Abstract
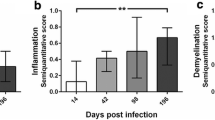
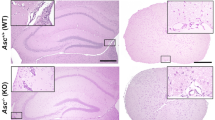
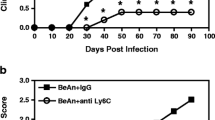
Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease (TMEV-IDD) is an important model of the progressive disability caused by irreversible CNS tissue injury, and provides an example of how a CNS pathogen can cause inflammation, demyelination, and neuronal damage. We were interested in which molecules, especially inflammatory mediators, might be upregulated in the CNS throughout TMEV-IDD. We quantitated by a real-time RT-PCR multi-gene system the expression of a pathway-focused panel of genes at 30 and 165 days post infection, characterizing both the early inflammatory and the late neurodegenerative stages of TMEV-IDD. Also, we measured 32 cytokines/chemokines by multiplex Luminex analysis in CSF specimens from early and late TMEV-IDD as well as sham-treated mice. Results indicate that, in the later stage of TMEV-IDD, activation of the innate immune response is most prominent: TLRs, type I IFN response genes, and innate immunity-associated cytokines were highly expressed in late TMEV-IDD compared to sham (p ≤ 0.0001) and early TMEV-IDD (p < 0.05). Conversely, several molecular mediators of adaptive immune response were highly expressed in early TMEV-IDD (all p ≤ 0.001). Protein detection in the CSF was broadly concordant with mRNA abundance of the corresponding gene measured by real-time RT-PCR in the spinal cord, since several cytokines/chemokines were increased in the CSF of TMEV-IDD mice. Results show a clear shift from adaptive to innate immunity from early to late TMEV-IDD, indicating that adaptive and innate immune pathways are likely involved in the development and progression of the disease to different extents. CSF provides an optimal source of biomarkers of CNS neuroinflammation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arikawa E QG, Han Y, Pan H, Yang J (2011) RT2 Profiler™ PCR arrays: pathway-focused gene expression profiling with qRT-PCR. SABiosciences
Begolka WS, Vanderlugt CL, Rahbe SM, Miller SD (1998) Differential expression of inflammatory cytokines parallels progression of central nervous system pathology in two clinically distinct models of multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 161:4437–4446
Chang JR, Zaczynska E, Katsetos CD, Platsoucas CD, Oleszak EL (2000) Differential expression of TGF-beta, IL-2, and other cytokines in the CNS of Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-infected susceptible and resistant strains of mice. Virology 278:346–360
Chastain EM, Duncan DS, Rodgers JM, Miller SD (2011) The role of antigen presenting cells in multiple sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:265–274
Croxford JL, Olson JK, Miller SD (2002) Epitope spreading and molecular mimicry as triggers of autoimmunity in the Theiler’s virus-induced demyelinating disease model of multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 1:251–260
Cunningham LA, Wetzel M, Rosenberg GA (2005) Multiple roles for MMPs and TIMPs in cerebral ischemia. Glia 50:329–339
da Silva FAFG, da Silva IDCG, Gonçalves GA, de Almeida FA, de Noronha SAAC, de Noronha SMR, Nakamura MU (2014) Viscum album modulates apoptotic related genes in melanoma tumor of mice. Am J Mol Biol 4:49–58
Dal Canto MC, Lipton HL (1975) Primary demyelination in Theiler’s virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Investig 33:626–637
Elgert KD (2009) Immunology: understanding the immune system. Wiley
Elliott R, Li F, Dragomir I, Chua MM, Gregory BD, Weiss SR (2013) Analysis of the host transcriptome from demyelinating spinal cord of murine coronavirus-infected mice. PLoS One 8:e75346
Fainardi E, Castellazzi M, Bellini T, Manfrinato MC, Baldi E, Casetta I, Paolino E, Granieri E, Dallocchio F (2006) Cerebrospinal fluid and serum levels and intrathecal production of active matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as markers of disease activity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 12:294–301
Fang L, Huber-Abel F, Teuchert M, Hendrich C, Dorst J, Schattauer D, Zettlmeissel H, Wlaschek M, Scharffetter-Kochanek K, Tumani H, Ludolph AC, Brettschneider J (2009) Linking neuron and skin: matrix metalloproteinases in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Neurol Sci 285:62–66
Gentilini D, Perino A, Vigano P, Chiodo I, Cucinella G, Vignali M, Di Blasio AM, Busacca M (2011) Gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in endometriosis identifies genes altered in non-gynaecologic chronic inflammatory diseases. Hum Reprod 26:3109–3117
Gonzalez-Navajas JM, Lee J, David M, Raz E (2012) Immunomodulatory functions of type I interferons. Nat Rev Immunol 12:125–135
Gragnani A, Cezillo MV, da Silva ID, de Noronha SM, Correa-Noronha SA, Ferreira LM (2014) Gene expression profile of cytokines and receptors of inflammation from cultured keratinocytes of burned patients. Burns 40:947–956
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Latz E (2014) Innate immune activation in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:463–477
Huang X, Yang Y (2010) Targeting the TLR9-MyD88 pathway in the regulation of adaptive immune responses. Expert Opin Ther Targets 14:787–796
Kandagaddala LD, Kang MJ, Chung BC, Patterson TA, Kwon OS (2012) Expression and activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and NADPH oxidase in tissues and plasma of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:109–114
Lehnardt S (2010) Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: the role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia 58:253–263
Li L, Narayan K, Pak E, Pachner AR (2006) Intrathecal antibody production in a mouse model of Lyme neuroborreliosis. J Neuroimmunol 173:56–68
Lipton HL (1975) Theiler’s virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun 11:1147–1155
