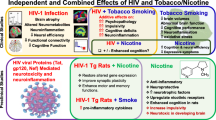
Abstract
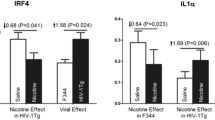
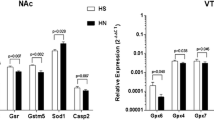
Cognitive impairment in HIV-1 infection is associated with the induction of chronic proinflammatory responses in the brains of infected individuals. The risk of HIV-related cognitive impairment is increased by cigarette smoking, which induces brain inflammation in rodent models. To better understand the role of smoking and the associated immune response on behavioral and motor function in HIV infection, wild-type F344 and HIV-1 transgenic (HIV1Tg) rats were exposed to either smoke from nicotine-containing (regular) cigarettes, smoke from nicotine-free cigarettes, or to nicotine alone. The animals were then tested using the rotarod test (RRT), the novel object recognition test (NORT), and the open field test (OFT). Subsequently, brain frontal cortex from the rats was analyzed for levels of TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6. On the RRT, impairment was noted for F344 rats exposed to either nicotine-free cigarette smoke or nicotine alone and for F344 and HIV1Tg rats exposed to regular cigarette smoke. Effects from the exposures on the OFT were seen only for HIV1Tg rats, for which function was worse following exposure to regular cigarette smoke as compared to exposure to nicotine alone. Expression levels for all three cytokines were overall higher for HIV1Tg than for F344 rats. For HIV1Tg rats, TNF-α, IL-1, and IL-6 gene expression levels for all exposure groups were higher than for control rats. All F344 rat exposure groups also showed significantly increased TNF-α expression levels. However, for F344 rats, IL-1 expression levels were higher only for rats exposed to nicotine-free and nicotine-containing CS, and no increase in IL-6 gene expression was noted with any of the exposures as compared to controls. These studies, therefore, demonstrate that F344 and HIV1Tg rats show differential behavioral and immune effects from these exposures. These effects may potentially reflect differences in the responsiveness of the various brain regions in the two animal species as well as the result of direct toxicity mediated by the proinflammatory cytokines that are produced by HIV proteins and by other factors that are present in regular cigarette smoke.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbondanzo SJ, Chang SL (2014) HIV-1 transgenic rats display alterations in immunophenotype and cellular responses associated with aging. PLoS One 9:e105256
Anderson E, Zink W, Xiong H, Gendelman HE (2002) HIV-1-associated dementia: a metabolic encephalopathy perpetrated by virus-infected and immune-competent mononuclear phagocytes. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 31(Suppl 2):S43–S54
Applied Biosystems (2008) Guide to performing relative quantitation of gene expression using real-time quantitative PCR. 1–70
Arnson Y, Shoenfeld Y, Amital H (2010) Effects of tobacco smoke on immunity, inflammation and autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 34:J258–J265
Ascherio A, Munger KL (2007) Environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Part II: noninfectious factors. Ann Neurol 61:504–513
Brack-Werner R (1999) Astrocytes: HIV cellular reservoirs and important participants in neuropathogenesis. AIDS 13:1–22
Brandt C, Zvolensky MJ, Woods SP, Gonzalez A, Safren SA, O'Cleirigh CM (2017) Anxiety symptoms and disorders among adults living with HIV and AIDS: a critical review and integrative synthesis of the empirical literature. Clin Psychol Rev 51:164–184
Bryant VE, Kahler CW, Devlin KN, Monti PM, Cohen RA (2013) The effects of cigarette smoking on learning and memory performance among people living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS Care 25:1308–1316
Burns DM (1991) Cigarettes and cigarette smoking. Clin. Chest Med 12:631–642
Cataldo JK, Prochaska JJ, Glantz SA (2010) Cigarette smoking is a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: an analysis controlling for tobacco industry affiliation. J Alzheimers Dis 19:465–480
Chana G, Everall IP, Crews L, Langford D, Adame A, Grant I, Cherner M, Lazzaretto D, Heaton R, Ellis R, Masliah E (2006) Cognitive deficits and degeneration of interneurons in HIV+ methamphetamine users. Neurology 67:1486–1489
Chang L, Lim A, Lau E, Alicata D (2017) Chronic tobacco-smoking on psychopathological symptoms, impulsivity and cognitive deficits in HIV-infected individuals. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 12:389–401
