Abstract
Baicalin is one of the major bioactive components of Scutellaria radix, a Chinese herb that has been used since ancient times. Baicalin has various pharmacological activities, including antitumor, antimicrobial, and antioxidant, and has wide clinical applications. Baicalin displays a distinct pharmacokinetic profile including gastrointestinal hydrolysis, enterohepatic recycling, carrier-mediated transport, and complicated metabolism. The in vivo disposition of baicalin is affected by combinations of other herbs and baicalin can interact with other co-administered drugs due to competition between metabolic enzymes and protein binding. Furthermore, baicalin exhibits altered pharmacokinetic properties under different pathological conditions. Due to its low bioavailability, emerging novel baicalin preparations including nano/micro-scale baicalin delivery systems show better absorption and higher bioavailability in preclinical studies, and show promise for future clinical applications. Thus, this current review offers a comprehensive report on the pharmacokinetic behavior of baicalin and strategies to improve its bioavailability.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao Q, Chen XY, Martin C. Scutellaria baicalensis, the golden herb from the garden of Chinese medicinal plants. Sci Bull (Beijing). 2016;61(18):1391–8.
Noh K, Kang Y, Nepal M, Jeong K, Oh D, Kang M, Lee S, Kang W, Jeong H, Jeong T. Role of intestinal microbiota in baicalin-induced drug interaction and its pharmacokinetics. Molecules. 2016;21(3):337.
Xing J, Chen X, Zhong D. Absorption and enterohepatic circulation of baicalin in rats. Life Sci. 2005;78(2):140–6.
Kalapos-Kovács B, Magda B, Jani M, Fekete Z, Szabó PT, Antal I, Krajcsi P, Klebovich I. Multiple ABC transporters efflux baicalin. Phytother Res. 2015;29(12):1987–90.
Zhang J, Cai W, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Wu X, Li Y, Lu J, Qiao Y. Profiling and identification of the metabolites of baicalin and study on their tissue distribution in rats by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2015;985:91–102.
Lai MY, Hsiu SL, Chen CC, Hou YC, Chao PD. Urinary pharmacokinetics of baicalein, wogonin and their glycosides after oral administration of Scutellariae radix in humans. Biol Pharm Bull. 2003;26(1):79–83.
Tian X, Cheng ZY, He J, Jia LJ, Qiao HL. Concentration-dependent inhibitory effects of baicalin on the metabolism of dextromethorphan, a dual probe of CYP2D and CYP3A, in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203(2):522–9.
Ma S, Zhao M, Liu H, Wang L, Zhang X. Pharmacokinetic effects of baicalin on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion after iv administration in rats. Chin Herbal Med. 2012;4(1):53–7.
Zhang Z, Qin L, Peng L, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Lu Z, Song Y, Gao X. Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling to study the antipyretic effect of Qingkailing injection on Pyrexia model rats. Molecules. 2016;21(3):317.
Taiming L, Xuehua J. Investigation of the absorption mechanisms of baicalin and baicalein in rats. J Pharm Sci. 2006;95(6):1326–33.
Li M, Shi A, Pang H, Xue W, Li Y, Cao G, Yan B, Dong F, Li K, Xiao W, He G, Du G, Hu X. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of a single ascending dose of baicalein chewable tablets in healthy subjects. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;156:210–5.
Fong YK, Li CR, Wo SK, Wang S, Zhou L, Zhang L, Lin G, Zuo Z. In vitro and in situ evaluation of herb–drug interactions during intestinal metabolism and absorption of baicalein. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;141(2):742–53.
Zhang R, Cui Y, Wang Y, Tian X, Zheng L, Cong H, Wu B, Huo X, Wang C, Zhang B. Catechol-O-methyltransferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in the metabolism of baicalein in different species. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017;42(6):1–12.
Akao T, Kawabata K, Yanagisawa E, Ishihara K, Mizuhara Y, Wakui Y, Sakashita Y, Kobashi K. Baicalin, the predominant flavone glucuronide of Scutellariae radix, is absorbed from the rat gastrointestinal tract as the aglycone and restored to its original form. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2000;52(12):1563–8.
