Abstract
Objective
To determine if vitamin D status is affected in term neonates with early onset sepsis and its association with outcome.
Methods
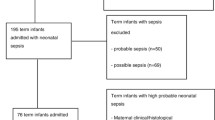
Study was done at a level 3 neonatal unit on 140 neonates. Term neonates with early onset sepsis (study group, 70 patients) and without sepsis (control group, 70 patients) were enrolled.
Results
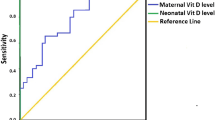
Mean neonatal vitamin D level in the study group was 16.00 (10.49) ng/mL and in the control group, was 29.07(8.36) ng/mL (P =0.061). In the study group 80% (n=56) babies had low vitamin D levels (<32 ng/mL) among whom 51.7% (n=29) had severe vitamin D deficiency (<11ng/mL). In the control group, 58.5% (n=41) had low vitamin D levels of whom, 9.8% (n=4) had severe vitamin D deficiency (P<0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). Mortality and highly probable sepsis were more common with vitamin D levels <11ng/mL in the study group (P= 0.005 and P=0.006, respectively).
Conclusion
Vitamin D is deficient in neonates with early onset sepsis and is associated with increased sepsis severity and mortality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clancy N, Onwuneme C, Carroll A, McCarthy R, McKenna MJ, Murphy N, et al. Vitamin D and neonatal immune function. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013; 26:639–46.
Kempker JA, Han JE, Tangpricha V, Ziegler TR, Martin GS. Vitamin D and sepsis: An emerging relationship. Dermatoendocrinol. 2012;4:101–8.
Sadeghi K, Berger A, Langgartner M, Prusa AR, Hayde M, Herkner K, et al. Immaturity of infection control in preterm and term newborns is associated with impaired toll-like receptor signalling. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:296–302.
Yang LR, Li H, Yang TY, Zhang T, Zhao RC. Relationship between vitamin D deficiency and early onset neonatal sepsis. Chin J Contemp Pediatr. 2016;18:791–5.
Cizmeci MN, Kara S, Kanburoglu MK, Simavli S, Duvan CI, Tatli MM. Detection of cord blood hepcidin levels as a biomarker for early-onset neonatal sepsis. Med Hypotheses. 2014;82:310–2.
Cetinkaya M, Cekmez F, Buyukkale G, Erener-Ercan T, Demir F. Lower vitamin D levels are associated with increased risk of early-onset neonatal sepsis in term infants. J Perinatol. 2015;35:3945.
Kanth SU, Reddy KA, Srinivas G. Association between vitamin D levels and early onset sepsis in infants: A prospective observational study. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016;3:1189–92.
Seliem MS, Haie OA, Mansour A, Salama S. The relation between vitamin D level and increased risk for early-onset neonatal sepsis in full-term infants. Med Res J. 2016;15:16–21.
Gitto E, Karbownik M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Cuzzocrea S, Chiurazzi P, et al. Effects of melatonin treatment in septic new-borns. Pediatr Res. 2001;50:756–60.
Mulligan ML, Felton SK, Riek AE, Bernal-Mizrachi C. Implications of vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and lactation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202:429e1-e-9.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the contribution in statistics to Dr Prakash Patel and Ms Swati Patel and to Dr Ajay Sethi for his inputs during the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contributors; PS: conceived the study, conceptualized study design, supervised data collection and analysis, and reviewed the intellectual outcome: drafted and critically revised the manuscript; VC: prepared study design, carried out the study, enrolled patients, collected data and prepared result: collected data, data analysis and drafted the manuscript. All authors have reviewed and approved of the final draft of the paper. Dr Poonam Singh will act as guarantor for the paper.
Funding: Under JSSK programme. (Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakaram)
Competing Interest: None stated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Chaudhari, V. Association of Early-Onset Sepsis and Vitamin D Deficiency in Term Neonates. Indian Pediatr 57, 232–234 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1757-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-020-1757-2