Abstract
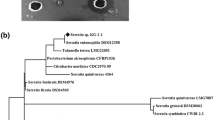
The fibrinolytic enzyme has been found in the traditional fermented foods including the traditional shrimp paste product. In this study, six Vietnamese traditional shrimp paste products collected in three regions (north, south and middle of Vietnam) were screened for fibrinolytic enzyme and the related bacteria were isolated and identified. The fibrinolytic enzyme was found in all Vietnamese shrimp paste products, in which the products in the middle of Vietnam had higher fibrinolytic enzyme activity (2.43–2.95 FU/ml) than those in other regions. The isolated bacterium which produced the highest fibrinolytic enzyme was identified as a strain of Bacillus sp., closely related to the species of Bacillus weihenstephanensis with 99 % identities. The optimal fermentation conditions were also investigated using response surface methodology based on Box–Behnken design for high fibrinolytic enzyme production by the isolated strain. As a result, the fibrinolytic enzyme activity reached to 6.85 FU/ml at the optimal fermentation condition of 1.50 % of shrimp shell powder, 1.44 % of NaCl, at 33 °C and 32-h fermentation. Thus, the fibrinolytic enzyme produced by the strain of Bacillus sp. in this study might be used as a thrombolytic agent in pharmaceutical industries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mine Y., Wong A.H.K.W., Jiang B.: Fibrinolytic enzymes in Asian traditional fermented foods. Food Res. Int. 3, 243–250 (2005)
Mathers C.D., Loncar D.: Projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030. PLoS Med. 3, e442 (2006)
Blann A.D., Landray M.J., Lip G.Y.H.: ABC of antithrombotic therapy: an overview of antithrombotic therapy. Br. Med. J. 325, 762–765 (2002)
Bode R.W., Runge C., Smalling M.: The future of thrombolysis in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 17, 55–60 (1996)
Wu X.C., Ye R., Duan Y., Wong S.L.: Engineering of plasmin-resistant forms of streptokinase and their production in Bacillus subtilis: streptokinase with longer functional half-life. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 824–829 (1998)
Sumi H., Hamada H., Tsushima H., Mihara H., Muraki H.: A novel fibrinolytic enzyme (nattokinase) in the vegetable cheese Natto, a typical and popular soybean food in the Japanese diet. Experientia 43, 1110–1111 (1987)
Mihara H., Sumi H., Yoneta T., Mizumoto H., Ikeda R., Seiki M., Maruyama M.: A novel fibrinolytic enzyme extracted from the earthworm, Lumbricus rubellus. Jpn. J. Physiol. 41, 461–472 (1991)
Sumi H., Nikajima N., Mihara H.: Fibrinolysis relating substances in marine creatures. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 102, 163–167 (1992)
Chang C.T., Wang P.M., Hung Y.F., Chung Y.C.: Purification and biochemical properties of a fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus subtilis-fermented red bean. Food Chem. 133, 1611–1617 (2012)
Choi D.B., Cha W.S., Park N., Kim H.W., Lee J.H. et al.: Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from fruiting bodies of Korean Cordyceps militaris. Bioresour. Tech. 102, 3279–3285 (2011)
Chung D.M., Choi N.S., Maeng P.J., Chun H.K., Kim S.H.: Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from chive (Allium tuberosum). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 19, 697–702 (2010)
Wong A.H.K.W., Mine Y.: Novel fibrinolytic enzyme in fermented shrimp paste, a traditional Asian fermented seasoning. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 980–986 (2004)
Peng Y., Yang X., Zhang Y.: Microbial fibrinolytic enzymes: an overview of source, production, properties, and thrombolytic activity in vivo. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 69, 126–132 (2005)
Peng Y., Huang Q., Zhang R.H., Zhang Y.Z.: Purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DC-4 screened from douchi, a traditional Chinese soybean food. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 134, 45–52 (2003)
Wang S.H., Zhang C., Yang Y.L., Diao M., Bai M.F.: Screening of a high fibrinolytic enzyme producing strain and characterization of the fibrinolytic enzyme produced from Bacillus subtilis LD-8547. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 457–482 (2008)
Kim S.H., Choi N.S.: Purification and characterization of subtilisin DJ-4 secreted by Bacillus sp. strain DJ-4 screened from Doen-Jang. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64, P 1722–1725 (2000)
Kim W., Choi K., Kim Y.: Purification and characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme produced from Bacillus sp. strain CK 11-4 screened from Chungkook-Jang. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 2482–2488 (1996)
Wang S.L., Chen H.J., Liang T.W., Lin Y.D.: A novel nattokinase produced by Pseudomonas sp. TKU015 using shrimp shells as substrate. Process Biochem. 44, 70–76 (2009)
Wang S.L., Yeh P.Y.: Purification and characterization of a chitosanese from a nattokinase producing strain Bacillus subtilis TKU007. Process Biochem. 43, 132–138 (2008)
Box G.E.P., Behnken D.W.: Some new three level designs for the study of quantitative variables. Technometrics 2, 455–475 (1960)
Khuri A.I., Mukhopadhyay S.: Response surface methodology. WIREs Comp. Stat. 2, 128–149 (2010)
Prafulla M.M., Sagar V.G., Smita S.L.: Production of nattokinase using Bacillus natto NRRL 3666: media optimization, scale up, and kinetic modeling. Food Sci. Biotech. 19, 1593–1603 (2010)
Wang S.L., Wu Y.Y., Liang T.W.: Purification and biochemical characterization of a nattokinase by conversion of shrimp shell with Bacillus subtilis TKU007. New Biotechnol. 28, 196–202 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anh, D.B.Q., Mi, N.T.T., Huy, D.N.A. et al. Isolation and Optimization of Growth Condition of Bacillus sp. from Fermented Shrimp Paste for High Fibrinolytic Enzyme Production. Arab J Sci Eng 40, 23–28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1506-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-014-1506-8