanoparticles with an atomic force microscope. Appl. Phys. Lett. 66(26), 3627–3629 (1995)
Resch R., Baur Ch., Bugacov A., Koel B.E., Echternach P.M., Madhukar A., Montoya N., Requicha A.A.G., Will P.: Linking and manipulation of gold multinanoparticle structures using dithiols and scanning force microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 103, 3647–3650 (1999)
Resch R., Baur Ch., Bugacov A., Koel B.E., Madhukar A., Requicha A.A.G., Will P.: Building and manipulating three-dimensional and linked two-dimensional structures of nanoparticles using scanning force microscopy. Langmuir 14(23), 6613–6616 (1998)
Sitti, M.; Hirahara, K.; Hashimoto, H.: “2-D micro particle assembly using atomic force microscope. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, International Conference on Micromechatronics and Human Systems, pp. 143–148 (1998)
Sitti M., Hashimoto H.: Force controlled pushing of nanoparticles: modeling and experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 5, 199–211 (2000)
Burnham, N.A.; Kulik A.J.: Surface forces and adhesion. In: Bhushan, B (ed.) Hand Book of Micro/Nanotribology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL (1999)
Sitti M., Hashimoto H.: Teleoperated touch feedback from the surfacesat the nanoscale: modelling and experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 8(1), 1–12 (2003)
Kim, D.H.; Park, J.; Kim, B.; Kim, K.: Modeling and simulation of nanorobotic manipulation with an AFM probe. In: International Conference on Computer Applications in Shipbuilding (2002)
Li, G.; Xi, N.; Yu, M.; Fung, W.K.: Modeling of 3-D interactive forces in nanomanipulation. In: Proceedings of IEEHRSJ, International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems October 2003 (2003)
Tafazzoli, A.; Sitti, M.: Dynamic modes of nano-particle motion during nanoprobe based manipulation. In: Proceedings of IEEE, international conference on nanotechnology, August 2004 (2004)
Tafazzoli, A.; Sitti, M.: Dynamic behavior and simulation of nanoparticles sliding during nanoprobe-based positioning. In: Proceedings of IMECE, ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress, November 2004 (2004)
Korayem M.H., Motaghi A., Zakeri M.: Dynamic modeling of submerged nanoparticle pushing based on atomic force microscopy in liquid medium. J. Nanopart. Res. 13(10), 5009–5019 (2011)
Korayem M.H., Noroozi M., Daeinabi Kh.: Control of an atomic force microscopy probe during nano-manipulation via the sliding mode method. Sci. Iran. B 19(5), 1346–1353 (2012)
Korayem M.H., Daeinabi Kh.: Indentation analysis of nano-particle using nano-contact mechanics models during nano-manipulation based on atomic force microscopy. J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 1075–1091 (2011)
Korayem M.H., Taheri M., Korayem A.H.: Simulating the biomanipulation of DNA and yeast micro/nanoparticles based on the atomic force microscope. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. K 228(4), 414–425 (2014)
Korayem M.H., Badkoobeh Hezaveh H., Taheri M.: Dynamic modeling and simulation of rough cylindrical micro/nanoparticles manipulation by means of the AFM. Microsc. Microanal. 20(6), 1692–1707 (2014)
Korayem M.H., Omidi E.: Robust controlled manipulation of nanoparticles using atomic force microscopy. Micro Nano Lett. 7(9), 927–931 (2012)
Korayem M.H., Taheri M., Zakeri M.: Sensitivity analysis of nanoparticles manipulation based on different friction models. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 6713–6722 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korayem, A.H., Korayem, M.H. & Taheri, M. Robust Controlled Manipulation of Nanoparticles Using the AFM Nanorobot Probe. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 2685–2699 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1730-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-015-1730-x