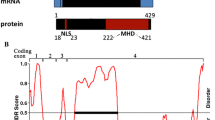
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common cancer among the male population. Conventional therapies target androgen signalling, which drives tumour growth; however, they provide limited survival benefits for patients. It is essential, therefore, to develop a more specific biomarker than the current gold standard, PSA testing. The Wnt signalling pathway induces expression of target genes through cell surface receptors. A non-canonical member of this family, Wnt-11, is evolutionarily highly conserved and is normally expressed by various cells in the developing embryo, as well as in the heart, liver and skeletal muscle of adult humans. We comprehensively review several cell signalling pathways to explain how they interact with Wnt-11, demonstrating its use as a potential biomarker for PCa. Several studies have shown that the expression of Wnt-11 is associated with gastric, renal and colorectal adenocarcinomas and PCa. Moreover, Wnt-11 affects extracellular matrix composition and cytoskeletal rearrangement, and it is required for proliferation and/or survival during cell differentiation. It was found that PCa cell lines express high levels of Wnt-11, which allows differentiation of the epithelial prostate tumour cells to neuron-like (NE) cells. The NE cells produce additional factors that can cause regression after treatment. Accumulating evidence shows that Wnt-11 could be a potential biomarker in diagnosing PCa. Many studies have shown both non-canonical and canonical Wnts interact with several signalling cascades such as PKC, JNK, NF-κB, Rho, PKA and PI3K. In particular, evidence demonstrates Wnt-11 is involved in the progression of PCa, thus it could have the potential to become both a specific disease marker and an important therapeutic target.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilt TJ, Ahmed HU. Prostate cancer screening and the management of clinically localized disease. BMJ (Clinical research ed). 2013;346:f325.
Cary K, Cooperberg M. Biomarkers in prostate cancer surveillance and screening: past, present and future. Ther Adv Urol. 2013;5(6):318–29.
Makarov DV, Loeb S, Getzenberg RH, Partin AW. Biomarkers for prostate cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2009;60:139–51.
Bjurlin M, Loeb S. PSA velocity in risk stratification of prostate cancer. Rev Urol. 2013;15(4):204–6.
Hagglof C, Hammarsten P, Stromvall K, Egevad L, Josefsson A, Stattin P. TMPRSS2-ERG expression predicts prostate cancer survival and associated with stromal biomarkers. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e86824.
Hausmann G, Banziger C, Basler K. Helping wingless take flight: how WNT proteins are secreted. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(4):331–6.
Komiya Y, Habas R. Wnt signal transduction pathways. Organogenesis. 2008;4(2):68–75.
Heuberger J, Birchmeier W. Interplay of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(2):a002915.
Wang Y. Wnt/planar cell polarity signalling: a new paradigm for cance therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(8):2103–9.
Schlessinger K, Hall A, Tolwinski N. Wnt signalling pathways meet Rho GTPases. Genes Dev. 2009;23:265–77.
Kypta RM, Waxman J. Wnt/B-catenin signalling in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2012;9:418–28.
Uysal-Onganer P, Kypta RM. Wnt11 in 2011—the regulation and function of a non-canonical Wnt. Acta Physiol. 2012;204(1):52–64.
Zhu H, Mazor M, Kawano Y. Analysis of Wnt gene expression in prostate cancer: mutual inhibition by WNT11 and the androgen receptor. Cancer Res. 2004;64(21):7918–26.
Sun Y, Niu J, Huang J. Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2009;1(2):148–62.
Uysal-Onganer P, Kawano Y, Caro M, Walker MM, Diez S, Darrington RS, et al. Wnt-11 promotes neuroendocrine-like differentiation, survival and migration of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:55.
Newton A. Protein Kinase C: poised to signal. Am J Phsiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298(3).
Garg R, Blando J, Perez C, Wang H, Benavides F, Kazaniez M. Activation of nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) in prostate cancer is mediated by protein kinase C ε (PKCε). J Biol Chem. 2012;287(44):37570–82.
Luna-Ulloa L, Hernandez-Maqueda J, Castaneda-Patlan M, Robles-Flores M. Protein Kinase C in Wnt signalling: implications in cancer initiation and progression. IUBMB Life. 63(10):915–21.
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O, Kolch W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26(22):3279–90.
Saadeddin A, Babaei-Jadidi R, Spencer-Dene B, Nateri A. The links between transcription, beta-catenin/JNK signalling, and carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(8):1189–96.
Guo X, Wang XF. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009;19(1):71–88.
Ma J, Zhang L, Han W, Shen T, Ma C, Liu Y, et al. Activation of JNK/c-Jun is required for the proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis induced by EET in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Lipid Res. 2012;53(6):1093–105.
Bode AM, Dong Z. The functional contrariety of JNK. Mol Carcinog. 2007;46(8):591–8.
