Abstract
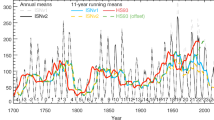
A Tibetan ozone low was found in the 1990s after the Antarctic ozone hole. Whether this ozone low has been recovering from the beginning of the 2000s following the global ozone recovery is an intriguing topic. With the most recent merged TOMS/SBUV (Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer/Solar Backscatter Ultra Violet) ozone data, the Tibetan ozone low and its long-term variation during 1979–2010 are analyzed using a statistical regression model that includes the seasonal cycle, solar cycle, quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO), ENSO signal, and trends. The results show that the Tibetan ozone low maintains and may become more severe on average during 1979–2010, compared with its mean state in the periods before 2000, possibly caused by the stronger downward trend of total ozone concentration over the Tibet. Compared with the ozone variation over the non-Tibetan region along the same latitudes, the Tibetan ozone has a larger downward trend during 1979–2010, with a maximum value of −0.40±0.10 DU yr−1 in January, which suggests the strengthening of the Tibetan ozone low in contrast to the recovery of global ozone. Regression analyses show that the QBO signal plays an important role in determining the total ozone variation over the Tibet. In addition, the long-term ozone variation over the Tibetan region is largely affected by the thermal-dynamical proxies such as the lower stratospheric temperature, with its contribution reaching around 10% of the total ozone change, which is greatly different from that over the non-Tibetan region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, J., K. Tourpali, E. Rozanov, et al., 2008: Coupled chemistry climate model simulations of the solar cycle in ozone and temperature. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D11306, doi: 10.1029/2007JD009391.
Baldwin, M. P., L. J. Gray, T. J. Dunkerton, et al., 2001: The quasi-biennial oscillation. Rev. Geophys., 39, 179–229.
Bian Jianchun, Li Weiliang, and Zhou Xiuji, 1997: Analysis of the seasonal variation feature of the wind structure over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Ozone Changes Over China and Its Influences on Climate and Environment. Zhou Xiuji, Ed., China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 257–273.
Bodeker, G. E., J. C. Scott, K. Kreher, et al., 2001: Global ozone trends in potential vorticity coordinates using TOMS and GOME intercompared against the Dobson network: 1978–1998. J. Geophys. Res., 106, 23029–23042.
Cong Chunhua, Li Weiliang, and Zhou Xiuji, 2001: The air mass exchange between the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Chinese Sci. Bull., 46(22), 1914–1918. (in Chinese)
Farman, J. C., B. G. Gardiner, and J. D. Shanklin, 1985: Large losses of total ozone in Antarctica reveal seasonal ClOx/NOx interaction. Nature, 315, 207–210, doi: 10.1038/315207a0.
Fioletov, V. E., G. E. Bodeker, A. J. Miller, et al., 2002: Global and zonal total ozone variations estimated from ground-based and satellite measurements. J. Geophys. Res., 107(D22), 4647, doi: 10.1029/2001JD001350.
Fu Chao, Li Weiliang, and Zhou Xiuji, 1997: Numerical simulation of the formation of ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings. Ozone Changes Over China and Its Influences on Climate and Environment. Zhou Xiuji, Ed., China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 274–285.
Guillas, S., M. L. Stein, D. J. Wuebbles, et al., 2004: Using chemistry transport modeling in statistical analysis of stratospheric ozone trends from observations. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D22303, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005049.
Guo Dong, Wang Panxing, Zhou Xiuji, et al., 2012: Dynamic effects of the South Asian high on the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 26(2), 216–228, doi: 10.1007/s13351-012-0207-2.
Liu Yu and Li Weiliang, 2001: Deepening of ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau and its possible influences. Acta Meteor. Sinica, 59, 97–106. (in Chinese)
—, Li Weiliang, Zhou Xiuji, et al., 2003: Mechanism of formation of the ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau in summer-Transport and chemical process of ozone. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 20(1), 103–109.
Manney, G. L., L. Froidevaux, J. W. Waters, et al., 1994: Chemical depletion of ozone in the Arctic lower stratosphere during winter 1992–93. Nature, 370, 429–434.