Huang P, Gao JW, Shi Z, Zou JL, Lu YS, Yuan YM, Yao MC. A novel UPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of rhein, emodin, berberine and baicalin in rat plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study. Bioanalysis. 2012;4(10):1205.
Zhao Y, Kong H, Sun Y, Feng H, Zhang Y, Su X, Qu H, Wang Q. Assessment of baicalin in mouse blood by monoclonal antibody-based icELISA. Biomed Chromatogr. 2014;28(12):1864–8.
Zhang J, Zhang S, Teng S, Zhai L. An LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of four flavonoids from Semen Oroxyli in rat plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016;1020:96–102.
Zhang ZQ, Liua W, Zhuang L, Wang J, Zhang S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin, wogonoside, baicalein and wogonin in plasma after oral administration of pure baicalin, radix Scutellariae and Scutellariae–Paeoniae couple extracts in normal and ulcerative colitis rats. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013;12(3):399–409.
Lu T, Song J, Huang F, Deng Y, Xie L, Wang G, Liu X. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin after oral administration of pure baicalin, radix Scutellariae extract and Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang to rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;110(3):412–8.
Shaw LH, Lin LC, Tsai TH. HPLC-MS/MS analysis of a traditional Chinese medical formulation of Bu-Yang-Huan-Wu-Tang and its pharmacokinetics after oral administration to rats. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43848.
Tong L, Wan M, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Sun H, Bi K. Simultaneous determination of baicalin, wogonoside, baicalein, wogonin, oroxylin A and chrysin of radix Scutellariae extract in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;70:6–12.
Song JZ, Li LJ, Ji L, Shun L, Rui Y. The pharmacokinetics of Tiangou antihypertensive capsule in rat in vivo. Biomed Rep. 2017;6(1):113–9.
Tang Y, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Huang C. Determination of human plasma protein binding of baicalin by ultrafiltration and high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr. 2006;20(10):1116–9.
Liu H, Bao W, Ding H, Jang J, Zou G. Binding modes of flavones to human serum albumin: insights from experimental and computational studies. J Phys Chem B. 2010;114(40):12938–47.
Zhang L, Lin G, Kovacs B, Jani M, Krajcsi P, Zuo Z. Mechanistic study on the intestinal absorption and disposition of baicalein. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007;31(3–4):221–31.
Akao T, Sato K, Hanada M. Hepatic contribution to a marked increase in the plasma concentration of baicalin after oral administration of its aglycone, baicalein, in multidrug resistance-associated protein 2-deficient rat. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009;32(12):2079–82.
Wei Y, Pi C, Yang G, Xiong X, Lan Y, Yang H, Zhou Y, Ye Y, Zou Y, Zheng W, Zhao L. LC-UV determination of baicalin in rabbit plasma and tissues for application in pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution studies of baicalin after intravenous administration of liposomal and injectable formulations. Molecules. 2016;21(4):444.
Zhu H, Qian Z, He F, Liu M, Pan L, Zhang Q, Tang Y. Novel pharmacokinetic studies of the Chinese formula Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang in MCAO rats. Phytomedicine. 2013;20(10):767–74.
Tarragó T, Kichik N, Claasen B, Prades R, Teixidó M, Giralt E. Baicalin, a prodrug able to reach the CNS, is a prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16(15):7516–24.
Tsai PL, Tsai TH. Pharmacokinetics of baicalin in rats and its interactions with cyclosporin A, quinidine and SKF-525A: a microdialysis study. Planta Med. 2004;70(11):1069–74.
Fong S, Li C, Ho YC, Li R, Wang Q, Wong YC, Xue H, Zuo Z. Brain uptake of bioactive flavones in Scutellariae radix and its relationship to anxiolytic effect in mice. Mol Pharm. 2017;14(9):2908–16.
Zhang L, Xing D, Wang W, Wang R, Du L. Kinetic difference of baicalin in rat blood and cerebral nuclei after intravenous administration of Scutellariae radix extract. J Ethnopharmacol. 2006;103(1):120–5.
Huang H, Zhang Y, Yang R, Tang X. Determination of baicalin in rat cerebrospinal fluid and blood using microdialysis coupled with ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008;874(1–2):77–83.
