Abstract
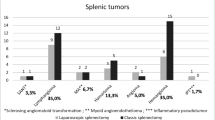
Laparoscopic splenectomy in the case of massive or supermassive splenomegaly has been associated with higher conversion rates and morbidity. The purpose of our study is to evaluate the feasibility and safety of laparoscopic splenectomy for massive spleens and to identify if there are limits beyond which the laparoscopic approach is not recommended in massive and supermassive spleens. This is a retrospective study of 93 consecutive laparoscopic splenectomies in adult patients performed by a single surgeon, from January 2008 to December 2017. The data collected included the patient’s age, sex, ASA, spleen weight, volume and dimension, type of disease, hospital stay, surgical technique, operative time. Median splenic weight was 400 g (range 65–3800 g) and median volume was 1365 cc (range 600–3800). Median operative time was 120 min and the overall conversion rate was 5.4%. Globally, 52 patients (55.9%) had a normal-weight spleen, 25 (26.9%) had massive and 16 (17.2%) had supermassive splenomegaly. In splenomegaly group (n = 41), patient’s age, percentage of malignant diagnosis, spleen weight, anteroposterior (AP), medio-lateral (ML) and craniocaudal (CC) diameter, surgical time and conversion rate were significantly higher compared to normal-weight spleen patients. None of the normal-weight spleen patients underwent open conversion, while 5 patients among 41 splenomegalic cases underwent laparotomic conversion (12.2%). Comparing massive and super-massive patients, the latter showed longer operative time and hospital length of stay, and higher conversion rate. We identified as significant cut-off limits for higher conversion risk a spleen weight ≥ 1300 g and a spleen CC diameter ≥ 22 cm. In our experience laparoscopy was the gold standard in the case of spleen weight and diameter equal to or less than 1300 g and 22 cm, but it was safe and feasible also in the case of larger spleens, taking into account the greater risk of conversion.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Delaitre B, Maignien B, Icard P (1992) Laparoscopic splenectomy. Br J Surg 79:1334
Bai YN, Jiang H, Prasoon P (2012) A meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic splenectomy for hematological disorders. World J Surg 36:2349–2358
Casaccia M, Torelli P, Pasa A, Sormani MP, Rossi E, Centers IRLSS (2010) Putative predictive parameters for the outcome of laparoscopic splenectomy: a multicenter analysis performed on the Italian Registry of Laparoscopic Surgery of the Spleen. Ann Surg 251:287–291
Somasundaram SK, Massey L, Gooch D, Reed J, Menzies D (2015) Laparoscopic splenectomy is emerging ‘gold standard’ treatment even for massive spleens. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 97:345–348
Grahn SW, Alvarez J 3rd, Kirkwood K (2006) Trends in laparoscopic splenectomy for massive splenomegaly. Arch Surg 141:755–761
Kercher KW, Matthews BD, Walsh RM, Sing RF, Backus CL, Heniford BT (2002) Laparoscopic splenectomy for massive splenomegaly. Am J Surg 183:192–196
Habermalz B, Sauerland S, Decker G, Delaitre B, Gigot JF, Leandros E, Lechner K, Rhodes M, Silecchia G, Szold A, Targarona E, Torelli P, Neugebauer E (2008) Laparoscopic splenectomy: the clinical practice guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES). Surg Endosc 22:821–848
Silecchia G, Boru CE, Fantini A, Raparelli L, Greco F, Rizzello M, Pecchia A, Fabiano P, Basso N (2006) Laparoscopic splenectomy in the management of benign and malignant hematologic diseases. JSLS 10:199–205
Fan Y, Wu S (2012) Laparoscopic splenectomy in the treatment of hereditary spherocytosis. Surg Curr Res 2:3–5
Boddy AP, Mahon D, Rhodes M (2006) Does open surgery continue to have a role in elective splenectomy? Surg Endosc 20:1094–1098
Schlachta CM, Poulin EC, Mamazza J (1999) Laparoscopic splenectomy for hematologic malignancies. Surg Endosc 13:865–868
Park AE, Birgisson G, Mastrangelo MJ, Marcaccio MJ, Witzke DB (2000) Laparoscopic splenectomy: outcomes and lessons learned from over 200 cases. Surgery 128:660–667
Wang X, Li Y, Crook N, Peng B, Ting N (2013) Laparoscopic splenectomy: a surgeons experience of 302 patients with analysis of postoperative complications. Surg Endosc 27:3564–3571
Terrosu G, Baccarani U, Bresadola V, Sistu MA, Uzzau A, Bresadola F (2002) The impact of splenic weight on laparoscopic splenectomy for splenomegaly. Surg Endosc 16:103–107
Targarona EM, Espert JJ, Balague C, Piulachs J, Artigas V, Trias M (1998) Splenomegaly should not be considered a contraindication for laparoscopic splenomegaly. Ann Surg 228:35–39
Targarona EM, Espert JJ, Cerdàn G, Balaguè C, Piulachs J, Sugranes G, Artigas G, Trias M (1999) Effect of spleen size on splenectomy outcome. A comparison of open and laparoscopic surgery. Surg Endosc 13:559–562
Owera A, Hamade AM, Bani Hani OI, Ammori BJ (2006) Laparoscopic versus open splenectomy for massive splenomegaly: a comparative study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 16:241–246
Zhou J, Wu Z, Cai Y, Wang Y, Peng B (2011) The feasibility and safety of laparoscopic splenectomy for massive splenomegaly: a comparative study. J Surg Res 171:55–60
Ardestani A, Tavakkoli A (2012) Laparoscopic versus open splenectomy: the impact of spleen size on outcomes. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 23:760–764
Filicori F, Stock C, Andrew D, Schweitzer XM, Keutgen MD, LaGratta RZ, Thomas J, Fahey III (2013) Three-dimensional CT volumetry predicts outcomes of laparoscopic splenectomy for splenomegaly: retrospective clinical study. World J Surg 37:52–58
Patel AG, Parker JE, Wallwork B, Kau KB, Donaldson N, Rhodes MR, O'Rourke N, Nathanson L, Fielding G (2003) Massive splenomegaly is associated with significant morbidity after laparoscopic splenectomy. Ann Surg 238:235
Chen B, Hu SY, Wang L, Wang KX, Zhang GY, Zhang HF, Xuan SJ, Wachtel MS, Frezza EE (2008) Laparoscopic splenectomy: a 12-year single-center experience. Chin Med J 121:766–768
Horowitz J, Smith JL, Weber TK, Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Petrelli NJ (1997) Postoperative complications after splenectomy for hematologic malignancies. Ann Surg 223(3):290–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MS and GS drafted the main manuscript; MS and PD managed the manuscript conception and design of the work; GL, PP, DC and GS contributed to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; GS made the statistical analysis. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Research involving human participants
The ethics committee and review board in our institute approved the study and treatment protocol.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santarelli, M., Lo Secco, G., Celi, D. et al. Are there any limits for laparoscopy in splenomegaly? Our experience. Updates Surg 73, 1937–1944 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00876-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-020-00876-6