Abstract
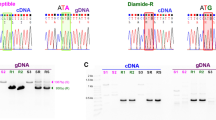
Genotyping for the previously reported G4946E mutation site of the ryanodine receptor (RyR) gene was conducted individually in Plutella xylostella Linnaeus strains with different sensitivities to diamide insecticides. Results obtained by direct sequencing using primers previously reported for the mutation site were not indicative for the resistance status of the strains examined, possibly because of gene duplication. A typical example is that the RyR gene sequences with the G4946E mutation were found in the laboratory-susceptible strain. However, all clones with the G4946E mutation lacked introns, suggesting that the mutation encoded in intronless sequences does not function as a resistance factor. Primers exclusively amplifying the RyR gene sequences with introns were designed based on data obtained by cloning and nucleotide sequencing of RyR gene sequences amplified from 28 insects belonging to six strains. Using the primers, genotyping for the mutation site was conducted individually. Results showed that resistant strains contain more insets of resistant homozygote.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Anthony N, Unruh T, Ganser D, ffrench-Constant R (1998) Duplication of the Rdl GABA receptor subunit gene in an insecticide-resistant aphid, Myzus persicae. Mol Gen Genet 260:165–175
Calvalho R, Yang Y, Field LM, Gorman K, Moores G, Williamson MS, Bass C (2012) Chlorpyrifos resistance is associated with mutation and amplification of the acetylcholinesterqase-1 gene in the tomato red spider mite, Tetranychus evansi. Pestic Biochem Physiol 104:143–149
Charpentier A, Fournier D (2001) Levels of total acetylcholinesterase in Drosophila melanogaster in relation toinsecticide resistance. Pestic Biochem Physiol 70:100–107
Cordova D, Benner EA, Sacher MD, Rauh JJ, Sopa JS, Lahm GP, Selby TP, Stevenson TM, Flexner L, Gutteridge S, Rhoades DF, We L, Smith RM, Tao Y (2006) Anthranilic diamides: a new class of insecticides with a novel mode of action, ryanodine receptor activation. Pestic Biochem Physiol 84:196–214
Fahmy AR, Miyata T (1991) Development and reversion of chlorfluazuron resistance in diamondback moth. In: Talekar NS (ed) Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on the Management of Diamondback Moth, pp 403–410
Guo L, Tang B, Dong W, Liang P, Gao X (2012) Cloning, characterization and expression profiling of the cDNA encoding the ryanodine receptor in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pest Manag Sci 68:1605–1614
Guo L, Liang P, Zhou X, Gao X (2014a) Novel mutations and mutation combinations of ryanodine receptor in a chlorantraniliprole resistant population of Plutella xylostella (L.). Sci Rep 4:6924
Guo L, Wang Y, Zhou X, Li Z, Liu S, Pei L, Gao X (2014b) Functional analysis of a point mutation in the ryanodine receptor of Plutella xylostella (L.) associated with resistance to chlorantraniliprole. Pest Manag Sci 70:1083–1089
Hakamata Y, Nakai J, Takeshima H, Imoto K (1992) Primary structure and distribution of a novel ryanodine receptor/calcium release from rabbit brain. FEBS Lett 312:229–235
Kwon DH, Clark JM, Lee SH (2010) Extensive gene duplication of acetylcholinesterase associated with organophosphate resistance in the two-spotted spider mite. Insect Mol Biol 19:195–204
Labbe P, Berthomieu A, Berticat C, Alout H, Raymond M, Lenormand T, Weill M (2007a) Independent duplications of the acetylcholinesterase gene conferring insecticide resistance in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Mol Biol Evol 24:1056–1067
Labbe P, Berticat C, Berthomieu A, Unal S, Bernard C, Weill M, Lenormand T (2007b) Forty years of erratic insecticide resistance evolution in the mosquito Culex pipiens. PLoS Genet 3:e205
Lahm GP, Selby TP, Freudenberger JH, Stevenson TM, Myers BJ, Seburyamo G, Smith BK, Flexner L, Clark CE, Cordova D (2005) Insecticidal anthranilic diamides: a new class of potent ryanodine receptor activators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:4898–4906