Akao T, Sato K, He JX, Ma CM, Hattori M. Baicalein 6-O-beta-d-glucopyranuronoside is a main metabolite in the plasma after oral administration of baicalin, a flavone glucuronide of Scutellariae radix, to rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 2013;36(5):748–53.
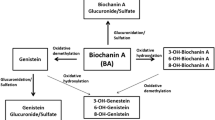
Wang Y, Yang J, Li X, Wang J. The metabolism of baicalin in rat and the biological activities of the metabolites. Evid-Based Complement Altern. 2012;2012:1–06.
Lu Q, Zhang L, Moro A, Chen MC, Harris DM, Eibl G, Go VW. Detection of baicalin metabolites baicalein and oroxylin-A in mouse pancreas and pancreatic xenografts. Pancreas. 2012;41(4):571–6.
Yu J, Guo X, Zhang Q, Peng Y and Zheng J. Metabolite profile analysis and pharmacokinetic study of emodin, baicalin and geniposide in rats. Xenobiotica. 2017:1–11.
Jiang S, Xu J, Qian D, Shang E, Liu P, Su S, Leng X, Guo J, Duan J, Du L, Zhao M. Comparative metabolites in plasma and urine of normal and type 2 diabetic rats after oral administration of the traditional Chinese Scutellaria–coptis herb couple by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B. 2014;965:27–32.
Zeng MF, Pan LM, Zhu HX, Zhang QC, Guo LW. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin in plasma after oral administration of Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Tang or pure baicalin in MCAO and sham-operated rats. Fitoterapia. 2010;81(6):490–6.
Wang Z, Hu H, Chen F, Lan K, Wang A. Reduced system exposures of total rhein and baicalin after combinatory oral administration of rhein, baicalin and berberine to beagle dogs and rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;145(2):442–9.
Shi R, Zhou H, Liu Z, Ma Y, Wang T, Liu Y, Wang C. Influence of coptis Chinensis on pharmacokinetics of flavonoids after oral administration of radix Scutellariae in rats. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 2009;30(7):398–410.
Zhu Z, Zhao L, Liu X, Chen J, Zhang H, Zhang G, Chai Y. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin and wogonoside by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry after oral administration of Xiaochaihu Tang and radix Scutellariae extract to rats. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010;878(24):2184–90.
Huo X, Wang B, Zheng L, Cong H, Xiang T, Wang S, Sun C, Wang C, Zhang L, Deng S, Wu B, Ma X. Comparative pharmacokinetic study of baicalin and its metabolites after oral administration of baicalin and Chaiqin Qingning capsule in normal and febrile rats. J Chromatogr B. 2017;1059:14–20.
Zhu ML, Liang XL, Zhao LJ, Liao ZG, Zhao GW, Cao YC, Zhang J, Luo Y. Elucidation of the transport mechanism of baicalin and the influence of a radix Angelicae Dahuricae extract on the absorption of baicalin in a Caco-2 cell monolayer model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150(2):553–9.
Liang XL, Zhang J, Zhao GW, Li Z, Luo Y, Liao ZG, Yan DM. Mechanisms of improvement of intestinal transport of baicalin and puerarin by extracts of Radix Angelicae Dahuricae. Phytother Res. 2015;29(2):220–7.
Yang YF, Li Z, Xin WF, Wang YY, Zhang WS. Pharmacokinetics and brain distribution differences of baicalin in rat underlying the effect of Panax notoginsenosides after intravenous administration. Chin J Nat Med. 2014;12(8):632–40.
Xing J, Chen X, Sun Y, Luan Y, Zhong D. Interaction of baicalin and baicalein with antibiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2005;57(6):743–50.
Gao N, Zou D, Qiao HL. Concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of Baicalin on the plasma protein binding and metabolism of chlorzoxazone, a CYP2E1 probe substrate, in rats in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53038.
Tian X, Cheng ZY, Jin H, Gao J, Qiao HL. Inhibitory effects of baicalin on the expression and activity of CYP3A induce the pharmacokinetic changes of midazolam in rats. Evid Based Complement Altern Med. 2013;2013:179643.
