Abstract
Background
In low- and middle-income countries, sedentary behavior is widely prevalent in the young. Reliable and valid instruments are essential for evaluating sedentary behavior and physical activity in children and adolescents.
Objective
To evaluate the reliability and validity of an easy to use physical activity questionnaire for children and adolescents from India.
Study design
Evaluation of a questionnaire tool.
Participants
104 children and adolescents belonging to the age group of 10–17 years were selected using a purposive sampling technique.
Methods
The Madras Diabetes Research Foundation — Physical Activity Questionnaire for Children and Adolescents [MPAQ(c)] was used to assess the various dimensions of physical activity. Physical activity was also objectively assessed using accelerometer worn around the waist for five complete days. The baseline administration of MPAQ(c) was done between November and December, 2017. Reliability of MPAQ was assessed by repeat administration after 2 weeks for upto a month later. Validity of MPAQ(c) was measured against accelerometer using Spearman’s correlation and Bland and Altman agreements.
Results
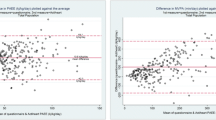
Test-retest reliability of the questionnaire revealed good agreement (ICC: 0.77 min/wk). Correlation coefficients (95% CI) for sedentary behavior and moderate to vigorous physical activity for MPAQ(c) against accelerometer were 0.52 (0.36, 0.64) and 0.41 (0.23, 0.55), respectively indicating moderate correlation. Good agreement was present between MPAQ(c) and accelerometer for sedentary behavior [mean bias = −4.9 (±2SD -197.1 to 187.3) min/d].
Conclusion
MPAQ(c) is a valid and reliable instrument for evaluating physical activity in Indian children aged 10–17 years.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caspersen CJ, Powell KE, Christenson GM. Physical activity, exercise, and physical fitness: Definitions and distinctions for health-related research. Public Health Reports. 1985;100:126–31.
Guthold R, Cowan MJ, Autenrieth CS, Kann L, Riley LM. Physical activity and sedentary behavior among schoolchildren: A 34-country comparison. J Pediatr. 2010;157:43–9.e1.
Bauman A, Phongsavan P, Schoeppe S, Owen N. Physical activity measurement — a primer for health promotion. Promot Educ. 2006;13:92–103.
Sallis JF. Measuring physical activity: Practical approaches for program evaluation in Native American communities. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2010;16:404–10.
Skender S, Ose J, Chang-Claude J, Paskow M, Brühmann B, Siegel EM, et al. Accelerometry and physical activity questionnaires — A systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:515.
Welk GJ, Schaben JA, Morrow JR, Jr. Reliability of accelerometry-based activity monitors: A generalizability study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:1637–45.
Cossio BM, Mendez CJ, Luarte RC, Vargas VR, Canqui FB, Gomez CR. Physical activity patterns of school adolescents: Validity, reliability and percentiles proposal for their evaluation. Revista Chilena de Pediatria. 2017;88:73–82.
Anjana RM, Sudha V, Lakshmipriya N, Subhashini S, Pradeepa R, Geetha L, et al. Reliability and validity of a new physical activity questionnaire for India. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2015;12:40.
Sasaki JE, John D, Freedson PS. Validation and comparison of ActiGraph activity monitors. J Sci Med Sport. 2011;14: 411–6.
Santos-Lozano A, Santin-Medeiros F, Cardon G, Torres-Luque G, Bailon R, Bergmeir C, et al. Actigraph GT3X: Validation and determination of physical activity intensity cut points. Int J Sports Med. 2013;34:975–82.
Ridley K, Ainsworth BE, Olds TS. Development of a compendium of energy expenditures for youth. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Activity. 2008;5:45.
Butte NF, Watson KB, Ridley K, Zakeri IF, McMurray RG, Pfeiffer KA, et al. A Youth Compendium of Physical Activities: Activity codes and metabolic intensities. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50:246–56.
Cicchetti DV. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psych Assess. 1994;6:284–90.
Freedson PS, Melanson E, Sirard J. Calibration of the computer science and applications, Inc. accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1998;30:777–81.
Chinapaw MJ, Slootmaker SM, Schuit AJ, van Zuidam M, van Mechelen W. Reliability and validity of the activity questionnaire for adults and adolescents (AQuAA). BMC Med Res Methodol. 2009;9:58.
Chinapaw MJ, Mokkink LB, van Poppel MN, van Mechelen W, Terwee CB. Physical activity questionnaires for youth: A systematic review of measurement properties. Sports Med. 2010;40:539–63.
Lockwood J, Jeffery A, Schwartz A, Manlhiot C, Schneiderman JE, McCrindle BW, et al. Comparison of a physical activity recall questionnaire with accelerometry in children and adolescents with obesity: A pilot study. Obesity. 2017;12:e41–45.
Voss C, Dean PH, Gardner RF, Duncombe SL, Harris KC. Validity and reliability of the physical activity questionnaire for children (PAQ-C) and adolescents (PAQ-A) in individuals with congenital heart disease. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0175806.
Mathews E, Salvo D, Sarma PS, Thankappan KR, Pratt M. Adapting and validating the global physical activity questionnaire (GPAQ) for Trivandrum, India, 2013. Prev Chronic Disease. 2016;13:E53.
Adamo KB, Prince SA, Tricco AC, Connor-Gorber S, Tremblay M. A comparison of indirect versus direct measures for assessing physical activity in the pediatric population: a systematic review. Int J Obesity: 2009;4:2–27.
Schnurr TM, Bech B, Nielsen TRH, Andersen IG, Hjorth MF, Aadahl M, et al. Self-reported versus accelerometer-assessed daily physical activity in childhood obesity treatment. Percept Mot Skills. 2017;124:795–811.
Ward DS, Evenson KR, Vaughn A, Rodgers AB, Troiano RP. Accelerometer use in physical activity: Best practices and research recommendations. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37:S582–8.
Vanhelst J, Hardy L, Gottrand F, Beghin L. Technical aspects and relevance of physical activity assessment in children and adolescents in free-living conditions. Arch Pediatr. 2012;19:1219–25.
Funding
Funding: None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Contributors: TSM: involved in conduct of the study, writing the first draft of manuscript and carrying out consecutive revisions; HR: co-ordinated the study, helped in data analysis and revisions of the manuscript; CA: analyzed the data and helped in data interpretation; NJ: collected the data and gave inputs to the manuscript; MP,VM: contributed to critical revisions for intellectual content of the manuscript; RMA: conceptualized the study, contributed inputs to data analysis and revisions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical clearance: Institutional ethics committee of Madras Diabetes Research foundation; No. IRB00002640, December, 2014.
Competing interest: None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehreen, T.S., Ranjani, H., Anitha, C. et al. Reliability and Validity of a Physical Activity Questionnaire for Indian Children and Adolescents. Indian Pediatr 57, 707–711 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1912-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1912-9