Abstract
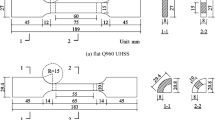
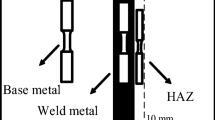
Compared with the conventional steel structure, the high-strength steel structures are at more risk of brittle fracture, especially in cold regions. In the present study, a series of tests (such as uniaxial tensile test, Charpy impact test and three-point bending test) were carried out at low temperature to investigate the mechanical properties and toughness of Q460C steel and its butt welded joint, fracture micro-mechanisms were analyzed as well. The ductility indices and the toughness indices all decrease with temperature decreases, the heat affected zone (HAZ) in welded joint is more critical to fracture than the base material. The fracture toughness of high-strength steel Q460C is relatively lower than the other three conventional steels (i.e. Q235, Q345 and Q390). In this study, rich experimental data were collected so as to provide reference for the fracture resistant design of high-strength steel structures in cold regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barsom, J. M. and Rolfe, S. T. (1999). Fracture and fatigue control in structures: Applications of fracture mechanics. ASTM, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
Chang, K. H. and Lee, C. H. (2007). “Residual stresses and fracture mechanics analysis of a crack in welds of high strength steels.” Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 74, pp. 980–994.
Duan, L. (2010). Mechanical characteristics of high performance steel HPS 485W and bending behavior study of hybrid girder. Chang’an University, Xi’an, China (in Chinese).
EN 1993-1-12 (2007). Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures, Part 1-12: Additional rules for the extension of EN 1993 up to steel grades S700. British Standard Institution, London, U.K.
GB/T 228-2002 (2002). Metallic materials-Tensile testing at ambient temperature. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
GB/T 13239-2006 (2006). Metallic materials-Tensile testing at low temperature. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
GB/T 229-2007 (2007). Metallic materials-Charpy pendulum impact test method. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
GB/T 21143-2007 (2007). Metallic materials-Unified method of test of determination for quasistatic fracture toughness. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Hu, Z. W. (2010). Research for mechanical properties of brittle fracture of structural steel thick plate and its weld. Tsinghua University, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Jing, H. Y., Huo, L. X., Zhang, Y. F., Toyoda, M., and Fujita, A. (1996). “Effect of yield ratio on fracture toughness for high strength steel.” Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 32(3), pp. 265–268.
JGJ 81-2002 (2002). Technical specification for welding of steel structure of building. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Liu, X. Y., Wang, Y. Q., Shi, Y. J., and Chen, H. (2012). “Progress on research for brittle facture of steel structure constructed with high-strength steel.” Steel Structure, S, pp. 135–145 (in Chinese).
Rogers, C. A. and Hancock, G. J. (2001). “Fracture toughness of G550 sheet steels subjected to tension.” Journal of Construction Steel Research, 57, pp. 71–89.
Shi, G. Shi, Y. J., and Wang, Y. Q. (2008). “Engineering application of ultra-high strength steel structure.” Progress in Steel Building Structure, 10(4), pp. 32–38.
Toribio, J. (1997). “A fracture criterion for high-strength steel notched bars.” Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 4(57), pp. 391–404.
Vojvodic, T. J. and Sedmak, A. (2004). “Analysis of the unstable fracture behaviour of a high strength low alloy steel weldment.” Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 71, pp. 1435–1451.
Wu, Y. M. (2004). Research for mechanism of brittle fracture of structural steel and its engineering design method. Tsinghua University, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Wu, Y. M., Wang, Y. Q., Shi, Y. J., Jiang, J. J. (2004). “Effects of low temperature on properties of structural steels.” Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 11(5), pp. 442–448.
Wang, Y.Q., Zhou, H., Shi, Y. J., Feng, B. R. (2002). “Mechanical properties and fracture toughness of rail steels and thermite welds at low temperature.” International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 19(5), pp. 409–420.
Zhou, Z. L., Xie, M., Lin, W. J., and Liu, Z. C. (1999). “Influence of heat input on the HAZ fracture toughness and microstructure of WEL-TEN780A high strength steel.” Weld Joining, 10, pp. 8–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Xy., Wang, Yq., Zong, L. et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties and toughness of Q460C high-strength steel and its butt welded joint at low temperature. Int J Steel Struct 14, 457–469 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-014-3003-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-014-3003-z