Abstract
Objective: To assess the kidney growth and function in appropriate for date and small for date (SGA) preterm neonates.
Methods: Appropriate for date and SGA preterm neonates with gestation <35 weeks, at 12–18 months of corrected age, attending the follow-up outpatient clinic of a Tertiary care level III neonatal unit. Renal function was assessed by measuring the serum creatinine level and estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) was calculated by using modified Schwartz formula. Kidney size was determined by ultrasonography using a 5 MHz sector probe with an accuracy of 1.0 mm.
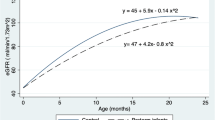
Results: The mean (SD) serum creatinine and eGFR in the 120 children enrolled were 0.39 (0.16) mg/dL and 109.05 (44.66) mL/min/1.73 m2, respectively. The mean (SD) lengths of right and left kidney were 54.3 (4.9) mm and 55.2 (4.77) mm, respectively. The kidney length, serum creatinine and eGFR were significantly lower in preterm SGA infants as compared to preterm AGA infants.
Conclusion: Preterm infants, especially SGA infants, at 12 to 18 months of corrected age have impaired renal growth with small kidney size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luyckx VA, Brenner BM. Birth weight, malnutrition and kidney-associated outcomes–A global concern. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11:135–49.
Stelloh C, Allen KP, Mattson DL, Lerch-Gaggl A, Reddy S, El-Meanawy A. Prematurity in mice leads to reduction in nephron number, hypertension, and proteinuria. Transl Res J Lab Clin Med. 2012;159:80–9.
White SL, Perkovic V, Cass A, Chang CL, Poulter NR, Spector T, et al. Is low birth weight an antecedent of CKD in later life? A systematic review of observational studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:248–61.
Drougia A, Giapros V, Hotoura E, Papadopoulou F, Argyropoulou M, Andronikou S. The effects of gestational age and growth restriction on compensatory kidney growth. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:142–8.
Schmidt IM, Chellakooty M, Boisen KA, Damgaard IN, Mau Kai C, Olgaard K, et al. Impaired kidney growth in low-birth-weight children: Distinct effects of maturity and weight for gestational age. Kidney Int. 2005;68:731–40.
Jetton JG, Askenazi DJ. Acute kidney injury in the neonate. Clin Perinatol. 2014;41:487–502.
Moore JF, Sharer JD. Methods for quantitative creatinine determination. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2017;93:A.3O.1-A.3O.7.
Schwartz GJ, Muñoz A, Schneider MF, Mak RH, Kaskel F, Warady BA, et al. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:629–37.
Otiv A, Mehta K, Ali U, Nadkarni M. Sonographic measurement of renal size in normal Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 2012;49:533–6.
Boer DP, de Rijke YB, Hop WC, Cransberg K, Dorresteijn EM. Reference values for serum creatinine in children younger than 1 year of age. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010;25:2107–13.
Hotoura E, Argyropoulou M, Papadopoulou F, Giapros V, Drougia A, Nikolopoulos P, et al. Kidney development in the first year of life in small-for-gestational-age preterm infants. Pediatr Radiol. 2005;35:991–4.
Rodríguez-Soriano J, Aguirre M, Oliveros R, Vallo A. Long-term renal follow-up of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20:579–84.
Rakow A, Johansson S, Legnevall L, Sevastik R, Celsi G, Norman M, et al. Renal volume and function in school-age children born preterm or small for gestational age. Pediatr Nephrol. 2008;23:1309–15.
Vanpée M, Blennow M, Linné T, Herin P, Aperia A. Renal function in very low birth weight infants: normal maturity reached during early childhood. J Pediatr. 1992;121:784–8.
Zaffanello M, Brugnara M, Bruno C, Franchi B, Talamini G, Guidi G, et al. Renal function and volume of infants born with a very low birth-weight: A preliminary cross-sectional study. Acta Paediatr. 2010;99:1192–8.
Kwinta P, Klimek M, Drozdz D, Grudzieñ A, Jaga M, Zasada M, et al. Assessment of long-term renal complications in extremely low birth weight children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26:1095–103.
Starzec K, Klimek M, Grudzieñ A, Jaga M, Kwinta P. Longitudinal assessment of renal size and function in extremely low birth weight children at 7 and 11 years of age. Pediatr Nephrol. 2016;31:2119–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Contributors: KVR: concept, study design, data collection, written the manuscript; DP: data collection; DM: performed Renal ultrasound for all children; MS, SM: reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval: Institutional Ethics Committee of Fernandez Hospital; No. 19/20016 dated June 27, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, K.V., Pawale, D., Shah, M. et al. Assessment of Renal Growth and Function in Preterm Infants at Corrected Age of 12–18 Month. Indian Pediatr 57, 411–414 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1813-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1813-y