Abstract
Objective
Analyze the profile and outcome of children with rhabdomyosarcoma from a pediatric-oncology unit.
Design
Retrospective analysis of case records over 23 years (1990–2012).
Setting
Government-run, tertiary-care, university hospital in Northern India.
Participants
159 children (<12-years) with a diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma were enrolled. The median age was 4 years; 13% were infants.
Main outcome measure
Five-year event free survival.
Results
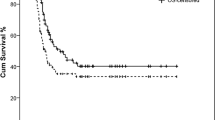
The median symptom interval was 2-months. Head and neck region was the most frequent site (44%), followed by tumors in the extremity (15.7%). The majority (67%) of the tumors were located at ‘unfavorable’ sites; 68% were >5 cm in size. The most frequent (58%) pathological subtype was embryonal. Treatment was based on the ‘Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study (IRS) Group’ risk-stratification. 33% were ‘low-risk’ children, 11% were ‘high-risk’. Treatment-refusal (18%) and abandonment (33%) were major impediments. The median ± SE five-year event free survival of those taking treatment was 43.6 ± 6%.
Conclusions
Large sized tumors, tumors at unfavorable locations, and treatment refusal/abandonment contributed to inferior outcome in children with rhabdomyosarcoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wexler LH, Meyer WH, Helman LJ. Rhabdomyosarcoma. In: Pizzo PA, Poplack DG. Principles and practice of pediatric oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2011. p.923.
Gatta G, Botta L, Rossi S, Aareleid T, Bielska-Lasota M, Clavel J, et al; EUROCARE Working Group. Childhood cancer survival in Europe 1999–2007: results of EUROCARE-5–a population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:35–47.
Raney RB, Anderson JR, Barr FG, Donaldson SS, Pappo AS, Qualman SJ, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma and undifferentiated sarcoma in the first two decades of life: A selective review of intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study group experience and rationale for intergroup rhabdomyosarcoma study V. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001;23:215–20.
Thavaraj V, Kumar R, Dawar R, Gupta DK, Mohanti BK, Singh R, et al. Treatment outcome and survival of rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) in children. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2001;37:286.
Mehta P, Swami A, Chaphekar M, Currimbhoy Z, Agarwal B. Soft tissue sarcoma (STS): Perspective from a paediatric cancer unit (PCU) at a trust hospital in Mumbai, India. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2004;43:475.
Dua V, Yadav SP, Prakash A, Sachdeva A. Encouraging treatment outcomes of pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma: a developing world experience. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;29:677–8.
Malempati S, Hawkins DS. Rhabdomyosarcoma: review of the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Committee experience and rationale for current COG studies. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2012;59:5–10.
Womer RB, Barr FG, Linardic CM. Rhabdomyosarcoma. In: Orkin SH, Fisher DE, Ginsburg D, Thomas Look A, Lux SE, Nathan DG. Nathan and Oski’s Hematology and Oncology of Infancy and Childhood. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2015. p.1929.
Ferrari A, Casanova M, Bisogno G, Zanetti I, Cecchetto G, De Bernardi B, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma in infants younger than one year old: a report from the Italian Cooperative Group. Cancer. 2003;97:2597–604.
Ognjanovic S, Linabery AM, Charbonneau B, Ross JA. Trends in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and survival in the United States, 1975–2005. Cancer. 2009;115:4218–26.
Ferrari A, Miceli R, Casanova M, Meazza C, Favini F, Luksch R, et al. The symptom interval in children and adolescents with soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer. 2010;116:177–83.
Ferrari A, Lo Vullo S, Giardiello D, Veneroni L, Magni C, Clerici CA, et al. The Sooner the better? How symptom interval correlates with outcome in children and adolescents with solid tumors: Regression Tree analysis of the findings of a prospective study. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2016;63: 479–85.
Sultan I, Qaddoumi I, Yaser S, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Ferrari A. Comparing adult and pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1973 to 2005: an analysis of 2,600 patients. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3391–7.
Maurer HM, Gehan EA, Beltangady M, Veneroni L, Magni C, Clerici CA, et al. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study-II. Cancer. 1993;71:1904–22
Uba FA, Chirdan LB. Clinical characteristics and outcome of surgical treatment of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A 7- year experience. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 2008;5:19–23.
Salman M, Tamim H, Medlej F, El-Ariss T, Saad F, Boulos F, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma treatment and outcome at a multidisciplinary pediatric cancer center in Lebanon. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;29:322–34.
Ma X, Huang D, Zhao W, Sun L, Xiong H, Zhang Y, et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: A ten-year retrospective multicenter study. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:17196–205.
Park JA, Kim EK, Kang HJ, Shin HY, Kim IH, Ahn HS. Initial response to treatment was highly associated with the prognosis of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma: a retrospective analysis of a single center experience in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2008;40:111–5.
Aung L, Soe TA, Chang KT, Quah TC. Singapore rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) experience: Shall we change our practice? Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2014;43:86–95.
Arora RS, Pizer B, Eden T. Understanding refusal and abandonment in the treatment of childhood cancer. Indian Pediatr. 2010;47:1005–10.
Arora RS, Eden T, Pizer B. The problem of treatment abandonment in children from developing countries with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;49:941–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, D., Das, A., Trehan, A. et al. Pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in India: A single-center experience. Indian Pediatr 54, 735–738 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1164-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1164-5