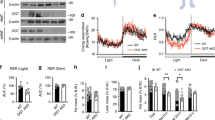
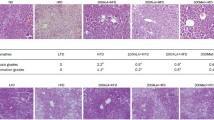
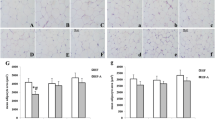
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is an expanding epidemic, closely linked to obesity. Peripheral insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion remain the core defects in T2DM. Despite significant advances in unraveling the underlying these defects, many of the metabolic pathways and regulators involved in insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction are not completely understood. This review proposes that manipulating the fatty acid (FA) composition by blocking ELOVL fatty acid elongase 6 (Elovl6) could protect against insulin resistance, impaired insulin secretion, and obesity-related disorders. The molecular mechanism of this new paradigm is also discussed. Elovl6 is a microsomal enzyme involved in the elongation of C16 saturated and monounsaturated FAs to form C18 FAs. We have reported that mice with Elovl6 deletion are protected against obesity-induced insulin resistance or β-cell failure when mated to leptin receptor-deficient db/db mice because the cellular FA composition is changed, even with concurrent obesity. Therefore, Elovl6 appears to be a crucial metabolic checkpoint, and limiting Elovl6 expression or activity could be a new therapeutic approach to treat T2DM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, Nag S, et al. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:2130–5.
Hill JO. Understanding and addressing the epidemic of obesity: an energy balance perspective. Endocr Rev. 2006;27:750–61.
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. 2006;444:840–6.
Unger RH. Lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of obesity-dependent NIDDM. Genetic Clin Implic Diabetes. 1995;44:863–70.
van Herpen NA, Schrauwen-Hinderling VB. Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol Behav. 2008;94:231–41.
Shulman GI. Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, cardiometabolic disease. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2237–8.
Guillou H, Zadravec D, Martin PG, Jacobsson A. The key roles of elongases and desaturases in mammalian fatty acid metabolism: Insights from transgenic mice. Prog Lipid Res. 2010;49:186–99.
Matsuzaka T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Yoshikawa T, Amemiya-Kudo M, Hasty AH, et al. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian fatty acyl-CoA elongase as a lipogenic enzyme regulated by SREBPs. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:911–20.
Moon YA, Shah NA, Mohapatra S, Warrington JA, Horton JD. Identification of a mammalian long chain fatty acyl elongase regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:45358–66.
Matsuzaka T, Shimano H, Yahagi N, Kato T, Atsumi A, Yamamoto T, et al. Crucial role of a long-chain fatty acid elongase, Elovl6, in obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2007;13:1193–202.
Petersen MC, Shulman GI. Roles of diacylglycerols and ceramides in hepatic insulin resistance. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38:649–65.
Zhao H, Matsuzaka T, Nakano Y, Motomura K, Tang N, Yokoo T, et al. Elovl6 deficiency improves glycemic control in diabetic db/db mice by expanding beta-cell mass and increasing insulin secretory capacity. Diabetes. 2017;66:1833–46.
Matsuzaka T, Kuba M, Koyasu S, Yamamoto Y, Motomura K, Arulmozhiraja S, et al. Hepatocyte ELOVL fatty acid elongase 6 determines ceramide acyl-chain length and hepatic insulin sensitivity in mice. Hepatology. 2020;71:1609–25.
Ruhanen H, Perttila J, Holtta-Vuori M, Zhou Y, Yki-Jarvinen H, Ikonen E, et al. PNPLA3 mediates hepatocyte triacylglycerol remodeling. J Lipid Res. 2014;55:739–46.
Mitsche MA, Hobbs HH, Cohen JC. Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 promotes transfer of essential fatty acids from triglycerides to phospholipids in hepatic lipid droplets. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:9232.
Chavez JA, Summers SA. A ceramide-centric view of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012;15:585–94.
Chaurasia B, Summers SA. Ceramides - lipotoxic inducers of metabolic disorders. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015;26:538–50.
Oaks J, Ogretmen B. Regulation of PP2A by sphingolipid metabolism and signaling. Front Oncol. 2014;4:388.
Mukhopadhyay A, Saddoughi SA, Song P, Sultan I, Ponnusamy S, Senkal CE, et al. Direct interaction between the inhibitor 2 and ceramide via sphingolipid-protein binding is involved in the regulation of protein phosphatase 2A activity and signaling. FASEB J. 2009;23:751–63.
Morcillo S, Martín-Núñez GM, Rojo-Martínez G, Almaraz MC, García-Escobar E, Mansego ML, et al. ELOVL6 genetic variation is related to insulin sensitivity: a new candidate gene in energy metabolism. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(6):e21198.
Liu Y, Wang F, Yu XL, Miao ZM, Wang ZC, Chen Y, et al. Genetic analysis of the ELOVL6 gene polymorphism associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013;46(7):623–8.
Maycotte-Cervantes ML, Aguilar-Galarza A, Anaya-Loyola MA, Anzures-Cortes ML, Haddad-Talancón L, Méndez-Rangel AS, et al. Influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms of ELOVL on biomarkers of metabolic alterations in the Mexican population. Nutrients. 2020;12(11):E3389.
Acknowledgements
This review is a summary of my presentation in the Lilly Award Lecture at the 63rd annual meeting of the Japan Diabetes Society, Otsu, Japan. I would like to express sincere gratitude to Professor Hitoshi Shimano, Professor Nobuhiro Yamada, and all members of department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, University of Tsukuba for their guidance and continuous support for my projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Human or animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuzaka, T. Role of fatty acid elongase Elovl6 in the regulation of energy metabolism and pathophysiological significance in diabetes. Diabetol Int 12, 68–73 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00481-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00481-3