Newchurch, M. J., E. -S. Yang, D. M. Cunnold, et al., 2003: Evidence for slowdown in stratospheric ozone loss: First stage of ozone recovery. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4507, doi: 10.1029/2003JD003471.
Newman, P. A., and W. J. Randel, 1988: Coherent ozonedynamical changes during the Southern Hemisphere spring, 1979–1986. J. Geophys. Res., 93, 12585–12606.
Randel, W. J., and J. B. Cobb, 1994: Coherent variations of monthly total ozone and lower stratosphereic temperature. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 5433–5447.
—, F. Wu, J. M. Russell III, et al., 1995: Ozone and temperature changes in the stratosphere following the eruption of Mount Pinatubo. J. Geophys. Res., 100, 16753–16764.
—, and M. Park, 2006: Deep convective influence on the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated tracer variability observed with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). J. Geophys. Res., 111, D12314, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006490.
Reinsel, G. C., E. C. Weatherhead, G. C. Tiao, et al., 2002: On detection of turnaround and recovery in trend for ozone. J. Geophys. Res., 107, 4078, doi: 10.1029/2001JD000500.
—, A. J. Miller, E. C. Weatherhead, et al., 2005: Trend analysis of total ozone data for turnaround and dynamical contributions. J. Geophys. Res., 110, D16306, doi: 10.1029/2004JD004662.
Tian, W. S., M. Chipperfield, and Q. Huang, 2008: Effects of the Tibetan Plateau on total column ozone distribution. Tellus, 60B, 622–635.
World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 2003: Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2002. Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 47, Geneva, Switzerland, 498 pp.
—, 2007: Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2006. Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 50, Geneva, Switzerland, 572 pp.
Xu Xiangde and Chen Lianshou, 2006: Advances of the study on Tibetan Plateau experiment of atmospheric sciences. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 17(6), 756–772.
Ye Zhuojia and Xu Yongfu, 2003: Climate characteristics of ozone over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res., 108(D20), 4654, doi: 10.1029/2002JD003139.
Zheng Xiangdong, Tang Jie, Li Weiliang, et al., 2000: Observational study on total ozone amount and its vertical profile over Lhasa in the summer of 1998. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci., 11, 173–179. (in Chinese)
Zhou, L. B., H. Akiyoshi, and K. Kawahira, 2003: Analysis of year-to-year ozone variation over the subtropical western Pacific region using EP_TOMS data and CCSR/NIES nudging CTM. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4627, doi: 10.1029/2003 JD003412.
Zhou Shunwu and Zhang Renhe, 2005: Decadal variations of temperature and geopotential height over the Tibetan Plateau and their relations with Tibetan ozone depletion. Geophys. Res. Lett., 32, L18705.
Zhou Xiuji and Luo Chao, 1994: Ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau, Acta. Meteror. Sinica, 8, 505–506.
—, —, Li Weiliang, et al., 1995: Variation of total ozone over China and the Tibetan Plateau low center. Chinese Sci. Bull., 40(15), 1396–1398. (in Chinese)
Ziemke, J. R., S. Chandra, R. D. McPeters, et al., 1997: Dynamical proxies of column ozone with applications to global trend models. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 6117–6129.
Zou Han, 1996: Seasonal variation and trends of TOMS ozone over Tibet. Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 1029–1032.
— and Gao Yongqi, 1997: Vertical ozone profile over Tibet using Sage I and II data. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 14, 505–512.
—, Ji Chongping, and Zhou Libo, 2000: QBO signal in total ozone over Tibet. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 17, 562–568.
—, —, —, et al., 2001: ENSO signal in total ozone over Tibet. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 231–238.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research and Development (973) Program of China (2009CB421403), State Oceanic Administration Public Science and Technology Research Fund (201005017-5), China Meteorological Administration Special Public Welfare Research Fund (GYHY201106018), and State Oceanic Administration Polar Environment Investigation and Assessment Project (CHINARE2012-04-04 and CHINARE2012-02-03).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, L., Zou, H., Ma, S. et al. The Tibetan ozone low and its long-term variation during 1979–2010. Acta Meteorol Sin 27, 75–86 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-013-0108-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-013-0108-9