Lahm GP, Stevenson TM, Selby TP, Freudenberger JH, Cordova D, Flexner L, Bellin CA, Dubas CM, Smith BK, Hughes KA, Hollingshaus JG, Clark CE, Benner EA (2007) Rynaxypyr™: a new insecticidal anthranilic diamide that acts as a potent and selective ryanodine receptor activator. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:6274–6279
Lee SH, Kwon DH (2011) Gene duplication in insecticide resistance. In: Friedberg F (ed), Gene duplication, ISBN: 978-953-307-387-3, InTech, Available from: http://www.intechopen.com/books/gene-duplication/gene-duplication-in-insecticide-resistance
Ogawa Y, Maruyama T, Kurebayashi N (1999) Comparison of properties of Ca2+ release channels between rabbit and frog skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biochem 190:191–201
Otsu K, Willard HF, Khanna VK, Zorzato F, Green NM, MacLennan DH (1990) Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 265:13472–13483
Ottini L, Marziali G, Conti AM, Charlesworth A, Sorrentino V (1996) Alpha and beta isoforms of ryanodine receptor from chicken skeletal muscle are the homologues of mammalian RyR1 and RyR3. Biochem J 315:207–216
Sonoda S, Shi X, Song D, Liang P, Gao X, Zhang Y, Li J, Liu Y, Li M, Matsumura M, Sanada-Morimura S, Minakuchi C, Tanaka T, Miyata T (2014) Duplication of acetylcholinesterase gene in diamondback moth strains with different sensitivities to acephate. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 48:83–90
Sparks TC, Nauen R (2015) IRAC: mode of action classification and insecticide resistance management. Pestic Biochem Physiol 121:122–128
Steinbach D, Gutbrod O, Lümmen P, Matthiesen S, Schorn C, Nauen R (2015) Geographic spread, genetics and functional characteristics of ryanodine receptor based target-site resistance to diamide insecticides in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 63:14–22
Takeshima H, Nishimura S, Matsumoto T, Ishida H, Kangawa K, Minamino N, Matsuo H, Ueda M, Hanaoka M, Horose T, Numa S (1989) Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature 339:439–445
Takeshima H, Nishi M, Iwabe N, Miyata T, Hosoya T, Masai I, Hotta Y (1994) Isolation and characterization of a gene for a ryanodine receptor/calcium release channel in Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS Lett 337:81–87
Talekar NS, Shelton AM (1993) Biology, ecology, and management of the diamondback moth. Ann Rev Entomol 38:275–301
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tohnishi M, Nakao H, Furuya T, Seo A, Kodama H, Tsubata K, Fujioka S, Kodama H, Hirooka T, Nishimatsu T (2005) Flubendiamide, a novel insecticide highly active against lepidopterous insect pests. J Pestic Sci 30:354–360
Troczka B, Zimmer CT, Elias J, Schorn C, Bass C, Davis TG, Field LM, Williamson MS, Slater R, Nauen R (2012) Resistance to diamide insecticides in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) is associated with a mutation in the membrane-spanning domain of the ryanodine receptor. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 42:873–880
Wang X, Wu Y (2012) High levels of resistance to chlorantraniliprole evolved in field populations of Plutella xylostella. J Econ Entomol 105:1019–1023
Wang X, Wu S, Yang Y, Wu Y (2012) Molecular cloning, characterization and mRNA expression of a ryanodine receptor gene from diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Pestic Biochem Physiol 102:204–212
Wang X, Khakame SK, Ye C, Yang Y, Wu Y (2013) Characterisation of field-evolved resistance to chlorantraniliprole in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella, from China. Pest Manag Sci 69:661–665
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Japan, through a research project titled Genomics-based Technology for Agricultural Improvement, and the Ohara Foundation for Agricultural Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonoda, S., Kataoka, Y. Genotyping for the G4946E site of ryanodine receptor gene in Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) considering gene duplication. Appl Entomol Zool 51, 195–204 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0385-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13355-015-0385-0