Abstract
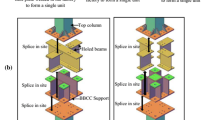
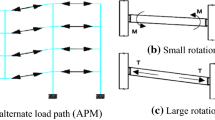
A kind of bolted beam-height adjustable beam-to-column connections (BHA connections) is proposed for moment-resisting steel frames. It is applicable when the height of beams change in small ranges. A BHA connection is composed of a T-shaped connector, an L-shaped connector with ellipse-type blot holes and bolts. A cyclic test on four full-scaled subassemblies and a series of numerical parametric analyses of BHA connections were conducted to study their mechanical performance. The test results show that the BHA connections with properly stiffened L-shaped connectors possessed good hysteretic properties, stabile secant stiffness and load-carrying capacity degradation and excellent energy dissipation capacity. And the effect of connector slippage and beam web eccentricity was negligible. It can be found in the parametric study that the flange thickness of T-shaped connectors played a pivotal role both in the load-carrying capacity and elastic stiffness of BHA connections, and the elastic stiffness was also affected by the thickness of T-shaped connector webs, L-shaped connector flanges and webs, and column stiffeners. Moreover, the numerical results also demonstrated that the column stiffeners in joint regions could improve the efficiency of load transfer between beams and columns. This kind of connections can be used to assemble steel frames expediently.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANSI/AISC 341. (2010) Seismic Provisions for Structural Steel Buildings. American Institute of Steel Construction, Chicago.
Chen C, Lee J and Lin M. (2003) Behaviour of steel moment connections with a single flange rib. Engineering Structures 25, pp. 1419–1428.
Chen S, Chu JM and Chou ZL. (1997) Dynamic behavior of steel frames with beam flanges shaved around connection. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 42, pp. 49–70.
Chen S, Yeh C and Chu J. (1996) Ductile Steel Beam-to-Column Connections for Seismic Resistance. Journal of Structural Engineering 122, pp. 1292–1299.
Engelhardt MD and Sabol TA. (1998) Reinforcing of steel moment connections with cover plates: benefits and limitations. Engineering Structures 20, pp. 510–520.
GB/T 11263. (2010) Hot-rolled H and cut T section steel. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Standard Press of China. (in Chinese)
GB/T 228.1. (2010) Metallic materials-Tensile testing-Part 1: Method of test at room temperature. Ministry of Housing and Urban–Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Standard Press of China. (in Chinese)
GB/T 2975 (1998) Steel and steel products-Location and preparation of test pieces for mechanical testing. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Standard Press of China. (in Chinese)
Iwankiw N and Zoruba S. (2002) Steel moment frames: resolution of recent seismic detailing and material shape issues. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 58, pp. 495–510.
JGJ 101. (2015) Specification for seismic test of buildings. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing, China Architecture & Building Press. (in Chinese)
Jones S, Fry G and Engelhardt M. (2002) Experimental Evaluation of Cyclically Loaded Reduced Beam Section Moment Connections. Journal of Structural Engineering 128, pp. 441–451.
Kim T, Whittaker A and Gilani A, et al. (2002) Experimental Evaluation of Plate-Reinforced Steel Moment-Resisting Connections. Journal of Structural Engineering 128, pp. 483–491.
Mahin SA. (1998) Lessons from damage to steel buildings during the Northridge earthquake. Engineering Structures 20, pp. 261–270.
Nakashima M, Inoue K and Tada M. (1998) Classification of damage to steel buildings observed in the 1995 Hyogoken-Nanbu earthquake. Engineering Structures 20, pp. 271–281.
Popov EP and Takhirov SM. (2002) Bolted large seismic steel beam-to-column connections Part 1: experimental study. Engineering Structures 24, pp. 1523–1534.
Ricles JM, Fisher JW and Lu L, et al. (2002) Development of improved welded moment connections for earthquakeresistant design. Journal of Constructional Steel Research 58, pp. 565–604.
Takhirov SM and Popov EP. (2002) Bolted large seismic steel beam-to-column connections Part 2: numerical nonlinear analysis. Engineering Structures 24, pp. 1535–1545.
Yu Q, Uang C and Gross J. (2000) Seismic Rehabilitation Design of Steel Moment Connection with Welded Haunch. Journal of Structural Engineering 126, pp. 69–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Z., Du, P., Fan, F. et al. Cyclic testing and parametric study of bolted beam-height adjustable steel beam-to-column connections. Int J Steel Struct 17, 77–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-016-0125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-016-0125-5