Abstract
Background and Objective
Dutasteride, an analog of testosterone, a 5α-reductase inhibitor is widely used in the treatment of moderate to severe symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia. The aim of this study was to compare the pharmacokinetic characteristics of dutasteride in beagle dogs after oral administration of a conventional soft gelatin capsule (Avodart®) and a novel solid-supersaturatable soft-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) tablet.
Methods
In this comparative dissolution study, the dissolution of dutasteride was pH-independent for both formulations. Noncompartmental analysis and modeling approaches were carried out to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of dutasteride.
Results
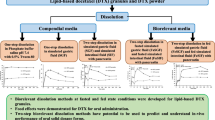
Approximately 90% of the drug dissolved in all media within 15 min, indicating that there was little difference in the dissolution rate of the solid-supersaturatable SMEDDS tablets and that of the commercial soft gelatin capsules. Using t test analysis, no statistically significant difference was detected in the pharmacokinetic parameters of the two formulations. The test/reference geometric mean ratios were 1.087 (90% confidence intervals 0.8529–1.3854) for the area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from 0 to the last time point (48 h) with a measurable concentration and 1.094 (90% confidence intervals 0.8909–1.3454) for maximum plasma concentration. Unfortunately, the bioequivalent criterium (0.8–1.25) was not met due to the small sample size, but the results of this study suggest a possible bioequivalence of dutasteride in the two formulations.
Conclusion
Based on the results of this study, the development of a tablet dosage form of dutasteride using a solid-supersaturatable SMEDDS should be considered for humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roehrborn CG, Boyle P, Nickel JC, Hoefner K, Andriole G. Efficacy and safety of a dual inhibitor of 5-alpha-reductase types 1 and 2 (dutasteride) in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology. 2002;60(3):434–41.
Fossler M, Zhu J, Roehrborn C, McAleese P, Manyak M. Impact of formulation on the pharmacokinetics of dutasteride: results from two phase I studies. Clin Drug Investig. 2016;36(9):763–7.
Savla R, Browne J, Plassat V, Wasan KM, Wasan EK. Review and analysis of FDA approved drugs using lipid-based formulations. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2017;43(11):1743–58.
Meyer MC, Straughn AB, Mhatre RM, Hussain A, Shah VP, Bottom CB, et al. The effect of gelatin cross-linking on the bioequivalence of hard and soft gelatin acetaminophen capsules. Pharm Res. 2000;17(8):962–6.
Gullapalli RP. Soft gelatin capsules (softgels). J Pharm Sci. 2010;99(10):4107–48.
Ofner CM III, Zhang YE, Jobeck VC, Bowman BJ. Crosslinking studies in gelatin capsules treated with formaldehyde and in capsules exposed to elevated temperature and humidity. J Pharm Sci. 2001;90(1):79–88.
Liu J-Y, Zhang X-X, Huang H-Y, Lee B-J, Cui J-H, Cao Q-R. Esomeprazole magnesium enteric-coated pellet-based tablets with high acid tolerance and good compressibility. J Pharm Investig. 2018;48(3):1–10.
Min M-H, Park J-H, Choi M-R, Hur J-H, Ahn B-N, Kim D-D. Formulation of a film-coated dutasteride tablet bioequivalent to a soft gelatin capsule (Avodart®): effect of γ-cyclodextrin and solubilizers. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2019;14(3):313–20.
Baek I-H, Ha E-S, Yoo J-W, Jung Y, Kim M-S. Design of a gelatin microparticle-containing self-microemulsifying formulation for enhanced oral bioavailability of dutasteride. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2015;9:3231.
Kim M-S, Ha E-S, Choo G-H, Baek I-H. Preparation and in vivo evaluation of a dutasteride-loaded solid-supersaturatable self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(5):10821–33.
Choo G-H, Park S-J, Hwang S-J, Kim M-S. Formulation and in vivo evaluation of a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of dutasteride. Drug Res. 2013;63(04):203–9.
Kim M-S. Soluplus-coated colloidal silica nanomatrix system for enhanced supersaturation and oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2013;41(6):363–7.
Kim M-S. Evaluation of in vitro dissolution and in vivo oral absorption of dutasteride-loaded eudragit E nanoparticles. Drug Res. 2013;63(06):326–30.
Park S-J, Choo G-H, Hwang S-J, Kim M-S. Quality by design: screening of critical variables and formulation optimization of Eudragit E nanoparticles containing dutasteride. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36(5):593–601.
Kim M-S. Influence of hydrophilic additives on the supersaturation and bioavailability of dutasteride-loaded hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin nanostructures. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:2029.
Beak I-H, Kim M-S. Improved supersaturation and oral absorption of dutasteride by amorphous solid dispersions. Chem Pharm Bull. 2012;60(11):1468–73.
Madhav KV, Kishan V. Self microemulsifying particles of loratadine for improved oral bioavailability: preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Pharm Investig. 2018;48(4):497–508.
Vadlamudi HC, Yalavarthi PR, Nagaswaram T, Rasheed A, Peesa JP. In-vitro and pharmacodynamic characterization of solidified self microemulsified system of quetiapine fumarate. J Pharm Investig. 2019;49(1):161–72.
Singh D, Bedi N, Tiwary AK. Enhancing solubility of poorly aqueous soluble drugs: critical appraisal of techniques. J Pharm Investig. 2018;48(5):509–26.
Ahsan MN, Verma PRP. Enhancement of in vitro dissolution and pharmacodynamic potential of olanzapine using solid SNEDDS. J Pharm Investig. 2018;48(3):269–78.
Kim R, Jang D-J, Kim Y, Yoon J-H, Min K, Maeng H-J, et al. Flurbiprofen-loaded solid SNEDDS preconcentrate for the enhanced solubility, in-vitro dissolution and bioavailability in rats. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10(4):247.
Nikolakakis I, Partheniadis I. Self-emulsifying granules and pellets: composition and formation mechanisms for instant or controlled release. Pharmaceutics. 2017;9(4):50.
Tong Y, Wang Y, Yang M, Yang J, Chen L, Chu X, et al. Systematic development of self-nanoemulsifying liquisolid tablets to improve the dissolution and oral bioavailability of an oily drug, vitamin K1. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10(3):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics10030096.
Baek I-H, Lee B-Y, Kang W, Kwon K-I. Pharmacokinetic analysis of two different doses of duloxetine following oral administration in dogs. Drug Res. 2013;63(08):404–8.
Research CfDEa. Guidance for industry: bioanalytical method validation. US Food & Drug Administration. 2001.
WinNonlin. User’s guide (ver. 5.2). Pharsight Corporation: Mountain View, CA, USA. 2007.
Baek I-H, Lee B-Y, Lee E-S, Kwon K-I. Pharmacokinetics of angiotensin II receptor blockers in the dog following a single oral administration. Drug Res. 2013;63(07):357–61.
Kuentz M, Nick S, Parrott N, Röthlisberger D. A strategy for preclinical formulation development using GastroPlus™ as pharmacokinetic simulation tool and a statistical screening design applied to a dog study. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;27(1):91–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Funding
This research was supported by Kyungsung University Research Grants in 2018.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
All animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the KPC laboratory, a non-clinical contract research organization. The experiments were conducted in compliance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the institute.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Ha, ES., Park, H. et al. Pharmacokinetic Study of a Soft Gelatin Capsule and a Solid-Supersaturatable SMEDDS Tablet of Dutasteride in Beagle Dogs. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 45, 235–241 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-019-00594-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-019-00594-4