Cho YE, Lee MH, Song BJ (2017) Neuronal cell death and degeneration through increased nitroxidative stress and tau phosphorylation in HIV-1 transgenic rats. PLoS One 12:e0169945
Clarke PB, Kumar R (1983) The effects of nicotine on locomotor activity in non-tolerant and tolerant rats. Br J Pharmacol 78:329–337
de Jonge WJ, Ulloa L (2007) The alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor as a pharmacological target for inflammation. Br J Pharmacol 151:915–929
Delgado-Velez M, Baez-Pagan CA, Gerena Y, Quesada O, Santiago-Perez LI, Capo-Velez CM, Wojna V, Melendez L, Leon-Rivera R, Silva W, Lasalde-Dominicci JA (2015) The alpha7-nicotinic receptor is upregulated in immune cells from HIV-seropositive women: consequences to the cholinergic anti-inflammatory response. Clin Transl Immunol 4:e53
Florek E, Marszalek A, Biczysko W, Szymanowski K (1999) The experimental investigations of the toxic influence of tobacco smoke affecting progeny during pregnancy. Hum Exp Toxicol 18:245–251
Galai N, Park LP, Wesch J, Visscher B, Riddler S, Margolick JB (1997) Effect of smoking on the clinical progression of HIV-1 infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 14:451–458
Geissmann F, Auffray C, Palframan R, Wirrig C, Ciocca A, Campisi L, Narni-Mancinelli E, Lauvau G (2008) Blood monocytes: distinct subsets, how they relate to dendritic cells, and their possible roles in the regulation of T-cell responses. Immunol Cell Biol 86:398–408
Glass JD, Fedor H, Wesselingh SL, McArthur JC (1995) Immunocytochemical quantitation of human immunodeficiency virus in the brain: correlations with dementia. Ann Neurol 38:755–762
Gonzalez-Lira B, Rueda-Orozco PE, Galicia O, Montes-Rodriguez CJ, Guzman K, Guevara-Martinez M, Elder JH, Prospero-Garcia O (2006) Nicotine prevents HIVgp120-caused electrophysiological and motor disturbances in rats. Neurosci Lett 394:136–139
Gorantla S, Poluektova L, Gendelman HE (2012) Rodent models for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. Trends Neurosci 35:197–208
Harrison, JD, Dochney, JA, Blazekovic, S, Leone, F, Metzger, D, Frank, I, Gross, R, Hole, A, Mounzer, K, Siegel, S, Schnoll, RA, Ashare, RL (2017) The nature and consequences of cognitive deficits among tobacco smokers with HIV: a comparison to tobacco smokers without HIV. J Neurovirol 23:550–557
Heaton RK, Marcotte TD, Mindt MR, Sadek J, Moore DJ, Bentley H, McCutchan JA, Reicks C, Grant I (2004) The impact of HIV-associated neuropsychological impairment on everyday functioning. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 10:317–331
Heaton RK, Franklin DR, Ellis RJ, McCutchan JA, Letendre SL, Leblanc S, Corkran SH, Duarte NA, Clifford DB, Woods SP, Collier AC, Marra CM, Morgello S, Mindt MR, Taylor MJ, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Wolfson T, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Simpson DM, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I (2011) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: differences in rates, nature, and predictors. J Neuro-Oncol 17:3–16
Helleberg M, Afzal S, Kronborg G, Larsen CS, Pedersen G, Pedersen C, Gerstoft J, Nordestgaard BG, Obel N (2013) Mortality attributable to smoking among HIV-1-infected individuals: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Clin Infect Dis 56:727–734
Jamal A, King BA, Neff LJ, Whitmill J, Babb SD, Graffunder CM (2016) Current cigarette smoking among adults-United States, 2005-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 65:1205–1211
June HL, Tzeng Yang AR, Bryant JL, Jones O, Royal W III (2009) Vitamin A deficiency and behavioral and motor deficits in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transgenic rat. J Neuro-Oncol 15:380–389
Khanna A, Guo M, Mehra M, Royal W III (2013) Inflammation and oxidative stress induced by cigarette smoke in Lewis rat brains. J Neuroimmunol 254:69–75
Kralic JE, Wheeler M, Renzi K, Ferguson C, O'Buckley TK, Grobin AC, Morrow AL, Homanics GE (2003) Deletion of GABAA receptor alpha 1 subunit-containing receptors alters responses to ethanol and other anesthetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:600–607
Lifson AR, Lando HA (2012) Smoking and HIV: prevalence, health risks, and cessation strategies. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 9:223–230