Gao N, Fang Y, Qi B, Jia LJ, Jin H, Qiao HL. Pharmacokinetic changes of unbound theophylline are due to plasma protein binding displacement and CYP1A2 activity inhibition by baicalin in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;150(2):477–84.
Gao N, Qi B, Liu FJ, Fang Y, Zhou J, Jia LJ, Qiao HL. Inhibition of baicalin on metabolism of phenacetin, a probe of CYP1A2, in human liver microsomes and in rats. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89752.
Noh K, Nepal MR, Jeong KS, Kim SA, Um YJ, Seo CS, Kang MJ, Park PH, Kang W, Jeong HG, Jeong TC. Effects of baicalin on oral pharmacokinetics of caffeine in rats. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015;23(2):201–6.
Cheng ZY, Tian X, Gao J, Li HM, Jia LJ, Qiao HL. Contribution of baicalin on the plasma protein binding displacement and CYP3A activity inhibition to the pharmacokinetic changes of nifedipine in rats in vivo and in vitro. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e87234.
He L, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu X, Yang Y, Gao Y, Wang X, Liu B, Wang X. Studies on the interaction between promethazine and human serum albumin in the presence of flavonoids by spectroscopic and molecular modeling techniques. Colloids Surf B. 2016;145:820–9.
Wang X, Guo XY, Xu L, Liu B, Zhou LL, Wang XF, Wang D, Sun T. Studies on the competitive binding of cleviprex and flavonoids to plasma protein by multi-spectroscopic methods: a prediction of food-drug interaction. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;175:192–9.
Wang X, He LL, Liu B, Wang X, Xu L, Wang XF, Sun T. Decrease of the affinity of theophylline bind to serum proteins induced by flavonoids and their synergies on protein conformation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;107(Pt A):1066–73.
Wang X, Liu Y, He LL, Liu B, Zhang SY, Ye X, Jing JJ, Zhang JF, Gao M, Wang X. Spectroscopic investigation on the food components-drug interaction: the influence of flavonoids on the affinity of nifedipine to human serum albumin. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015;78:42–51.
Liu B, Zhang J, Hao A, Xu L, Wang D, Ji H, Sun S, Chen B, Liu B. The increased binding affinity of curcumin with human serum albumin in the presence of rutin and baicalin: a potential for drug delivery system. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2016;155:88–94.
Li HT, Wu XD, Davey AK, Wang J. Antihyperglycemic effects of baicalin on streptozotocin—nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Phytother Res. 2011;25(2):189–94.
Liu L, Deng YX, Liang Y, Pang XY, Liu XD, Liu YW, Yang JS, Xie L, Wang GJ. Increased oral AUC of baicalin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats due to the increased activity of intestinal beta-glucuronidase. Planta Med. 2010;76(1):70–5.
He MY, Deng YX, Shi QZ, Zhang XJ, Lv Y. Comparative pharmacokinetic investigation on baicalin and wogonoside in type 2 diabetic and normal rats after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicine Huanglian Jiedu decoction. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155(1):334–42.
Wei X, Tao J, Cui X, Jiang S, Qian D, Duan J. Comparative pharmacokinetics of six major bioactive components in normal and type 2 diabetic rats after oral administration of Sanhuang Xiexin Decoction extracts by UPLC-TQ MS/MS. J Chromatogr B. 2017;1061–1062:248–55.
Zhang C, Xu Y, Xiang D, Yang J, Lei K, Liu D. Pharmacokinetic characteristics of baicalin in rats with 17α-ethynyl-estradiol-induced intrahepatic cholestasis. Curr Med Sci. 2018;38(1):167–73.
Wei Y, Guo J, Zheng X, Wu J, Zhou Y, Yu Y, Ye Y, Zhang L, Zhao L. Preparation, pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of baicalin-loaded liposomes. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9:3623–30.
Zhang S, Wang J, Pan J. Baicalin-loaded PEGylated lipid nanoparticles: characterization, pharmacokinetics, and protective effects on acute myocardial ischemia in rats. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(9):3696–703.
