Abstract
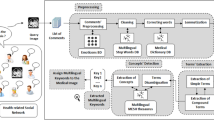
Patients are often anxious to quickly discover reliable analysis and concise explanation of their medical images while waiting for the physician decision. The fact of making important choices individually in his own corner may lead the physician to commit errors leading to malpractices and consequently to unforeseeable damages. In order to minimize medical errors by fostering collaboration between physicians and/or patients, we propose in this paper, as a first contribution, a medical social network destined to gather patients’ medical images and physicians’ annotations expressing their medical reviews and advices. The need, to automatically extract information and analyze opinions, becomes obviously a requirement due to the huge number of comments expressing specialists’ recommendations and/or remarks. For this purpose, we propose a second contribution consisting of providing a kind of comments’ summary which extracts the major current terms and relevant words existing on physicians’ reports. Furthermore, this extracted information will present a new and robust input for image indexation enhanced methods. In fact, significant extracted terms will be used later to index images in order to facilitate their search through the underlying social network. To overcome the above challenges, we propose an approach which focuses on algorithms mainly based on statistical methods and external semantic resources destined to filter selected extracted information.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almansoori W, Zarour O, Jarada TN, Karampales P, Rokne J, Alhajj R (2011) Applications of social network construction and analysis in the medical referral process. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE ninth international conference on dependable, autonomic and secure computing (DASC ‘11)
Blei D, Ng A, Jordan M (2003) Latent Dirichlet allocation. J Mach Learn Res 3(2003):993–1022
Bruyere C (2004) Medico-social networks and the coordination of knowledge. DEA in Management Sciences, Logistics and Organization. Mediterranean University (Aix-Marseille II)
Cavoukian A (2004) Privacy and healthcare: you need both. https://www.backbonemag.com/files/PDF/Speakers/2011-09-privacy-and-healthcare.pdf
Chorbev I, Sotirovska M, Mihajlov D (2011) Virtual communities for diabetes chronic disease healthcare. Int J Telemed Appl 2011:721654
Frakes WB, Fox CJ (2003) Strength and similarity of affix removal stemming algorithms. In: Newsletter of ACM SIGIR Forum Homepage archive, vol 37 Issue 1. New York, pp 26–30
Franklin V, Greene S (2007) Sweet talk: a text messaging support system. J Diabetes Nurs 11(1):22–26
Gaussier E, Maisonnasse L, Chevallet JP (2007) Multiplying concept sources for graph modeling. In: Proceedings of the 8th workshop of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum (CLEF), Budapest, Hungary, pp 585–592
Gong J, Sun S (2011) Individual doctor recommendation model on medical social network. In: Proceedings of the 7th international conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications (ADMA’11)
Grenier C (2003) The role of intermediate subject to understand the structuring of an organizational network of actors and technology—case of a care network. In: Proceedings of the 9th conference of the association information and management, Grenoble
Harrathi F (2010) Extraction de concepts et de relations entre concepts à partir des documents multilingues: approche statistique et ontologique. PhD Thesis, INSA Lyon
Hofmann T (1999) Probabilistic latent semantic indexing. In Proceeding of SIGIR ‘99 of the 22nd annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, New York, pp 50–57
Karbasi S (2007) Terms weighting in information retrieval; weighting model based on the ranking of terms in documents. PhD thesis, University Paul Sabatier
Li J (2014) Data protection in healthcare social networks. J IEEE Softw 31(1):46–53
Maisonnasse L, Gaussier E, Chevallet JP (2009) The combination of semantic analysis for searching medical information. In: Proceedings of the INFORSID Conference, Toulouse
Manning C, Raghavan P, Hinrich SH (2008) Introduction to information retrieval. Cambridge University Press Book, UK
Marion A, Omotayo O (2011) Development of a social networking site with a networked library and conference chat. J Emerg Trends Comput Inform Sci 2(8):396–401
Salton G, McGill MJ (1986) Introduction to modern information retrieval. McGraw-Hill, Inc., New York
Van Rijsbergen CJ (1979) Information retrieval. Butterworths, Information Retrieval Group, University of Glasgow, London
Williams J, Weber-Jahnke J (2010) Social networks for health care: addressing regulatory gaps with privacy-by-design. 8th Annual International Conference on Privacy Security and Trust (PST), Ottawa, pp 134–143
Xie Y, Chen Z, Cheng Y, Zhang K, Agrawal A, Liao WK, Choudhary A (2013) Detecting and tracking disease outbreaks by mining social media data. In: Proceedings of the twenty-third international joint conference on artificial intelligence (IJCAI’13)
Yin J, Lampert A, Cameron M, Robinson B, Power R (2012) Using social media to enhance emergency situation awareness. J IEEE Intell Syst 27(6):52–59
Zhou W, Yu C, Smalheiser N, Torvik V, Hong J (2007) Knowledge intensive conceptual retrieval and passage extraction of biomedical literature. In: Proceeding of SIGIR ‘07 of the 30th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval, New York, pp 655–662
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akaichi, J. A medical social network for physicians’ annotations posting and summarization. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 4, 225 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-014-0225-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13278-014-0225-1