Marks MJ, Grady SR, Collins AC (1993) Downregulation of nicotinic receptor function after chronic nicotine infusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:1268–1276
Midde NM, Gomez AM, Harrod SB, Zhu J (2011) Genetically expressed HIV-1 viral proteins attenuate nicotine-induced behavioral sensitization and alter mesocorticolimbic ERK and CREB signaling in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98:587–597
Moran LM, Booze RM, Mactutus CF (2013) Time and time again: temporal processing demands implicate perceptual and gating deficits in the HIV-1 transgenic rat. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 8:988–997
Nath A (2002) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins in neuropathogenesis of HIV dementia. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S193–S198
Nieman RB, Fleming J, Coker RJ, Harris JR, Mitchell DM (1993) The effect of cigarette smoking on the development of AIDS in HIV-1-seropositive individuals. AIDS 7:705–710
Reid W, Sadowska M, Denaro F, Rao S, Foulke J Jr, Hayes N, Jones O, Doodnauth D, Davis H, Sill A, O'Driscoll P, Huso D, Fouts T, Lewis G, Hill M, Kamin-Lewis R, Wei C, Ray P, Gallo RC, Reitz M, Bryant J (2001) An HIV-1 transgenic rat that develops HIV-related pathology and immunologic dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:9271–9276
Reid WC, Casas R, Papadakis GZ, Muthusamy S, Lee DE, Ibrahim WG, Nair A, Koziol D, Maric D, Hammoud DA (2016) Neurobehavioral abnormalities in the HIV-1 transgenic rat do not correspond to neuronal hypometabolism on 18F-FDG-PET. PLoS One 11:e0152265
Repunte-Canonigo V, Lefebvre C, George O, Kawamura T, Morales M, Koob GF, Califano A, Masliah E, Sanna PP (2014) Gene expression changes consistent with neuroAIDS and impaired working memory in HIV-1 transgenic rats. Mol Neurodegener 9:26
Rodriquiz RM, Wetsel WC (2006) Assessments of cognitive deficits in mutant mice. In: Levin ED, Buccafusco JJ (eds) Animal models of cognitive impairment. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 223–282
Royal W III, Zhang L, Guo M, Jones O, Davis H, Bryant JL (2012) Immune activation, viral gene product expression and neurotoxicity in the HIV-1 transgenic rat. J Neuroimmunol 247:16–24
Shah RS, Cole JW (2010) Smoking and stroke: the more you smoke the more you stroke. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 8:917–932
Song G, Nesil T, Cao J, Yang Z, Chang SL, Li MD (2016) Nicotine mediates expression of genes related to antioxidant capacity and oxidative stress response in HIV-1 transgenic rat brain. J Neuro-Oncol 22:114–124
Sopori M (2002) Effects of cigarette smoke on the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:372–377
Sopori ML, Kozak W, Savage SM, Geng Y, Soszynski D, Kluger MJ, Perryman EK, Snow GE (1998) Effect of nicotine on the immune system: possible regulation of immune responses by central and peripheral mechanisms. Psychoneuroendocrinology 23:189–204
Sultana S, Li H, Puche A, Jones O, Bryant JL, Royal W (2010) Quantitation of parvalbumin+ neurons and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) regulatory gene expression in the HIV-1 transgenic rat: effects of vitamin A deficiency and morphine. J Neuro-Oncol 16:33–40
Taylor BK, Joshi C, Uppal H (2003) Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens inhibits inflammatory pain. Brain Res 987:135–143
Vigorito M, Cao J, Li MD, Chang SL (2013) Acquisition and long-term retention of spatial learning in the human immunodeficiency virus-1 transgenic rat: effects of repeated nicotine treatment. J Neuro-Oncol 19:157–165
Wojna V, Robles L, Skolasky RL, Mayo R, Selnes O, de la Torre T, Maldonado E, Nath A, Melendez LM, Lasalde-Dominicci J (2007) Associations of cigarette smoking with viral immune and cognitive function in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive women. J Neuro-Oncol 13:561–568
Yang Z, Nesil T, Connaghan KP, Li MD, Chang SL (2016) Modulation effect of HIV-1 viral proteins and nicotine on expression of the immune-related genes in brain of the HIV-1 transgenic rats. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 11:562–571
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Royal, W., Can, A., Gould, T.D. et al. Cigarette smoke and nicotine effects on brain proinflammatory responses and behavioral and motor function in HIV-1 transgenic rats. J. Neurovirol. 24, 246–253 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-018-0623-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-018-0623-7