Liu Z, Zhang L, He Q, Liu X, Okeke CI, Tong L, Guo L, Yang H, Zhang Q, Zhao H, Gu X. Effect of baicalin-loaded PEGylated cationic solid lipid nanoparticles modified by OX26 antibody on regulating the levels of baicalin and amino acids during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Int J Pharm. 2015;489(1–2):131–8.
Yue PF, Li Y, Wan J, Wang Y, Yang M, Zhu WF, Wang CH, Yuan HL. Process optimization and evaluation of novel baicalin solid nanocrystals. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:2961–73.
Zhao L, Wei Y, Huang Y, He B, Zhou Y, Fu J. Nanoemulsion improves the oral bioavailability of baicalin in rats: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:3769–79.
Chen Y, Minh LV, Liu J, Angelov B, Drechsler M, Garamus VM, Willumeit-Römer R, Zou A. Baicalin loaded in folate-PEG modified liposomes for enhanced stability and tumor targeting. Colloids Surf B. 2016;140:74–82.
Liu Z, Zhao H, Shu L, Zhang Y, Okeke C, Zhang L, Li J, Li N. Preparation and evaluation of Baicalin-loaded cationic solid lipid nanoparticles conjugated with OX26 for improved delivery across the BBB. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2015;41(3):353–61.
Wu L, Bi Y, Wu H. Formulation optimization and the absorption mechanisms of nanoemulsion in improving baicalin oral exposure. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(2):266–75.
Li N, Je YJ, Yang M, Jiang XH, Ma JH. Pharmacokinetics of baicalin-phospholipid complex in rat plasma and brain tissues after intranasal and intravenous administration. Pharmazie. 2011;66(5):374.
Li B, Wen M, Li W, He M, Yang X, Li S. Preparation and characterization of baicalin-poly -vinylpyrrolidone coprecipitate. Int J Pharmaceut. 2011;408(1–2):91–6.
Li J, Jiang Q, Deng P, Chen Q, Yu M, Shang J, Li W. The formation of a host-guest inclusion complex system between beta-cyclodextrin and baicalin and its dissolution characteristics. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017;69(6):663–74.
Zhang H, Yang X, Zhao L, Jiao Y, Liu J, Zhai G. In vitro and in vivo study of Baicalin-loaded mixed micelles for oral delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016;23(6):1933–9.
Wu H, Long X, Yuan F, Chen L, Pan S, Liu Y, Stowell Y, Li X. Combined use of phospholipid complexes and self-emulsifying microemulsions for improving the oral absorption of a BCS class IV compound, baicalin. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2014;4(3):217–26.
Xie Y, Hu Y, Shen M, Ma Y, Zhong J, Zhang N, Tao J, Wei L. Dissolution and pharmacokinetic properties of alkaloids and flavonoids in a Xiexin multiple-unit drug delivery system. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2013;63(10):501–9.
Zhang ZQ, Liua W, Zhuang L, Wang J, Zhang S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of baicalin, wogonoside, baicalein and wogonin in plasma after oral administration of pure baicalin, radix Scutellariae and Scutellariae–Paeoniae couple extracts in normal and ulcerative colitis rats. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013;12(3):399–409.
Fan L, Zhang W, Guo D, Tan ZR, Xu P, Li Q, Liu YZ, Zhang L, He TY, Hu DL, Wang D, Zhou HH. The effect of herbal medicine baicalin on pharmacokinetics of rosuvastatin, substrate of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2008;83(3):471–6.
Li B, He M, Li W, Luo Z, Guo Y, Li Y, Zang C, Wang B, Li F, Li S, Ji P. Dissolution and pharmacokinetics of baicalin-polyvinylpyrrolidone coprecipitate. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;65(11):1670–8.
Jin SY, Han J, Jin SX, Lv QY, Bai JX, Chen HG, Li RS, Wu W, Yuan HL. Characterization and evaluation in vivo, of baicalin-nanocrystals prepared by an ultrasonic-homogenization-fluid bed drying method. Chin J, Nat Med. 2014;12(1):71–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No sources of funding were used to prepare this review.
Conflict of interest
All of the authors report no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, T., Liu, Y. & Zhang, C. Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability Enhancement of Baicalin: A Review. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 44, 159–168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-018-0509-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-018-0509-3