Abstract
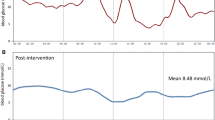
An 85-year-old woman was admitted to our hospital because of hypoglycemia and impairment of consciousness several hours after breakfast. Because the hypoglycemia predominantly occurred 2–4 h after meals, we diagnosed reactive hypoglycemia. An oral glucose tolerance test showed prolonged hyperinsulinemia following the postprandial hyperglycemia, with a subsequent rapid decrease in blood glucose concentration. The post-stimulus plasma C-peptide concentration was relatively low compared to the plasma insulin concentration. Abdominal computed tomography revealed an intrahepatic congenital portosystemic shunt (CPSS). On the basis of these findings, we concluded that the reactive hypoglycemia was induced by the CPSS, via a reduction in hepatic insulin extraction. Treatment with an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor resolved the reactive hypoglycemia. CPSS comprises anomalous vascular connections between the portal vein and the systemic venous circulation, and reactive hypoglycemia is a rare complication of this malformation, which has most frequently been reported in children, with only a few cases reported in adults. However, this case indicates that even in adult patients, imaging studies should be conducted to rule out CPSS as the cause of the reactive hyperglycemia.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in the present report are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hofeldt FD. Reactive hypoglycemia. Metabolism. 1975;24(10):1193–208.
Shah P, Rahman SA, Demirbilek H, et al. Hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia in children and adults. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(9):729–42.
Tsitouridis I, Sotiriadis C, Michaelides M, et al. Intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunts: radiological evaluation. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009;15(3):182–7.
Palvanov A, Marder RL, Siegel D. Asymptomatic intrahepatic portosystemic venous shunt: to treat or not to treat? Int J Angiol. 2016;25(3):193–8.
Pocha C, Maliakkal B. Spontaneous intrahepatic portal-systemic venous shunt in the adult: case report and review of the literature. Dig Dis Sci. 2004;49(7–8):1201–6.
Sokollik C, Bandsma RH, Gana JC, et al. Congenital portosystemic shunt: characterization of a multisystem disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;56(6):675–81.
Xu S, Zhang P, Hu L, et al. Case report: clinical features of congenital portosystemic shunts in the neonatal period. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:778–91.
Uchino T, Matsuda I, Endo F. The long-term prognosis of congenital portosystemic venous shunt. J Pediatr. 1999;135(2 Pt 1):254–6.
Paganelli M, Lipsich JE, Sciveres M, et al. Predisposing factors for spontaneous closure of congenital portosystemic shunts. J Pediatr. 2015;167(4):931–5.
Peček J, Fister P, Homan M. Abernethy syndrome in Slovenian children: five case reports and review of literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26(37):5731–44.
Bas S, Guran T, Atay Z, et al. Premature pubarche, hyperinsulinemia and hypothyroxinemia: novel manifestations of congenital portosystemic shunts (Abernethy malformation) in children. Horm Res Paediatr. 2015;83(4):282–7.
Senniappan S, Pitt K, Shah P, et al. Postprandial hyperinsulinaemic hypoglycaemia secondary to a congenital portosystemic shunt. Horm Res Paediatr. 2015;83(3):217–20.
Weigert A, Bierwolf J, Reutter H, et al. Congenital intrahepatic portocaval shunts and hypoglycemia due to secondary hyperinsulinism: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2018;12(1):336.
Yoshii K, Noda M, Naiki Y, et al. Portosystemic shunt as a cause of congenital hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Pediatr Int. 2017;59(4):512–4.
Ghasemi-Rad M, Smuclovisky E, Cleveland H, et al. Endovascular treatment of a portosystemic shunt presenting with hypoglycemia; case presentation and review of literature. Clin Imaging. 2022;83:131–7.
Duprey J, Gouin B, Benazet MF, et al. Glucose intolerance and post-stimulatory hypoglycemia secondary to a probably congenital intrahepatic portacaval anastomosis. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 1985;136(8):655–8 (Abstract only).
Chagnon SF, Vallee CA, Barge J, et al. Aneurysmal portahepatic venous fistula: report of two cases. Radiology. 1986;159(3):693–5.
Gouin B, Le Gal J, Duprey J, et al. Congenital intrahepatic portacaval anastomosis: analysis of manifested glucose abnormalities. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1984;8(5):464–8 (Abstract only).
Bratusch-Marrain PR, Waldhäusl WK, Gasić S, et al. Hepatic disposal of biosynthetic human insulin and porcine C-peptide in humans. Metabolism. 1984;33(2):151–7.
Meier JJ, Veldhuis JD, Butler PC. Pulsatile insulin secretion dictates systemic insulin delivery by regulating hepatic insulin extraction in humans. Diabetes. 2005;54(6):1649–56.
De León DD, Stanley CA. Determination of insulin for the diagnosis of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;27(6):763–9.
Harris MI, Cowie CC, Gu K, et al. Higher fasting insulin but lower fasting C-peptide levels in African Americans in the US population. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18(2):149–55.
Faber OK, Christensen K, Kehlet H, et al. Decreased insulin removal contributes to hyperinsulinemia in obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981;53(3):618–21.
Iwasaki Y, Ohkubo A, Kajinuma H, et al. Degradation and secretion of insulin in hepatic cirrhosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978;47(4):774–9.
Johnson DG, Alberti KG, Faber OK, et al. Hyperinsulinism of hepatic cirrhosis: diminished degradation or hypersecretion? Lancet. 1977;1(8001):10–3.
Heding LG, Rasmussen SM. Human C-peptide in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1975;11(3):201–6.
Kajinuma H, Kanazawa Y, Sando H, et al. Human plasma C-peptide immunoreactivity: its correlation with immunoreactive insulin in diabetes, and chronic liver and renal diseases. Endocrinol Jpn. 1979;26(1):65–73.
Joshi SR, Standl E, Tong N, et al. Therapeutic potential of α-glucosidase inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an evidence-based review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(13):1959–81.
Narita T, Yokoyama H, Yamashita R, et al. Comparisons of the effects of 12-week administration of miglitol and voglibose on the responses of plasma incretins after a mixed meal in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(3):283–7.
Miyake K, Takashi Y, Matsuzawa Y, et al. A case of severe postprandial hypoglycemia suspected to be caused by hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis. J Jpn Diabetes Soc. 2014;57(9):714–21.
Meneilly GS, Cheung E, Tuokko H. Altered responses to hypoglycemia of healthy elderly people. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;78(6):1341–8.
Shnayder MM, Dervishi M, Jo A, et al. Congenital portosystemic shunt occlusion with an Amplatzer PFO occlusion device: a case report. CVIR Endovasc. 2021;4(1):14.
Imhof A, Schneemann M, Schaffner A, et al. Reactive hypoglycaemia due to late dumping syndrome: successful treatment with acarbose. Swiss Med Wkly. 2001;131(5–6):81–3.
Kihara Y, Ogami Y, Tabaru A, et al. Safe and effective treatment of diabetes mellitus associated with chronic liver diseases with an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, acarbose. J Gastroenterol. 1997;32(6):777–82.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mark Cleasby, PhD, from Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first draft of the manuscript was written by AF. AF, SK, KU, and HF were in charge of treatment during hospitalization. AF and SK reviewed and edited the manuscript. NS, HF, and KU contributed to discussion. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Human and animal rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the Ethical Standards of the responsible National Committee on Human Experimentation and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent was obtained from the patient for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Fujiwara, A., Kanda, S., Ueno, K. et al. Reactive hypoglycemia owing to an intrahepatic congenital portosystemic shunt in an older patient. Diabetol Int 14, 298–303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-023-00627-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-023-00627-z