Lipton HL, Dal Canto MC (1976) Theiler’s virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science 192:62–64
Lorenzl S, Albers DS, LeWitt PA, Chirichigno JW, Hilgenberg SL, Cudkowicz ME, Beal MF (2003) Tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases are elevated in cerebrospinal fluid of neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Sci 207:71–76
Lorenzl S, Narr S, Angele B, Krell HW, Gregorio J, Kiaei M, Pfister HW, Beal MF (2006) The matrix metalloproteinases inhibitor Ro 28-2653 [correction of Ro 26-2853] extends survival in transgenic ALS mice. Exp Neurol 200:166–171
Mack CL, Vanderlugt-Castaneda CL, Neville KL, Miller SD (2003) Microglia are activated to become competent antigen presenting and effector cells in the inflammatory environment of the Theiler’s virus model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 144:68–79
Martinez NE, Karlsson F, Sato F, Kawai E, Omura S, Minagar A, Grisham MB, Tsunoda I (2014) Protective and detrimental roles for regulatory T cells in a viral model for multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol
Mecha M, Carrillo-Salinas FJ, Mestre L, Feliu A, Guaza C (2013) Viral models of multiple sclerosis: neurodegeneration and demyelination in mice infected with Theiler’s virus. Prog Neurobiol 101–102:46–64
Miller SD, Vanderlugt CL, Begolka WS, Pao W, Yauch RL, Neville KL, Katz-Levy Y, Carrizosa A, Kim BS (1997) Persistent infection with Theiler’s virus leads to CNS autoimmunity via epitope spreading. Nat Med 3:1133–1136
Mogensen TH, Melchjorsen J, Larsen CS, Paludan SR (2010) Innate immune recognition and activation during HIV infection. Retrovirology 7:54
Murray PD, Krivacic K, Chernosky A, Wei T, Ransohoff RM, Rodriguez M (2000) Biphasic and regionally-restricted chemokine expression in the central nervous system in the Theiler’s virus model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurovirol 6(Suppl 1):S44–S52
Olson JK, Girvin AM, Miller SD (2001) Direct activation of innate and antigen-presenting functions of microglia following infection with Theiler’s virus. J Virol 75:9780–9789
Olson JK, Miller SD (2004) Microglia initiate central nervous system innate and adaptive immune responses through multiple TLRs. J Immunol 173:3916–3924
Olson JK, Miller SD (2009) The innate immune response affects the development of the autoimmune response in Theiler’s virus-induced demyelinating disease. J Immunol 182:5712–5722
Pachner AR, Brady J, Narayan K (2007a) Antibody-secreting cells in the central nervous system in an animal model of MS: phenotype, association with disability, and in vitro production of antibody. J Neuroimmunol 190:112–120
Pachner AR, Li L, Lagunoff D (2011) Plasma cells in the central nervous system in the Theiler’s virus model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 232:35–40
Pachner AR, Li L, Narayan K (2007b) Intrathecal antibody production in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 185:57–63
Raddatz BB, Hansmann F, Spitzbarth I, Kalkuhl A, Deschl U, Baumgartner W, Ulrich R (2014) Transcriptomic meta-analysis of multiple sclerosis and its experimental models. PLoS One 9:e86643
Richards MH, Getts MT, Podojil JR, Jin YH, Kim BS, Miller SD (2011) Virus expanded regulatory T cells control disease severity in the Theiler’s virus mouse model of MS. J Autoimmun 36:142–154
Rosenberg GA (2002) Matrix metalloproteinases in neuroinflammation. Glia 39:279–291
Sato S, Reiner SL, Jensen MA, Roos RP (1997) Central nervous system cytokine mRNA expression following Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus infection. J Neuroimmunol 76:213–223
Sorgeloos F, Jha BK, Silverman RH, Michiels T (2013) Evasion of antiviral innate immunity by Theiler’s virus L* protein through direct inhibition of RNase L. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003474
Stavrou S, Feng Z, Lemon SM, Roos RP (2010) Different strains of Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus antagonize different sites in the type I interferon pathway. J Virol 84:9181–9189
Stomrud E, Bjorkqvist M, Janciauskiene S, Minthon L, Hansson O (2010) Alterations of matrix metalloproteinases in the healthy elderly with increased risk of prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 2:20
Tsunoda I, Iwasaki Y, Terunuma H, Sako K, Ohara Y (1996) A comparative study of acute and chronic diseases induced by two subgroups of Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus. Acta Neuropathol 91:595–602
Ulrich R, Kalkuhl A, Deschl U, Baumgartner W (2010) Machine learning approach identifies new pathways associated with demyelination in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. J Cell Mol Med 14:434–448
Virgin HW, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R (2009) Redefining chronic viral infection. Cell 138:30–50
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff of the Center for Comparative Medicine and Research (CCMR) at Dartmouth for their expert care of the mice used for this study. The authors also acknowledge Joanna Hamilton and Carol Ringelberg for their technical assistance with microarray experiments and analyses, as well as Emily Clough for her excellent administrative support.
Conflict of interest
FG has received research support from Biogen Idec. ARP has received personal compensation for activities with Biogen Idec, EMD Serono, Novartis, Hoffman-LaRoche, Schering AG, NovoNordisk, Biomonitor, and Teva Marion as a consultant. ARP has also received research support from Hoffman-LaRoche, Biogen Idec, and Sanofi-Aventis. LL is currently an employee of GenScript USA Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilli, F., Li, L. & Pachner, A.R. The immune response in the CNS in Theiler’s virus induced demyelinating disease switches from an early adaptive response to a chronic innate-like response. J. Neurovirol. 22, 66–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-015-0369-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-015-0369-4