Kunsch C, Rosen C. NF-kappa B subunit-specific regulation of the interleukin-8 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13(10):6137–46.
Spencer G, Utting J, Etheridge S, Arnett T, Genever P. Wnt signalling in osteoblasts regulates expression of the receptor activator of NFKappaB ligand and inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(9):1283–96.
Modder UI, Oursler MJ, Khosla S, Monroe DG. Wnt10b activates the Wnt, notch, and NFkappaB pathways in U2OS osteosarcoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(5):1392–402.
Lawrence T. The nuclear factor NK-kB pathway in inflammation. Inflammation. 2009:1–10.
Taylor S, Beuchler J, Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase:framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu.Rev.Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005.
Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR. The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(1):9–22.
Sarwar M, Persson JL. The protein kinase A (PKA) intracellular pathway and androgen receptor: a novel mechanism underlying the castration-resistant and metastatic prostate cancer. J Cancer Sci & Ther. 2012;01(S5).
Khor L, Bae K, Paulus R. MDM2 and Ki-67 predict for distant metastasis and mortality in men treated with radiotherapy and androgen deprivation for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(19).
Kim C, Xuong N, Taylor S. Crystal structure of a complex. Sci Mag. 2005;307:690–6.
Sainz R, Mayo J, Tan D, Len J, Manchester L, Resiter R. Melatonin reduces prostate cancer cell growth leading to neuroendocrine differentiation via a receptor and PKA independent mechanism. Prostate. 2005;63(1):29–75.
Shen R, Dorai T, Olsson C, Buttyan R, Katz A, Szaboles M. Transdifferentiation of cultured human prostate cancer cells to a neuroendocrine cell phenotype in a hormone-depleted medium. Urol Oncol. 1997;3(2):67–75.
Caretta A, Caretta C. Protein kinase A in cancer. Cancer. 2011;3(1):913–26.
Gallegos TF, Kouznetsova V, Kudlicka K, Sweeney DE, Bush KT, Willert K, et al. A protein kinase A and Wnt-dependent network regulating an intermediate stage in epithelial tubulogenesis during kidney development. Dev Biol. 2012;364(1):11–21.
Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 2001;114(15):2713–22.
Vega FM, Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(14):2093–101.
Kusama T, Mukai M, Endo T, Ishikawa O, Tatsuta M, Nakamura H, et al. Inactivation of Rho GTPases by p190 RhoGAP reduces human pancreatic cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2006;97(9):848–53.
Rathinam R, Berrier A, Alahari S. Role of Rho GTPases and their regulations in cancer progression. Front Biosci. 2011:2561–71.
Fernandez-Borja M, Janssen L, Verwoerd D, Horijk P, Neefjes J. RhoB regulates endosome transport by promoting actin assembly on endosomal membranes through Dia1. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(12):2661–70.
Huang M, Prendergast G. RhoB in cancer suppression. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21(1):213–8.
Lui M, Tang Q, Qui M, Lang N, Li M, Zheng Y, et al. miR-21 targets the tumor suppressor RhoB and regulates proliferation, invasion and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(19):2998–3005.
Wheeler AP, Ridley AJ. RhoB affects macrophage adhesion, integrin expression and migration. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(16):3505–16.
Vega FM, Thomas M, Reymond N, Ridley AJ. The Rho GTPase RhoB regulates cadherin expression and epithelial cell-cell interaction. Cell Commun Signal. 2015;13:6.
Sarker D, Reid AH, Yap TA, de Bono JS. Targeting the PI3K/AKT pathway for the treatment of prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;5(15):4799–805.
Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Husu EN, Pitsillides C, Vesole S, Azab AK, et al. Dual targeting of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as an antitumor strategy in Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood. 2010;115(3):559–69.
Majumder P, Sllers W. AKt-regulated pathways in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2005;24(50):7465–74.
Bitting RL, Armstrong AJ. Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr-Relat Cancer. 2013;20(3):R83–99.
Tomlins S, Rhodes D, Perner S, Dhanasekaran S, Mehra R, Sun X, et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005;310(5748):644–8.
Carver B, Tran J, Gopalan A, Chen Z, Shaikh S, Carracedo A, et al. Aberrant ERG expression cooperates with loss of PTEN to promote cancer progression in the prostate. Nat Genet. 2009;41(5):619–24.
Baron R, Kneissel M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179–92.
Staal FJT, Sen JM. The canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in lymphopoiesis and hematopoiesis. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(7):1788–94.
Czaja MJ. JNK regulation of hepatic manifestations of the metabolic syndrome. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010;21(12):707–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koushyar, S., Grant, G.H. & Uysal-Onganer, P. The interaction of Wnt-11 and signalling cascades in prostate cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 13049–13057 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5263-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5263-z