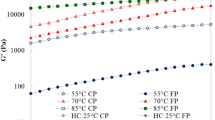
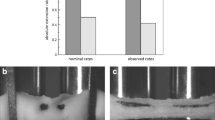
Abstract
This study examines the effects of various components of tested gluten-free doughs, such as corn starch, amaranth flour, pea protein isolate, and cellulose in the form of plantain fibers on rheological properties of such doughs. The rheological properties of gluten-free doughs were assessed by using the rheological fractional standard linear solid model (FSLSM). Parameter analysis of the Maxwell-Wiechert fractional derivative rheological model allows to state that gluten-free doughs present a typical behavior of viscoelastic quasi-solid bodies. We obtained the contribution dependence of each component used in preparations of gluten-free doughs (either hard-gel or soft-gel structure). The complicate analysis of the mechanical structure of gluten-free dough was done by applying the FSLSM to explain quite precisely the effects of individual ingredients of the dough on its rheological properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcoutlabi, M. and J.J. Martinez-Vega, 1998, Application of fractional calculus to viscoelastic behaviour modelling and to the physical ageing phenomenon in glassy amorphous polymers, Polymer 39, 6269–6277.
Edwards, N.M., J.E. Dexter, M.G. Scanlon, and S. Cenkowski, 1999, Relationship of creep-recovery and synamic oscillatory measurements to durum wheat physical dough properties, Cereal Chem. 76, 638–645.
Edwards, N.M., D. Peressini, J.E. Dexter, and S.J. Mulvaney, 2001, Viscoelastic properties of durum wheat and common wheat dough of different strengths, Rheol. Acta 40, 142–153.
Edwards, N.M., S.J. Mulvaney, M.G. Scanlon, and J.E. Dexter, 2003, Role of gluten and its components in determining durum semolina dough viscoelastic properties, Cereal Chem. 80, 755–763.
Fasano, A. and C. Catassi, 2001, Current approaches to diagnosis and treatment of celiac disease: an evolving spectrum, Gastroenterology 120, 636–651.
Gallagher, E., T.R. Gormley, and E.K. Arendt, 2004, Recent advances in the formulation of gluten-free cereal-based products, Trends Food Sci. Technol. 15, 143–152.
Gujral, H.S., I. Guardiola, J.V. Carbonell, and C.M. Rosell, 2003, Effect of cyclodextrinase on dough rheology and bread quality from rice flour, J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 3814–3818.
Haque, A. and E.R. Morris, 1994, Combined use of ispaghula and HPMC to replace or augment gluten in breadmaking, Food Res. Int. 27, 379–393.
Ikeda, S. and K. Nishinari, 2001, On solid-like rheological behaviors of globular protein solutions, Food Hydrocoll. 15, 401–406.
Janssen, A.M., T. van Vliet, and J.M. Vereijken, 1996b, Fundamental and empirical rheological behaviour of wheat flour doughs and comparison with bread making performance, J. Cereal Sci. 23, 43–54.
Kagnoff, M.F., 2007, Celiac disease: pathogenesis of a model immunogenetic disease, J. Clin. Invest. 117, 41–49.
Korus, J., M. Witczak, R. Ziobro, and L. Juszczak, 2009, The impact of resistant starch on characteristics of gluten-free dough and bread, Food Hydrocoll. 23, 988–995.
Lazaridou, A., D. Duta, M. Papageorgiou, N. Belc, and C.G. Biliaderis, 2007, Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations, J. Food Eng. 79, 1033–1047.
Lee, C.C. and S.J. Mulvaney, 2003, Dynamic viscoelastic and tensile properties of gluten and glutenin gels of common wheats of different strength, J. Agric. Food Chem. 51, 2317–2327.
Magalotti, D., U. Volta, A. Bonfiglioli, S. Ramilli, A. Berzigotti, and M. Zoli, 2003, Splanchnic haemodynamics in patients with coeliac disease: effects of a glutenfree diet, Dig. Liver Dis. 35, 262–268.
Mariotti, M., M. Lucisano, M.A. Pagani, and P. Ng, 2009, The role of corn starch, amaranth flour, pea isolate, and Psyllium flour on the rheological properties and the ultrastructure of gluten-free doughs, Food Res. Int. 42, 963–975.
Mours, M. and H.H. Winter, 1996, Relaxation patterns of nearly critical gels, Macromolecules 29, 7221–7229.
Neuhausen, S.L., M. Feolo, N.J. Camp, J. Farnham, L. Book, and J.J. Zone, 2002, Genome-wide linkage analysis for celiac disease in North American families, Am. J. Med. Genet. 111, 1–9.
Orczykowska, M. and M. Dziubiński, 2012, The fractional derivative rheological model and the linear viscoelastic behavior of hydrocolloids, Chem. Proc. Eng. 33, 141–151.
Phan-Thien, N. and M. Safari-Ardi, 1998, Linear viscoelastic properties of flour-water doughs at different water concentrations, J. Non-Newtonian Fluid Mech. 74, 137–150.
Pruska-Kedzior, A., 2006, Application of phenomenological rheology methods to quantification of wheat gluten viscoelastic properties (in Polish). Scientific Monographs, Vol. 373, The Agricultural University, Poznan.
Reyes-Melo, M.E., J.J. Martinez-Vega, C.A. Guerrero-Salazar, and U. Ortiz-Mendez, 2004, Modelling of relaxation phenomena in organic dielectric materials: Application of differential and integral operators of fractional order, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mat. 6, 1037–1043.
Rosell, C.M., J.A. Rojas, and C. Benedito de Barber, 2001, Influence of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality, Food Hydrocoll. 15, 75–81.
Safari-Ardi, M. and N. Phan-Thien, 1998, Stress relaxation and oscillatory tests to distinguish between doughs prepared from wheat flours of different varietal origin, Cereal Chem. 75, 80–84.
Shen, J.J., C.G. Li, H.T. Wu, and M. Kalantari, 2013, Fractional order viscoelasticity in characterization for atrial tissue, Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 25, 87–93.
Shen, Z.L., H. Kahn, R. Ballarini, and S.J. Eppell, 2011, Viscoelastic properties of isolated collagen fibrils, Biophys. J. 100, 3008–3015.
Sivaramakrishnan, H.P., B. Senge, and P.K. Chattopadhyay, 2004, Rheological properties of rice dough for making rice bread, J. Food Eng. 62, 37–45.
Stern, M., P.J. Ciclitira, R. van Eckert, C. Feighery, W. Janssen, E. Mendez, T. Mothes, R. Troncone, and H. Wieser, 2001, Analysis and clinical aspects of gluten in coeliac disease, Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 13, 741–747.
Wang, X., J.A. Schoen, and M.E. Rentschler, 2013, A quantitative comparison of soft tissue compressive viscoelastic model accuracy, J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 20, 126–136.
Weipert, D., 1990, The benefits of basic rheometry in studying dough rheology, Cereal Chem. 67, 311–317.
Ziobro, R., M. Witczak, L. Juszczak, and J. Korus, 2013, Supplementation of gluten-free bread with non-gluten proteins. Effect on dough rheological properties and bread characteristic, Food Hydrocoll. 32, 213–220.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orczykowska, M., Dziubiński, M. & Owczarz, P. Structural analysis of gluten-free doughs by fractional rheological model. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 27, 33–40 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-015-0005-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13367-015-0005-0